Free Marketing Curriculum Based on Data Insights

Data Insights
1. Module 1- Introduction to Data-Driven Marketing
Lesson 1.1: Understanding the Importance of Data in Marketing
Overview of Data-Driven Marketing:
In today's digital age, data has become the lifeblood of marketing. Data-driven marketing refers to the practice of using data and analytics to guide marketing strategies, decisions, and campaigns. It's a shift from traditional, intuition-based marketing to an approach that relies on concrete data and insights. This lesson will provide an overview of data-driven marketing and its key components.
Key Topics to Cover:
Definition of Data-Driven Marketing: Explain what data-driven marketing means and how it differs from traditional marketing approaches. Highlight the role of data in shaping marketing activities.
Data Sources: Discuss various sources of data used in marketing, including customer data, website analytics, social media metrics, and more. Emphasize the importance of collecting and organizing data effectively.
Analytics Tools: Introduce common analytics tools and platforms used in data-driven marketing, such as Google Analytics, marketing automation software, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
Personalization: Explain how data enables personalized marketing. Describe how companies can tailor their messaging and offers to individual customer preferences based on data insights.
Lesson 1.2: Key Marketing Metrics and KPIs
Introduction to Marketing Metrics and KPIs:
Begin the lesson by explaining that marketing metrics are quantifiable data points that help assess various aspects of marketing performance. KPIs, or Key Performance Indicators, are specific metrics chosen to track progress toward marketing goals.
Discuss why metrics and KPIs are crucial:
They provide insights into marketing effectiveness.
They enable data-driven decision-making.
They facilitate the measurement of ROI (Return on Investment).
Types of Marketing Metrics and KPIs:
Break down marketing metrics and KPIs into categories and provide examples within each category:
1. Traffic and Acquisition Metrics:
Website visits
Click-through rate (CTR)
Cost per click (CPC)
Conversion rate
2. Customer Engagement Metrics:
Time on site
Page views per session
Bounce rate
Social media likes, shares, and comments
3. Conversion and Sales Metrics:
Conversion rate
Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
Average order value (AOV)
Customer lifetime value (CLV)
4. Email Marketing Metrics:
Open rate
Click-through rate (CTR)
Conversion rate
Unsubscribe rate
5. Social Media Metrics:
Follower growth rate
Engagement rate
Reach and impressions
Click-through rate (CTR)
2. Module 2: Data Analysis Tools and Techniques
Objective: In this lesson, students will gain an understanding of essential data analysis tools used in marketing and how they enable data-driven decision-making. We will focus on two prominent tools, Google Analytics and Adobe Analytics, while also introducing other relevant options in the market.
Lesson 2.1: Introduction to Data Analysis Tools
Key Topics to Cover:
Introduction to Data Analysis Tools
Define data analysis tools as software applications that collect, process, and analyze data to provide insights into user behavior, website performance, and marketing effectiveness.
The Role of Data Analysis in Marketing
Emphasize the critical role of data analysis in modern marketing strategies. Discuss how it enables marketers to make informed decisions, measure ROI, and optimize campaigns.
Benefits of Data Analysis Tools
Highlight the benefits of using data analysis tools, including real-time data access, tracking user interactions, identifying trends, and improving website user experience.
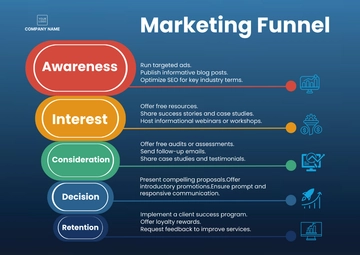
3. Module 3: Customer Segmentation and Targeting
Objective: In this lesson, students will learn the fundamental concept of customer segmentation and why it is a critical component of effective marketing strategies. They will gain an understanding of the importance of tailoring marketing efforts to specific customer segments.
Lesson 3.2: Creating Detailed Buyer Personas for Targeted Marketing
Key Topics to Cover:
Definition of Customer Segmentation
Define customer segmentation as the process of dividing a broad target market into smaller, distinct groups (segments) based on shared characteristics or behaviors.
Why Segment Customers?
Explain the primary objectives of customer segmentation, including:
Personalization: Tailoring marketing messages and offers to match segment needs.
Improved Targeting: Enhancing the precision of marketing campaigns.
Enhanced Customer Experience: Providing relevant content and experiences.
Efficiency: Maximizing marketing ROI by focusing resources where they are most effective.
Types of Segmentation
Introduce different segmentation criteria, such as:
Demographic: Age, gender, income, education.
Psychographic: Lifestyle, values, interests.
Behavioral: Purchase history, frequency, brand loyalty.
Geographic: Location, region, climate.
Firmographic (B2B): Industry, company size, revenue.
