Free Marketing Market Forecasting Management

Executive Summary
This Marketing Market Forecasting Management Strategy Plan outlines the steps and considerations for developing a comprehensive marketing strategy with a focus on market forecasting. It aims to provide a roadmap for achieving business goals and sustaining growth in a competitive market environment.
Introduction
In today's dynamic business landscape, effective marketing strategies are essential for achieving sustainable growth. Market forecasting plays a crucial role in guiding marketing efforts by providing insights into future market trends and consumer behavior. This plan outlines the process of developing a marketing strategy with a strong emphasis on market forecasting.
Market Research and Analysis
Industry Analysis
Understanding the broader industry landscape is paramount for informed decision-making. In this section, we embark on a comprehensive examination of the industry's current state, delving deep into its intricate trends, growth potential, and the emergence of both opportunities and threats on the horizon. Through this analysis, we gain invaluable insights that will not only shape our marketing strategy but also guide our organization's strategic direction in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Competitor Analysis
In the fiercely competitive arena, knowing thy competitors is the key to unlocking opportunities for differentiation and gaining a sustainable competitive advantage. In this section, we conduct an incisive examination of our competitors' strengths and weaknesses, unraveling the intricacies of their strategies, product offerings, and market positioning. This analysis serves as a compass, guiding us toward crafting strategies that will enable us to stand out and thrive in the market.
Consumer Behavior Analysis
In the age of the discerning consumer, understanding their preferences, purchasing behavior, and ever-evolving trends is the bedrock of effective marketing strategies. This section immerses us in the minds of our target audience, peeling back the layers of consumer psychology to reveal insights that will allow us to tailor our marketing strategies with laser precision. By aligning our efforts with consumer needs, we create not just customers, but loyal advocates of our brand.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps organizations gain a holistic understanding of their current position in the market. By examining internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats, an organization can make informed decisions and formulate effective strategies. Below is a tabular representation of what each element of SWOT represents:
STRENGTHS | WEAKNESSES | OPPORTUNITIES | THREATS |
Internal factors that give the organization an advantage. These can include resources, expertise, brand reputation, or unique capabilities. | Internal factors that hinder the organization's progress. These can include a lack of resources, outdated technology, or organizational inefficiencies. | External factors in the market or environment that can be leveraged to the organization's advantage. These can include emerging trends, new markets, or changes in consumer behavior. | External factors that pose a risk or challenge to the organization. These can include competition, economic downturns, or regulatory changes. |
Setting Marketing Objectives
Establishing clear and well-defined objectives is the compass that guides your efforts toward achieving meaningful outcomes. These objectives should be SMART, an acronym that stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound. Let's break down each element of SMART to better understand the criteria for effective marketing objectives:
ELEMENT | EXPLANATION | EXAMPLE |
Specific | Objectives must be precise and unambiguous. They should answer the questions of who, what, where, when, and why. | "Increase website traffic" is not specific, but "Increase organic website traffic by 20% within six months by optimizing SEO content" is specific because it outlines the what, by how much, and when. |
Measurable | Your objectives should include quantifiable metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) that allow you to track progress and measure success. | "Enhance brand awareness" is not measurable, but "Increase brand awareness as measured by a 10% growth in social media followers within three months" is measurable because it provides a specific metric to track. |
Achievable | Objectives should be realistic and attainable given your available resources and constraints. | Setting an objective to "Double our market share in one month with a minimal budget" may not be achievable, but "Increase market share by 10% in six months with a strategic marketing campaign" is more realistic. |
Relevant | Objectives should align with your broader organizational goals and the current state of your business. They need to be relevant to your industry, market conditions, and target audience. | Pursuing an objective to "Expand into international markets" may not be relevant if your organization is focused on local customers. |
Time-Bound | Set a specific timeframe or deadline for achieving your objectives. This adds a sense of urgency and helps in monitoring progress. | "Increase customer retention" lacks a timeframe, but "Increase customer retention rate by 15% within the next quarter" sets a clear time boundary for achieving the goal. |
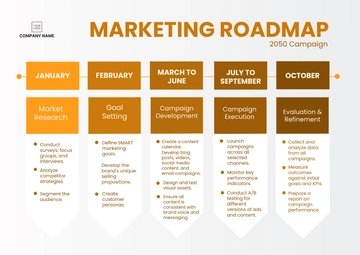
Market Forecasting Methods
Determine the most appropriate methods for forecasting market trends. Utilize a combination of historical data analysis, statistical models, expert opinions, and market segmentation.
Historical Data Analysis
Examine past sales data, market trends, and customer behavior to identify patterns and predict future trends.
