Free Accounting Software User Guide

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction to [Product Name]................................................................................3
Getting Started: Installation and Setup....................................................................4
Overview of the Dashboard.......................................................................................5
Creating and Managing Invoices...............................................................................6
Generating Financial Reports.....................................................................................7
Multiple Users and Access Control...........................................................................8
Setting up Automatic Backups...................................................................................9
Seeking Help and Support..........................................................................................10
Introduction to [Product Name]
[Product Name] stands at the forefront of accounting solutions, offering an unparalleled platform for managing and documenting financial transactions with utmost ease and efficiency. Our software is crafted to streamline your accounting process, transforming complex financial management into a smooth and intuitive experience.
Within this user guide, you will embark on a walkthrough the functionalities of [Product Name]. Each section is dedicated to acquainting you with the diverse features our software offers, ensuring you grasp its full potential to satisfy your accounting requirements adeptly. We aim to equip you with the knowledge and skills to utilize [Product Name] not just as a tool, but as an integral ally in your financial management endeavors.
Getting Started: Installation and Setup
This section is dedicated to guiding you through the initial stages of deploying [Product Name] on your computing system. The installation process has been engineered for simplicity and efficiency, ensuring that you can swiftly and effectively integrate [Product Name] into your operational framework. Detailed herein are comprehensive, step-by-step instructions tailored to facilitate a seamless installation and configuration process for first-time users.
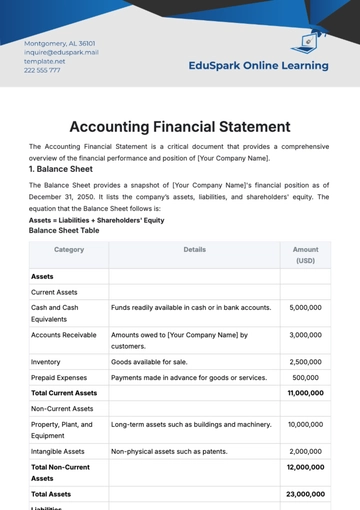
Preparation: Before proceeding with the installation, it is of utmost importance to validate that your computer aligns with the specified minimum system requirements. Below outlines the necessary hardware specifications, operating system compatibility, and storage requirements. Please review these parameters carefully to ensure your system is adequately equipped to support [Product Name].
Requirement Category
Minimum Specification
Operating System
Windows 10, macOS Monterey
Processor
Intel Core i3 or higher
RAM
4GB
Hard Disk Space
500GB available space
Graphics Card
Integrated Intel HD Graphics
Network
Broadband Internet connection
Downloading the Installer: Access the official [Product Name] website and navigate to the download section. Select the version appropriate for your operating system and download the installer file.
Initiating Installation: Locate the downloaded installer file on your computer, typically found in your 'Downloads' folder. Double-click the file to initiate the installation process.
User Account Control: If prompted by User Account Control (UAC), confirm that you wish to allow the installer to make changes to your system. This is a standard security measure on many operating systems.
Installation Wizard: The [Product Name] Installation Wizard will now launch. Follow the on-screen instructions. You will be required to read and accept the End User License Agreement (EULA) to proceed.
Customizing Settings: During the installation, you may be presented with options to customize settings such as the installation directory, shortcut creations, and additional components. Select your preferences as needed.
Installation Progress: The wizard will display the installation progress. Depending on your system, this may take several minutes. It is crucial that the installation process is not interrupted.
Completing Installation: Once the installation is complete, you will typically see a confirmation message. You may be prompted to restart your computer to finalize the installation.
Software Activation: After restarting, launch [Product Name]. The first time you run the software, you may be prompted to enter a product key or log in with an account to activate your copy of the software.
Initial Setup: Follow any additional on-screen instructions to complete the initial setup, which may include configuring basic settings, importing data, or setting up user accounts.
Update and Security Check: Ensure that [Product Name] is updated to the latest version. It’s also recommended to run a security check, if such a feature is available, to verify the integrity of the installation.
Final Steps: Familiarize yourself with the user interface and explore the various features available. Consult the help documentation or user manual for detailed guidance on using [Product Name].
Should you require any assistance during the installation process, do not hesitate to reach out to our support team at [Your Company Email]. Our professionals are committed to providing you with a smooth and trouble-free installation experience.
Overview of the Dashboard
The dashboard of [Product Name] is the cornerstone of your accounting management system, engineered to be both intuitive and comprehensive. It is designed to facilitate immediate access to a wide array of powerful functionalities, ensuring that every aspect of your accounting needs is within easy reach. As you explore the dashboard, you will discover the following key features:
Main Navigation Panel: This is strategically located for easy access, allowing you to swiftly navigate between different accounting modules such as ledger entries, financial reporting, and transaction management.
Quick Access Toolbar: Here, you'll find shortcuts to frequently used tools and functions, significantly speeding up your workflow.
Real-Time Financial Overview: The dashboard offers a dynamic display of your financial status, including current assets, liabilities, and cash flow, enabling you to grasp your financial health at a glance.