Lesson 3.2: Creating Detailed Buyer Personas for Targeted Marketing
Key Topics to Cover:
Definition of Buyer Personas
Define buyer personas as semi-fictional representations of ideal customers based on research and data. These personas encompass demographics, behaviors, goals, and pain points.
Purpose of Buyer Personas
Explain that buyer personas serve as a tool to better understand and empathize with customers, helping marketers create more relevant and effective marketing strategies.
Demographic Information
Discuss the importance of demographic details such as age, gender, income, education, and job title in shaping buyer personas.
Psychographic Information
Explain how psychographic data, including lifestyle, values, interests, and pain points, provides insights into the motivations and behaviors of target customers.
Behavioral Insights
Highlight the significance of understanding customer behavior, including their buying habits, preferred communication channels, and decision-making processes.
4. Module 4: Content Marketing and SEO
Objective: In this lesson, students will learn the fundamentals of developing a content marketing strategy. They will understand how a well-crafted content strategy aligns with business goals, target audience needs, and helps create engaging and relevant content.
Lesson 4.1: Developing a Content Marketing Strategy
Key Topics to Cover:
Definition of Content Marketing Strategy
Define content marketing strategy as a comprehensive plan that outlines how content will be created, distributed, and used to achieve specific marketing goals.
Importance of Content Strategy
Explain the significance of a content strategy in guiding content creation, ensuring consistency, and maximizing the impact of content marketing efforts.
Aligning with Business Goals
Emphasize the importance of aligning content marketing goals with broader business objectives, such as increasing brand awareness, driving website traffic, generating leads, or boosting sales.
SMART Goals
Introduce the concept of SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) and how they should be applied to content marketing objectives.
Lesson 4.2: Search Engine Optimization (SEO) - On-page and Off-page Techniques
Key Topics to Cover:
Definition of SEO
Define SEO as the process of optimizing a website to improve its visibility in search engine results, thereby increasing organic (non-paid) traffic.
Importance of SEO
Explain why SEO is vital for businesses, including its role in driving targeted traffic, increasing brand visibility, and potentially boosting sales.
Keyword Research
Describe the process of keyword research to identify relevant search terms. Explain how to choose keywords based on relevance, search volume, and competition.
Keyword Optimization
Discuss the placement of keywords in essential on-page elements, including:
Title tags
Meta descriptions
Header tags (H1, H2, H3)
Content body
Image alt text
Content Quality and Relevance
Emphasize the importance of creating high-quality, relevant content that meets user intent. Explain how search engines reward valuable content.
Page Speed and Mobile Optimization
Introduce the significance of page speed and mobile-friendliness in SEO. Discuss tools and best practices for optimizing website performance.
5. Module 5: Email Marketing and Automation
Objective: In this lesson, students will learn the essential best practices for designing effective email marketing campaigns. They will understand how to create compelling email content and optimize various elements for better engagement and conversions.
Lesson 5.1: Designing Effective Email Campaigns - Email Marketing Best Practices
Key Topics to Cover:
Definition of Email Marketing
Define email marketing as a digital marketing strategy that involves sending emails to a list of subscribers or customers with the aim of promoting products, services, or building relationships.
Importance of Email Marketing
Explain why email marketing is a valuable tool, highlighting its effectiveness in reaching a targeted audience, nurturing leads, and driving conversions.
Email Layout and Structure
Discuss the importance of a clean, mobile-responsive email layout. Explain the use of a header, body content, and a clear call-to-action (CTA).
Eye-catching Subject Lines
Teach students the significance of subject lines in email open rates. Discuss best practices for crafting compelling and concise subject lines.
Engaging Content
Highlight the importance of providing valuable and engaging content in emails. Discuss the use of images, text, and multimedia elements to captivate the audience.
Lesson 5.2: Implementing Marketing Automation Tools
Key Topics to Cover:
Definition of Marketing Automation
Define marketing automation as the use of software and technology to automate repetitive marketing tasks, nurture leads, and deliver personalized content to prospects and customers.
Why Marketing Automation?
Explain the benefits of marketing automation, such as improved efficiency, lead nurturing, increased engagement, and better customer retention.
Email Marketing Automation
Discuss how marketing automation tools streamline email marketing by automating email sends, drip campaigns, and personalized email content.
