Free Health & Safety Committee User Guide

I. Introduction
A. Overview
This guide is a comprehensive resource designed to facilitate a clear understanding of the roles, responsibilities, and processes of our company's Health and Safety Committee. As an integral component of our commitment to a safe and healthy workplace, this guide outlines the committee's structure, functions, and essential procedures.
B. Purpose
The primary purpose of this user guide is to provide detailed insights into the functioning of the Health and Safety Committee, elucidating its purpose, objectives, and the vital role it plays in maintaining a secure work environment. By understanding the committee's functions and procedures, members can actively contribute to creating and sustaining a culture of safety within our company.
C. Target Audience
This guide is tailored for Health and Safety Committee members, comprising representatives from both management and employees. It is also a valuable resource for employees interacting with the committee, providing them with insights into how the committee operates and how they can engage with it effectively.
D. Scope
The scope of this guide extends to all aspects of the Health and Safety Committee's activities within our company. From the structure of the committee to its specific functions, meeting procedures, communication strategies, and emergency response planning.
E. Objectives
The main objectives of this guide are:
Facilitate Safety Awareness
Equip stakeholders with essential information to foster a workplace culture where safety is a shared responsibility, enhancing awareness through clear communication strategies.
Guide Effective Committee Functions
Provide a comprehensive reference for committee members, enabling them to conduct efficient meetings, investigations, and policy reviews within the company's health and safety framework.
Promote Continuous Improvement
Encourage a proactive approach to health and safety by facilitating continuous improvement initiatives within the committee, supporting regular reviews and updates for ongoing enhancement.
II. Committee Structure and Composition
The committee is a diverse assembly, combining management and employee representatives, each contributing unique insights to ensure a comprehensive approach to workplace safety.
The following table provides a concise overview of the Health and Safety Committee's structure, showcasing the names of key members along with their designated roles and responsibilities.
Name | Role | Responsibilities |
[Richard Franklin] | [Co-Chair] | [Provide leadership and guidance to the committee.] |
The inclusion of both management and employee representatives ensures that all perspectives are considered, promoting a more comprehensive and effective approach to identifying, addressing, and mitigating workplace hazards. This diversity contributes to a shared responsibility for safety, enhancing overall engagement and commitment to maintaining a secure and healthy work environment. Through this collaborative structure, the committee is better equipped to drive initiatives, implement preventive measures, and continuously improve our safety protocols.
III. Committee Functions
The Health and Safety Committee plays a pivotal role in proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating workplace health and safety risks. The following outlines the key functions of the committee:
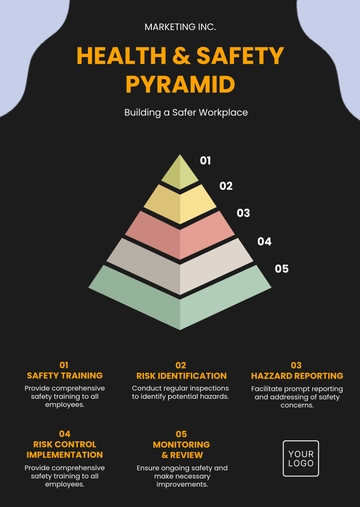
A. Hazard Identification
Actively engage in regular workplace inspections to identify potential hazards.
Encourage employees to report safety concerns and participate in hazard assessments.
B. Incident Investigation
Investigate workplace incidents, accidents, or near misses to determine root causes.
Collaborate with relevant parties to implement corrective actions based on investigation findings.
C. Safety Training and Awareness
Develop and oversee safety training programs for employees.
Promote awareness campaigns to ensure all employees are informed about safety protocols.
D. Policy Review and Development
Regularly review existing health and safety policies and procedures.
Contribute to the development of new policies to address emerging safety concerns.
E. Emergency Response Planning
Participate in the development and testing of emergency response plans.
Ensure employees are trained on emergency procedures and evacuation protocols.
IV. Meeting Procedures
The efficient functioning of the Health and Safety Committee relies on well-organized meeting procedures. The following list outlines the key aspects of conducting committee meetings:
A. Scheduling and Frequency
Meetings are scheduled providing regular opportunities for discussion.
The agenda is circulated in advance to allow members to prepare for discussions.
B. Agenda Setting
The agenda includes items such as hazard reports, incident investigations, and safety program updates.
Members are encouraged to propose agenda items to ensure comprehensive coverage.
C. Conducting Discussions
Meetings are conducted in a collaborative and inclusive manner.
All members are encouraged to actively participate in discussions and share insights.
D. Decision-Making Process
Decisions are made through consensus, fostering a sense of shared responsibility.
Voting may be employed when necessary, ensuring a fair and democratic decision-making process.
E. Minutes and Documentation
Minutes are recorded during each meeting and distributed to all members.
Documentation includes action items, decisions made, and plans for follow-up.
V. Reporting Mechanisms
Reporting mechanisms are fundamental to the effectiveness of the Health and Safety Committee. The following outlines the procedures for reporting safety concerns, incidents, and hazards:
A. Safety Concerns
Employees are encouraged to report safety concerns through our designated channels. Anonymous reporting options are available to promote open communication without fear of reprisal.
B. Incident Reporting
All workplace incidents, accidents, and near misses are to be reported promptly. Reporting forms are easily accessible and provide a structured format for incident details.