Interactive Reporting Graphs: These graphs provide visual representations of various financial metrics, aiding in better understanding and analysis of financial trends and patterns.
Notification and Alert System: Stay informed with real-time alerts and notifications about critical financial updates, pending tasks, and reminders.
Customization Options: Tailor the dashboard to suit your specific preferences and requirements, allowing you to prioritize the information that matters most to your business.
Search Functionality: Quickly locate specific transactions, records, or reports using the powerful search feature, saving valuable time and effort.
User Management and Access Control: Efficiently manage user roles and permissions, ensuring secure access to sensitive financial data.
Integration Hub: Access and manage integrations with other business tools and platforms seamlessly from the dashboard.
Understanding and utilizing these functionalities effectively will greatly enhance your efficiency in managing accounting tasks. As you become more familiar with its layout and capabilities, you will find that managing your accounting tasks becomes significantly more streamlined and effective.
Creating and Managing Invoices
This section is guides you through the process of creating, managing, and dispatching invoices using [Product Name], a task central to the financial health of your business. The following steps outline how to utilize [Product Name] for these essential tasks:
Accessing the Invoice Module: Begin by navigating to the Invoice module within [Product Name]. This can typically be found on the dashboard or within the main menu under financial transactions.
Creating a New Invoice: Click on the option to create a new invoice. You will be prompted to enter essential details such as client information, invoice date, payment terms, and due date.
Adding Line Items: For each service or product provided, add a line item, including descriptions, quantities, and prices. [Product Name] may also offer features to add pre-defined items or services from a database, saving time and ensuring consistency.
Applying Taxes and Discounts: If applicable, add tax calculations and discounts. [Product Name] should automatically calculate the total amount based on these inputs.
Customizing Invoice Templates: Utilize the customization options to align the invoice's appearance with your brand identity. This may include adding logos, changing color schemes, or modifying the layout.
Reviewing and Sending the Invoice: Before sending, review the invoice for accuracy. Then, use [Product Name]'s integrated emailing system or other provided methods to send the invoice directly to your client.
Tracking Invoice Status: After sending the invoice, you can track its status (e.g., sent, viewed, paid, overdue) within [Product Name]. This enables you to have real-time insights into your accounts receivable.
Setting Up Automated Reminders: For unpaid invoices, set up automated reminder emails to be sent to clients. You can customize the timing and frequency of these reminders based on your payment terms.
Receiving Payments and Updating Status: Upon receiving payment, update the status of the invoice in [Product Name]. The software may also support direct payment options, making it easier for clients to pay online.
Reporting and Analysis: Utilize the reporting tools in [Product Name] to generate insights on your invoicing, such as identifying frequent late payers or analyzing your cash flow patterns.
By following these steps, you will not only capitalize on the robust invoicing capabilities of [Product Name] but also enhance your overall financial management efficiency. This systematic approach to creating and managing invoices will facilitate a more organized, professional, and timely billing process.
Generating Financial Reports
This crucial section of the guide focuses on the process of generating financial reports using [Product Name], a vital function for any business seeking to maintain robust financial health and strategic oversight. The ability to create accurate and detailed reports is essential for effective financial analysis, decision-making, and compliance. Follow these steps to utilize [Product Name]'s robust reporting features:
Accessing the Reporting Module: Navigate to the Reporting module within [Product Name], typically located on the dashboard or within the main menu under financial analysis.
Selecting the Type of Report: Choose the type of financial report you wish to generate. [Product Name] likely offers a variety of reports, including income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and more.
Setting Report Parameters: Define the parameters for your report, such as the reporting period (e.g., monthly, quarterly, yearly), specific accounts to include, and any other relevant criteria. This customization ensures the report is tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Applying Filters and Segments: Use filters and segmentation options to drill down into more detailed views of your financial data. This could include departmental expenses, revenue streams by product line, or financials for specific projects.
Generating the Report: Once you have set your parameters, generate the report. [Product Name] will process your inputs and produce a detailed report based on real-time data.
Analyzing Report Data: Review the generated report for insights into your business’s financial health. Look for trends, anomalies, or areas of concern that may require action or further investigation.
Exporting and Sharing Reports: Export your reports into various formats such as PDF, Excel, or CSV for further analysis or sharing with stakeholders. [Product Name] may also offer options to directly share reports via email or integrate with other business platforms.
Scheduling Regular Reports: Automate the generation of routine financial reports by scheduling them at regular intervals. This ensures you regularly receive updated financial insights without manually generating reports each time.
Compliance and Archiving: Ensure that your reports comply with relevant financial reporting standards and regulations. Utilize [Product Name]’s archiving features to securely store reports for future reference and compliance purposes.
Utilizing Advanced Analytics: If available, take advantage of [Product Name]'s advanced analytics features to gain deeper insights, such as predictive analysis or trend forecasting based on your financial data.
By following these steps, you can effectively leverage [Product Name] to produce detailed, accurate financial reports that are essential for strategic business planning, performance tracking, and compliance.