6. Module 6: Capstone Project
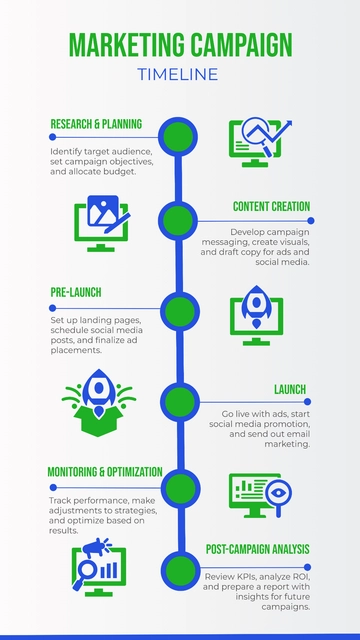
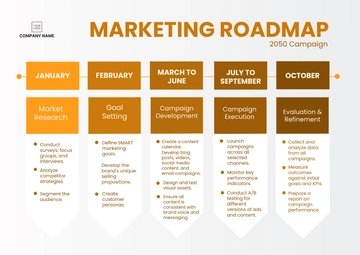
Objective: In this capstone project, students will apply the knowledge and skills acquired throughout the curriculum to plan, execute, and measure a comprehensive data-driven marketing campaign for an IT company. This project will serve as an opportunity for students to showcase their understanding of marketing strategies, data analysis, content creation, and marketing automation.
Part 1: Project Kick-off and Company Briefing
Key Activities:
Client Meeting: Students will meet with a representative from the IT company to understand their goals, target audience, products/services, and any specific challenges or opportunities.
Project Scope: Define the scope of the marketing campaign, including objectives, budget, and timeline.
Part 2: Research and Data Analysis
Key Activities:
Audience Research: Conduct thorough research to understand the target audience, including demographics, psychographics, and pain points.
Competitive Analysis: Analyze competitors' marketing strategies, strengths, and weaknesses.
Keyword Research: Identify relevant keywords and search terms to inform content creation and SEO efforts.
7. Conclusion
In this comprehensive marketing curriculum, students have embarked on a transformative journey into the world of data-driven marketing, armed with knowledge, skills, and strategies to excel in the dynamic field of digital marketing for IT companies. As we draw this curriculum to a close, let's reflect on the key takeaways and the immense value it brings to both students and the IT industry.
The Power of Data-Driven Decision-Making: Throughout this curriculum, students have delved deep into the power of data in marketing. They have learned how to collect, analyze, and leverage data to make informed decisions, identify trends, and maximize ROI. By understanding the significance of data insights, students are now well-equipped to navigate the complex landscape of the IT industry, where data-driven strategies are paramount.
Audience-Centric Approach: Students have learned the importance of understanding and segmenting their audience. They now appreciate that effective marketing begins with a profound understanding of customer demographics, behaviors, and preferences. The development of buyer personas and segmentation strategies ensures that marketing efforts resonate with specific customer groups, enhancing engagement and conversion rates.
Content Excellence: This curriculum has emphasized the significance of creating compelling, relevant, and high-quality content. Students have honed their content creation skills, learning how to tailor content to specific audience segments, optimize it for search engines, and utilize various formats and channels. They have grasped the art of storytelling and the science of content strategy.
Automation for Efficiency: Marketing automation has emerged as a powerful tool in the modern marketer's toolkit. Students have acquired the knowledge to implement marketing automation tools effectively, streamlining processes, nurturing leads, and delivering personalized content. Automation not only increases efficiency but also enhances customer experiences and fosters brand loyalty.
This marketing curriculum has empowered students with the tools and insights to thrive in the ever-evolving IT industry. By embracing data-driven decision-making, audience-centric approaches, and ethical marketing practices, they are well-prepared to drive innovation, foster growth, and make a significant impact on the marketing landscape of IT companies.
As graduates of this curriculum, students are not just marketers; they are strategic data-driven marketing professionals poised to lead IT companies into a future where data is the currency of success. Their journey doesn't end here; it's the beginning of an exciting and dynamic career in the realm of digital marketing for the IT sector.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Transform your marketing strategy with the Marketing Curriculum Based on Data Insights Template, available exclusively on Template.net. This editable and customizable resource empowers you to align your curriculum with cutting-edge data trends. Tailor it effortlessly to your needs with the added convenience of being editable in our Ai Editor Tool, ensuring a data-driven edge.
You may also like
- Marketing Google Slide
- Marketing Letter
- Marketing Quotation
- Marketing Report
- Marketing Strategic Plan
- Marketing Plan
- Marketing Proposal
- Marketing Flyer
- Marketing Presentation
- Real Estate Marketing Plan
- Marketing Contract
- Marketing Agreement
- Marketing Resume
- Marketing Checklist
- Marketing Brochure
- Marketing Banner
- Marketing Schedule
- Marketing Vector
- Marketing Logo
- Marketing Chart
- Marketing Campaign Plan
- Marketing Budget
- Marketing Postcard
- Marketing Poster
- Marketing Facebook Post
- Marketing Instagram Post
- Marketing Newsletter
- Marketing Infographic