Free Account Budget SOP

I. Introduction
This Account Budget Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) serves as a cornerstone for financial stewardship within [Your Company Name]. Its primary goal is to establish a standardized framework for budget management, ensuring fiscal responsibility and alignment with the organization's overarching objectives. Applicable across all departments, this SOP sets the stage for transparent and accountable budgeting practices, promoting a culture of financial discipline and strategic resource allocation.
II. Roles and Responsibilities
The Finance Department maintains the crucial responsibility of protecting the financial integrity of the organization. This involves playing a significant role in coordinating the budgeting process, ensuring that it runs smoothly and is effectively aligned with the organization's financial goals and frameworks. Budget Managers, unlike other means, are given the task of being stewards for individual budgets. Their involvement in the budgeting process does not end merely at planning. Instead, they also shoulder the responsibility of executing the planned budget efficiently. Moreover, it falls under their jurisdiction to carry out continuous monitoring and assessment of the budget, ensuring its alignment with the outlined objectives and making necessary adjustments where required.
Senior Management is involved strategically, providing strong leadership and guidelines that provide the context within which budget decisions are made. Their role is to ensure alignment between budget decisions and the broader mission of the organization. They assess, adjust and approve these decisions, making sure that, ultimately, the allocated resources and finances will directly contribute towards achieving the organization's mission. Lastly, the role of Compliance Officers is integral in establishing a consistent adherence to internal policies and regulatory standards. They help foster a budgeting environment that is conscious of compliance and is deeply rooted in maintaining an ethical stance. They ensure that the budget management and allocation process complies with all internal and external rules and regulations, which ultimately leads towards sustaining a strong financial reputation of the organization.
III. Budget Planning
The initiation of the budget planning cycle is marked by an in-depth analysis and consideration of the organization's overall objectives and goals. This process also includes an extensive assessment of historical financial data, as well as discerning the implicit external factors that greatly influence economic and fiscal outcomes. This particular type of approach, which can be labelled as proactive, provides the basis for establishing a strong and robust budget. The inclination of this reinforced budget adapts to the dynamic and shifting characteristics inherent in the business environment. Furthermore, the method of laying out a detailed schedule and timeline for the preparation and approval of the budget significantly contributes to the systematization of the process, making it more orderly and time-bound. This strategic maneuver ensures the timely execution of the budget and presents opportunities for strategic adjustments as a response mechanism towards situations that bring about changes in circumstances. Such practice allows for the sharpening and recalibrating of budget reviews and resolutions in order to seamlessly synchronize with real-time changes.
IV. Budget Development
The process of setting budget targets involves a comprehensive and detailed analysis of the projected expenses of the organization. This analysis should take into consideration the revenue forecasts, noting the expected income that the organization hopes to generate in the future. In addition to these financial factors, the strategic priorities that have been outlined in the organization’s roadmap should also be held in mind, as these will influence where funds will need to be allocated. The allocation of resources is a crucial aspect of developing the budget. It requires a holistic understanding of the unique needs of the different departments within the organization, and needs to be guided by the overarching goals of the organization. This ensures that the resources are distributed in a manner that drives the organization towards its larger objectives and vision.
Additionally, when constructing the budget, consideration should also be given to the diversity of the revenue sources. By depending on multiple sources of income, the budget is less vulnerable to financial uncertainties and is thus more resilient. This diversity helps to ensure that the financial plans of the organization are balanced and robust.
Taking all these elements into account helps to sustain the organization’s growth trajectory. This is because a well-constructed budget tides the organization through uncertain times while also facilitating growth and expansion as per the strategic priorities outlined in its roadmap.
V. Budget Monitoring and Control
The establishment of a vigilant, ongoing monitoring process, whose main aim is to track and compare actual expenses against planned, budgeted amounts, is discussed in this section. The implication of this system is that the business or institution can keep an eye on its expenditure, ensuring that it does not deviate from the budget. In order to make this process more insightful and beneficial, the usage of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is incorporated as they can provide a more comprehensive, detailed analysis. Their use allows for a more in-depth, instructive investigation into the data which, in turn, can facilitate more strategic, informed decision making. One of the key factors emphasized in this section is the value of completing these evaluations in real-time. This method allows for the immediate identification and awareness of any discrepancies between the planned budget and actual expenses. The rapid recognition of these variances and deviations is crucial as it can prevent potential financial losses or mismanagement. Established procedures outline how to escalate these identified variances. This system is created with an objective to ensure that they are dealt with and corrected promptly. The agreed upon steps include taking immediate corrective actions to resolve the issue, making necessary adjustments to the current spending plans to avoid such discrepancies in the future, or reallocating resources as necessary. This could involve moving resources to different sectors or areas of the business where they are needed most. The flexibility and adaptability of these measures underline the forward-thinking, proactive nature of the monitoring process, ensuring that the business adapts and evolves based on its financial realities and needs.
VI. Budget Amendments and Adjustments
In acknowledging the ever-changing and fluid nature of environments within organizations, this particular section provides a detailed explanation of the criteria that should be followed for one to begin making amendments to the budget. To ensure that decisions relating to the budget are made wisely and judiciously, a meticulously designed approval process is set in place. This process calls for the active involvement of all relevant stakeholders, among them being those holding high-ranking management positions and members of the finance department. To promote transparency and the ability to conduct audits, as well as to create a complete and thorough historical record of all budget modifications, there are stringent requirements outlined for documentation. Every budget adjustment is expected to be rigorously documented in order to abide by these mandates.