Statistical Models
Utilize statistical tools and models such as regression analysis, time-series forecasting, and predictive analytics to make data-driven predictions.
Expert Opinions
Consult industry experts, market analysts, and thought leaders to gain insights into future market developments.
Market Segmentation
Segment the market based on demographics, psychographics, and behavioral factors to target specific customer groups effectively.
Marketing Budget Allocation
Advertising: This includes expenses related to online and offline advertising, such as pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns, social media advertising, print media, and broadcast advertising.
Content Marketing: Funds allocated for creating and promoting valuable content, such as blog posts, videos, infographics, and other materials that engage and inform your target audience.
Market Research: Budget set aside for market research and analysis, which includes expenses for data collection, surveys, competitive analysis, and market intelligence tools.
Events and Sponsorships: Funds dedicated to hosting or participating in industry events, conferences, and sponsorships that help raise brand awareness and connect with potential customers.
Digital Marketing: This category encompasses expenses for website development, search engine optimization (SEO), email marketing, and any other digital marketing initiatives.
Public Relations: Budget for managing the organization's public image, including press releases, media outreach, and crisis management.
Social Media: Resources allocated to social media marketing, including content creation, social media management tools, and paid advertising on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Sales Promotions: Budget for running sales promotions, discounts, and incentives to attract and retain customers.
Marketing Technology: Funds set aside for marketing software, automation tools, and analytics platforms that support marketing efforts.
Miscellaneous: A small portion of the budget is allocated for unexpected or miscellaneous expenses that may arise during the marketing campaign.
KEY AREAS | ALLOCATION |
Advertising | 20% |
Content Marketing | 15% |
Market Research | 10% |
Events and Sponsorships | 8% |
Digital Marketing | 18% |
Public Relations | 7% |
Social Media | 12% |
Sales Promotions | 5% |
Marketing Technology | 4% |
Miscellaneous | 1% |
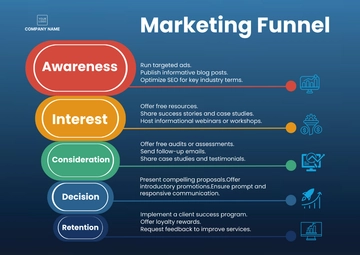
Marketing Mix and Strategies
Develop marketing strategies for each element of the marketing mix:
Product
Product positioning: This involves defining how your product is perceived by your target audience in comparison to competitors. It's about identifying a unique selling proposition (USP) and communicating it effectively. For example, if you're selling smartphones, your product positioning might focus on innovation, reliability, or affordability.
Features and benefits: Understand the specific features of your product and translate them into benefits that resonate with your customers. For instance, if you're marketing a car, features like advanced safety technology can be translated into the benefit of a safer driving experience for families.
Price
Pricing strategies: Decide on the pricing strategy that aligns with your business goals and market dynamics. Common pricing strategies include cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, or competitive pricing. Consider factors such as production costs, competitor pricing, and customer willingness to pay.
Market conditions: Stay attuned to market conditions, including supply and demand fluctuations, economic trends, and competitor pricing changes. Adjust your pricing strategy accordingly to remain competitive and profitable.
Customer perceptions: Understand how your target audience perceives pricing. Some customers may associate higher prices with higher quality, while others may be price-sensitive. Tailor your pricing strategy to match customer perceptions.
Place
Distribution channels: Determine the most effective distribution channels to make your product accessible to customers. This might involve selling through physical stores, e-commerce platforms, wholesalers, or a combination of these. Consider factors like customer convenience and reach when selecting distribution channels.
Locations: Choose physical locations strategically. If you're in the food industry, for example, the location of your restaurant or grocery store can significantly impact foot traffic and sales. Consider factors like demographics, foot traffic, and proximity to competitors.
Promotion
Marketing campaigns: Develop comprehensive marketing campaigns that align with your objectives. This includes creating a marketing mix that incorporates advertising, public relations, social media, and content marketing. Your campaigns should communicate your product's value proposition and benefits.
Tactics: Determine the specific tactics you'll use within your campaigns. These might include online advertising, email marketing, influencer partnerships, or events. Each tactic should have a clear purpose and tie back to your overall marketing objectives.
Brand awareness: Focus on building brand awareness and recognition. Use storytelling, consistent branding, and creative messaging to make your brand memorable in the minds of your target audience.