C. Hazard Reports
Employees are empowered to report potential hazards they identify during their work. Hazard reports undergo prompt review by the committee, leading to timely corrective actions.
D. Recommendations and Feedback
The committee welcomes recommendations and feedback from all members. A feedback loop is established to acknowledge and address suggestions for improvement.
VI. Training and Development
Continuous training and development are essential components of a dynamic Health and Safety Committee. This list below outlines initiatives for member education and skill enhancement:
A. Training Programs
The committee organizes regular training sessions on various safety-related topics.
Training programs include hands-on sessions, workshops, and seminars to cater to diverse learning styles.
B. Resource Availability
Members have access to a repository of safety-related resources, guidelines, and reference materials.
External experts may be invited to conduct specialized training sessions on emerging safety trends.
C. Professional Development
Committee members are encouraged to participate in external safety conferences and workshops.
Opportunities for certifications and accreditations related to occupational health and safety are supported.
D. Knowledge Sharing
A culture of knowledge sharing is fostered within the committee.
Best practices, lessons learned from incident investigations, and industry updates are regularly disseminated.
Scenario Simulations
Realistic scenario simulations are conducted to enhance preparedness for emergency situations.
Simulations allow members to apply theoretical knowledge in practical, simulated environments.
VII. Communication Strategies
Effective communication lies at the heart of successful health and safety initiatives. The Health and Safety Committee employs the following strategies to ensure transparent and impactful communication:
A. Regular Updates
Committee members receive regular updates on safety-related activities, initiatives, and changes in procedures.
Updates are disseminated through multiple channels, including email, notice boards, and team meetings.
B. Open Forum Discussions
Scheduled open forum discussions provide a platform for committee members to share insights, experiences, and concerns.
The committee actively seeks input from all members to foster a collaborative decision-making environment.
C. Feedback Channels
Establishing formal and informal feedback channels ensures that committee members and employees can voice their opinions.
Periodic surveys may be conducted to gauge the effectiveness of communication strategies.
D. Visual Communication Aids
Effective use of visual aids, such as posters, infographics, and digital displays, enhances the visibility of key safety messages.
Visual aids serve as reminders of safety protocols and reinforce the importance of adherence.
E. Emergency Communication Protocols
Clear and concise protocols are in place for emergency communication, ensuring swift dissemination of information during crisis situations.
Regular drills and simulations are conducted to test the efficiency of emergency communication systems.
VIII. Emergency Response and Incident Investigation
A swift and coordinated response to emergencies and thorough incident investigation are critical components of the Health and Safety Committee's responsibilities. The following strategies are employed to address emergency situations and conduct comprehensive investigations:
A. Emergency Response Planning
The committee actively contributes to the development and periodic review of emergency response plans.
Emergency response drills and simulations are conducted to test the effectiveness of response procedures.
B. Incident Investigation
Standardized procedures for incident investigation are followed, ensuring a systematic and thorough approach.
Root cause analysis is a key component of investigations, providing insights for preventive actions.
C. Interdepartmental Collaboration
Collaboration with other company departments is emphasized during emergency response and incident investigations.
Cross-functional teams may be formed to ensure a holistic approach to incident resolution.
D. Corrective Action Implementation
Prompt implementation of corrective actions identified during incident investigations is a priority.
The committee monitors and evaluates the effectiveness of implemented corrective measures.
E. Continuous Improvement
Lessons learned from incidents are documented, shared, and utilized to improve safety protocols.
Continuous improvement initiatives focus on refining emergency response plans and incident investigation procedures.
IX. Committee Review and Evaluation
Ensuring the ongoing effectiveness of the Health and Safety Committee involves regular review and evaluation processes. The following strategies are employed to assess the committee's performance and guide continuous improvement:
A. Periodic Self-Assessment
The committee conducts self-assessment exercises to evaluate its effectiveness in meeting its objectives.
Members reflect on their contributions, identify areas for improvement, and propose enhancements.
B. External Audits
External audits, conducted by health and safety professionals or regulatory bodies, provide an objective evaluation of the committee's practices.
Audit findings are carefully analyzed, and recommendations are considered for integration into committee activities.
C. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establishing KPIs enables the committee to measure its performance against predefined benchmarks.
KPIs may include incident reduction rates, response times, and the effectiveness of safety training programs.
D. Stakeholder Feedback
Soliciting feedback from employees, management, and other stakeholders provides valuable insights into the committee's impact.
A feedback loop is established to address concerns and incorporate suggestions for improvement.
E. Documentation Review
Regular reviews of committee documentation, including meeting minutes, incident reports, and corrective action plans, help identify trends and areas for improvement.
Documented lessons learned contribute to the evolution of best practices.
X. Conclusion
The Health and Safety Committee plays a pivotal role in shaping a workplace culture centered on the safety and well-being of all individuals. Through collaborative efforts, the committee actively engages with employees, management, and external stakeholders to mitigate risks, respond effectively to challenges, and enhance safety measures. The commitment to communication strategies, comprehensive emergency response, incident investigation, and continuous improvement initiatives reflects our collective responsibility to maintain a safe and healthy work environment.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Elevate workplace safety with the Health & Safety Committee User Guide Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable guide, crafted with our advanced Ai Editor Tool, equips you to establish robust safety protocols effortlessly. Safeguard your workforce and operations effectively with Template.net's innovative solutions.