VII. Reporting and Analysis
Budget reports are created with a consistent regularity, taking into consideration the differences between the actual expenses made and what has been budgeted for. These reports include detailed analyses of any variances as well as providing valuable insights that can be acted upon. The frequency at which these reports are generated, as well as the format they are presented in, have been deliberately chosen to ensure that department heads and members of the senior management team are provided with information that is both timely and relevant. The prime objective of this is to facilitate well-informed decision-making procedures. Additionally, it is also meant to encourage a sense of accountability among those involved. Furthermore, this process assists in establishing a recurring feedback cycle, the aim of which is to refine and adjust the budget continually based on the insights and information gathered.
VIII. Compliance and Governance
This section places significant emphasis on the importance of integrity, indicating that it is crucial for organizations to abide by set internal policies, adhere to industry regulations, and follow accounting standards. In addition, internal controls and audit trails are put in place as additional measures to bolster proper governance. These controls and audits pay particular attention to the organization's budgeting practices as they are thoroughly reviewed to ensure they satisfy the specified legal requirements. More than simply meeting these regulations, however, the controls ensure that the practices align with the highest possible standards of financial transparency and accountability, demonstrating the organization's commitment to operative excellence and ethical conduct.
IX. Training and Communication
In order to empower budget managers and stakeholders with the essential knowledge and skills needed for effective management of budgets, specific training programs are established and implemented. These programs have been thoughtfully created to provide the necessary guidance and knowledge required to effectively deal with budget-related issues, challenges, and opportunities. In sync with this, communication strategies are subsequently devised with the utmost care and precision. Their primary aim being to assure the spread and percolation of all budget-related data, such strategies also ensure the information shared is both precise and delivered in a timely manner. In doing so, they aid in fostering a mutual comprehension of the financial goals amongst all those involved and thereby contribute to maintaining an open line of communication. This constant exchange of feedback and ideas is crucial for the continuous bettering and refining of the tactics, strategies, and the overall approach towards efficient budget management.
X. Documentation and Record-Keeping
The particular segment in discussion highlights the crucial role that precise and detailed maintenance of records plays. It goes on to describe the particular requirements that need to be met for the accurate and consistent documentation of all activities related to budgeting. By establishing specified periods during which records must be preserved, and in line with the organization's policy on record retention, it is ensured that data and information concerning past budgeting remains available and accessible. This also serves to ensure that there is compliance with all the necessary legal and regulatory standards, enforcing a sense of consistency in record keeping.
XI. Review and Revision
The Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is strategically designed with a focus on fostering continual improvement within the organization. In order to monitor its effectiveness and relevancy within the operational environment, it is brought under assessment through an annual review process. The criteria for this assessment are multifold. Firstly, it weighs if the outlined protocols have been successful in adhering to the set budget targets to ensure fiscal responsibility. Secondly, the review process examines whether the protocol is in strict compliance with internal and external regulatory policies, cementing its legitimacy and integrity. Finally, the feedback received from various stakeholders, whose interests and concerns the SOP addresses and safeguards, is an invaluable part of the assessment process. All these evaluation criteria contribute to the shaping of a dynamic and responsive framework that allows for effective and efficient budget management on an ongoing basis.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Introducing the Account Budget SOP Template from Template.net! Streamline financial management effortlessly with this editable and customizable SOP. Crafted for precision, it features an intuitive AI Editor Tool, ensuring seamless adaptation to your organization's needs. Elevate your budgeting process – efficiently, effectively, and with the convenience of user-friendly customization. Transform financial protocols effortlessly!
You may also like
- Budget Sheet
- Personal Budget
- Non Profit Budget
- Monthly Budget
- Project Budget
- HR Budget
- Company Budget
- Home Budget
- Weekly Budget
- College Budget
- Business Budget
- Construction Budget
- Small Business Budget
- Hotel Budget
- Annual Budget
- Home Renovation Budget
- Household Budget
- Student Budget
- Grocery Budget
- Marketing Budget
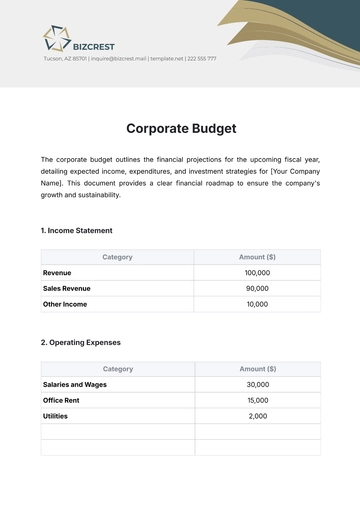
- Corporate Budget
- Startup Budget
- Manufacturing Budget
- Church Budget
- University Budget
- Annual Budget Plan
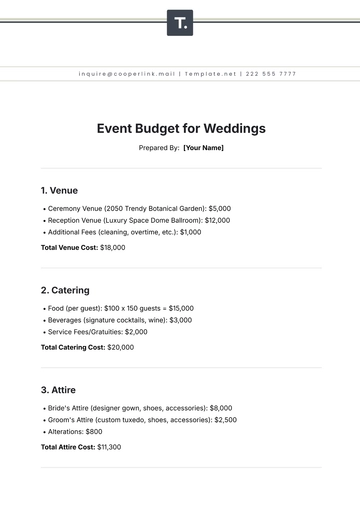
- Event Budget
- Operating Budget
- Travel Budget
- Food Budget
- IT and Software Budget
- School Budget
- Real Estate Budget
- Sales Budget
- Conference Budget
- Budget Finance
- Freelancer Budget
- Budget Advertising