Free Professional Legal Case Note

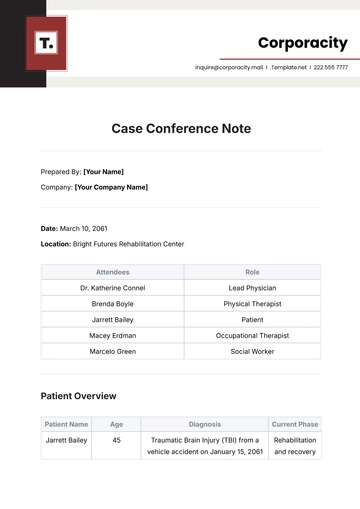
Prepared By: [Your Name]
Company: [Your Company Name]
Case Name and Citation
Renner v. MultiCorp
Citation: [2060] SC 125
Facts of the Case
On March 15, 2060, Clint Renner, an employee of MultiCorp, filed a lawsuit alleging wrongful termination. Renner was dismissed after raising concerns about the company’s environmental compliance. MultiCorp argued the termination was due to performance issues unrelated to the complaints. The events leading to the lawsuit included documented emails, internal reports, and testimonies from colleagues.
Legal Issues
Primary Issue: Was Clint Renner’s termination a violation of whistleblower protection laws under the Employee Rights Act of 2055?
Secondary Issue: Did MultiCorp breach contractual obligations related to employee performance reviews?
Decision/Ruling
The Supreme Court ruled in favor of Clint Renner on July 12, 2061. The court found that MultiCorp violated Section 12 of the Employee Rights Act of 2055, which protects employees from retaliation for reporting potential legal violations.
Reasoning
The court held that:
Whistleblower Protections: The court affirmed that Renner’s internal report constituted protected activity under the Employee Rights Act of 2055.
Lack of Just Cause: MultiCorp was unable to provide compelling evidence to justify Renner’s dismissal. Instead, internal emails revealed discussions among senior management suggesting retaliatory intent.
Company Procedures: The court found that MultiCorp failed to follow its established employee performance review procedures, undermining its claims of poor performance.
Legal Principles/Precedents
Employee Rights Act of 2055, Section 12: Protects employees who report legal violations or unethical practices from retaliation.
Jones v. TechCorp 2058: Established a framework for evaluating whether an employer’s actions were retaliatory.
Walker v. EcoSystems Inc. 2057: Highlighted the need for documented and consistent performance evaluations when justifying employee terminations.
Impact/Implications
This case reaffirms protections for whistleblowers and emphasizes the importance of documented, objective performance evaluations by employers. It sets a strong precedent for employees raising concerns about regulatory compliance in large corporations.
Critical Analysis/Commentary
The ruling highlights the evolving balance between corporate autonomy and employee protections in the 2060s. The court’s reliance on digital evidence, such as emails, reflects the increasing importance of technology in legal arguments. While the decision strengthens whistleblower protections, it raises questions about the limits of employer discretion in termination decisions.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Introducing Legal Case Note from Template.net – your key to organized legal documentation. Crafted for efficiency, this editable and customizable template ensures precision in every detail. Tailor your case notes effortlessly using our Ai Editor Tool, streamlining your workflow for a seamless and professional legal experience.
You may also like
- Delivery Note
- Notes Release
- Concept Note
- Class Note
- Hospital Note
- Apology Note
- Credit Note
- Handover Note
- Personal Note
- Excuse Note
- Case Note
- Sample Doctor Note
- Lesson Note
- Appointment Note
- Piano Note
- School Note
- Progress Note
- Business Note
- SOAP Note Templates
- Therapy Note
- Briefing Note
- Summary Note
- Sample Note
- Printable Note