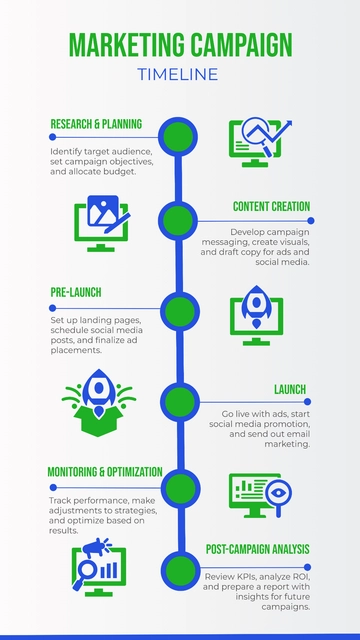
Implementation and Monitoring
Action Plan
A well-structured action plan serves as the backbone of successful marketing execution. It provides a clear roadmap for turning strategies into tangible results. The action plan should encompass the following components:
Tasks | List all the specific activities that need to be accomplished. Ensure that tasks are granular, allowing for clear accountability. |
Responsibilities | Clearly define who is responsible for each task. Assigning roles ensures that team members understand their duties and can collaborate effectively. |
Timelines | Set realistic timeframes for task completion. Deadlines are crucial for keeping the team on track and ensuring that campaigns align with the overall marketing calendar. |
Milestones | Identify significant milestones or checkpoints within each initiative. These milestones help track progress and ensure that the marketing plan remains on course. |
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics that provide insights into the effectiveness of marketing efforts. They enable you to gauge the success of your strategies and make data-driven decisions. Common KPIs that should be considered include:
Sales Growth: Monitor the increase in sales revenue over time. It is a fundamental indicator of marketing and business success.
Market Share: Measure your brand's market share relative to competitors. This KPI reflects your brand's positioning and competitive strength.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculate the cost incurred to acquire each new customer. A lower CAC indicates efficient customer acquisition strategies.
Return on Marketing Investment (ROMI): Evaluate the return on investment from marketing initiatives. ROMI compares the gains from marketing against the costs, helping assess campaign profitability.
Conversion Rates: Analyze the percentage of website visitors, leads, or prospects who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Assess the long-term value of a customer relationship. A higher CLV justifies marketing investments in retaining and nurturing existing customers.
Website Traffic and Engagement: Monitor website traffic, page views, bounce rates, and user engagement metrics. This provides insights into the effectiveness of your online presence.
Contingency Planning
In the unpredictable world of marketing, having contingency plans in place is imperative. These plans serve as a safety net, allowing your organization to respond effectively to unforeseen challenges or shifts in market conditions. Contingency planning should involve the following steps:
Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and challenges that could impact your marketing initiatives. These may include economic downturns, supply chain disruptions, or unexpected competitive moves.
Scenario Analysis: Develop scenarios based on the identified risks. Consider various "what-if" scenarios and their potential consequences on your marketing strategy.
Response Strategies: Outline specific strategies to mitigate or respond to each scenario. This could involve reallocating budgets, shifting marketing messaging, or adjusting campaign timelines.
Communication Plan: Clearly define how internal and external stakeholders will be informed in the event of a contingency. Effective communication is essential to maintain trust and transparency.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitor the market for early signs of potential issues. Regularly assess the effectiveness of your contingency plans and make adjustments as necessary.
Conclusion
This Marketing Market Forecasting Management Strategy Plan offers a meticulously structured framework for crafting a robust marketing strategy that harnesses the power of market forecasting. By undertaking comprehensive research, establishing precise objectives, and executing data-driven strategies, organizations position themselves to not only navigate the ever-evolving market landscape but also secure a pathway to enduring prosperity. In an era of unprecedented change and opportunity, the integration of market forecasting into marketing strategies stands as a beacon, guiding businesses toward sustainable, long-term success.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Gain strategic insights with Template.net's Marketing Market Forecasting Management Template. This editable and customizable tool, accessible in our Ai Editor Tool, empowers you to predict market trends accurately. Tailor it to your business effortlessly, ensuring informed decision-making and staying ahead in the competitive landscape.
You may also like
- Marketing Google Slide
- Marketing Letter
- Marketing Quotation
- Marketing Report
- Marketing Strategic Plan
- Marketing Plan
- Marketing Proposal
- Marketing Flyer
- Marketing Presentation
- Real Estate Marketing Plan
- Marketing Contract
- Marketing Agreement
- Marketing Resume
- Marketing Checklist
- Marketing Brochure
- Marketing Banner
- Marketing Schedule
- Marketing Vector
- Marketing Logo
- Marketing Chart
- Marketing Campaign Plan
- Marketing Budget
- Marketing Postcard
- Marketing Poster
- Marketing Facebook Post
- Marketing Instagram Post
- Marketing Newsletter
- Marketing Infographic