Multiple Users and Access Control
Efficiently managing user access and permissions is paramount in ensuring the security and integrity of your financial data. [Product Name] provides robust capabilities for managing multiple users and access control, allowing you to grant or restrict access to various parts of the system based on roles and responsibilities. The following steps outline how to effectively manage multiple users and access control within [Product Name]:
Accessing User Management: Navigate to the User Management module within [Product Name]. This module is typically located in the settings or administration section of the software.
User Roles and Permissions: [Product Name] offers predefined user roles such as Admin, Accountant, and Sales. Assign specific roles to users based on their responsibilities. Each role may have predefined permissions, or you can customize them as needed.
Creating User Accounts: To add a new user, input their details, including name, email, and contact information. Assign them to a role and specify their access permissions.
Setting Access Levels: Define the specific areas of the software that each user or role can access. This includes modules, reports, and functions. Use the access control settings to ensure users only have access to what is necessary for their job.
Password and Security Policies: Establish strong password policies to enhance security. [Product Name] may offer options for password complexity, expiration, and multi-factor authentication for added protection.
User Onboarding: When adding new users, provide them with training and guidance on using [Product Name]. Ensure they understand their role and responsibilities within the system.
Monitoring User Activity: Regularly monitor user activity and access logs within [Product Name]. This helps in detecting any unauthorized or unusual behavior.
Managing Changes: As your organization evolves, update user roles and permissions as needed. Remove access for users who no longer require it, and grant access to new users as they join your team.
Data Security and Compliance: Ensure that your user management practices align with data security and compliance regulations relevant to your industry. [Product Name] may provide features for data encryption and audit trails.
Support and Assistance: Should you encounter any challenges or require assistance in user management, reach out to [Product Name]'s support team for guidance and support.
Now, let's explore a table outlining common user roles and their associated permissions within [Product Name]:
User Role | Description | Permissions |
|---|---|---|
Administrator | Full control over system settings and data. | Access to all modules and functions. |
Accountant | Responsible for financial data management. | Access to accounting modules and reports. |
Sales | Focus on sales and client interactions. | Access to customer data and sales modules. |
Analyst | Data analysis and reporting. | Access to reporting and analytics tools. |
Viewer | Read-only access for data review. | View-only access, no data modification. |
By following these guidelines and utilizing [Product Name]'s robust user management features, you can ensure that your financial data remains secure, accessible only to authorized personnel, and compliant with regulatory standards. Effective user management is a key pillar of successful financial administration.
Setting up Automatic Backups
One of the most critical aspects of maintaining the integrity and security of your financial data is setting up automatic backups within [Product Name]. Regular backups ensure that in the event of data loss or system failures, you can quickly restore your financial information, minimizing downtime and potential data loss. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to establish automatic backups effectively:
Accessing Backup Settings: Navigate to the Backup and Recovery section within [Product Name]. This section is typically found in the system settings or administration menu.
Select Backup Frequency: Choose how frequently you want backups to occur. Options may include daily, weekly, or custom intervals. Select a frequency that aligns with your organization's needs and data update frequency.
Backup Destination: Specify the backup destination. This could be an external hard drive, a network-attached storage (NAS) device, a cloud storage service, or a combination of these for redundancy.
Data Selection: Define which data should be included in the backups. Most backup systems allow you to select specific modules, databases, or directories to back up. Ensure that financial data and configurations are included.
Retention Policy: Establish a retention policy that dictates how long backups should be retained. This policy ensures that older backups are automatically deleted, optimizing storage usage.
Encryption and Security: Enable encryption for your backups to protect sensitive financial data. Ensure that only authorized personnel have access to the backup system.
Testing Backups: Periodically test your backups to ensure they can be successfully restored. This practice verifies the integrity of your backup files and the restoration process.
Automated Notifications: Set up automated notifications to alert you in case of backup failures or irregularities. Prompt action can be taken to address any issues promptly.
Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly monitor the backup process and review backup logs. Many backup systems provide reporting features to track the status of backups.
Disaster Recovery Plan: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that outlines the steps to follow in case of data loss or system failure. Ensure all relevant team members are familiar with this plan.
Documentation: Document your backup procedures, including backup schedules, retention policies, and encryption methods. This documentation is essential for compliance and auditing purposes.
Regular Updates: Keep your backup software up to date to benefit from the latest security patches and improvements.
Setting up automatic backups is a fundamental element of a robust data protection strategy. By following these steps and best practices, you can safeguard your financial data within [Product Name], ensuring its availability and integrity in the face of unexpected challenges.
Seeking Help and Support
For any assistance or questions regarding [Product Name], please don't hesitate to reach out to us at [Your Company Email] or call us at [Your Company Number]. You can also explore our online knowledge base at [Your Company Website] for comprehensive guidance and FAQs.
We're committed to delivering the best support to ensure your effective use of [Product Name], and we welcome your valuable feedback and suggestions for continuous improvement. Your success is our priority.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Harness the convenience of understanding your accounting software with Template.net's Accounting Software User Guide Template. It offers editable and customizable features that are alterable using our Ai Editor Tool. It provides step-by-step instructions to ensure an easy software navigation process. Experience a simplified user guide creation with this ready-to-use template.