Free Annual Account Budgeting and Forecasting Report

Executive Summary
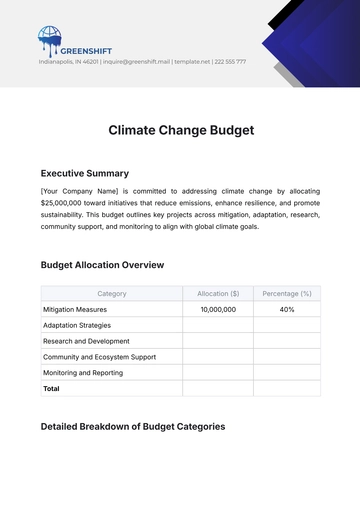
In this report, [Your Company Name] seeks to highlight the budgeting and forecasting activities for the fiscal year [Year]. It encompasses a firm analysis of financial performance, future projections and intended strategic financial directives. Guided by thorough investigations and analysis, the main objective of this report is to outline, analyze, and plan our financial resources ensuring that our organization remains not only economically viable but also financially successful.
Historical Financial Performance Analysis
In the fiscal year [Year], [Your Company Name] achieved a total revenue of $[x] million, with a year-over-year growth of [x]%. This growth can be attributed to successful marketing campaigns, increased market penetration, and the introduction of new products.
Operating expenses totaled $[x] million, comprising salaries, marketing expenses, rent, utilities, and other overhead costs. Despite a slight increase in expenses compared to the previous year, careful cost management initiatives led to a healthy profit margin.
Market expansion initiatives, including entering new geographical regions and diversifying product offerings, contributed significantly to revenue growth. Additionally, strategic partnerships and alliances enhanced distribution channels and market reach.
Investments in technology and automation streamlined operations, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced production costs. This allowed [Your Company Name] to maintain competitive pricing while preserving profit margins.
Budget Development Process
Budget development at [Your Company Name] is a collaborative effort involving department heads, finance team members, and senior management. The process typically begins six months before the start of the fiscal year to allow for comprehensive planning and analysis.
Departmental budget submissions are based on historical performance, market trends, and strategic priorities. These submissions are then reviewed and refined by the finance team to ensure alignment with overall corporate objectives and financial constraints.
The zero-based budgeting approach is employed to ensure that all expenses are justified based on their merits and contribution to organizational goals. This approach fosters accountability and encourages cost-conscious decision-making at all levels of the organization.
Budget assumptions are carefully considered and documented, taking into account factors such as projected revenue growth, inflation rates, changes in market conditions, and regulatory compliance requirements. Sensitivity analysis is conducted to assess the potential impact of varying assumptions on budget outcomes.
Revenue Forecasting
Revenue Source | Forecasted Amount ($) | Growth Rate (%) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
Product Sales | $[x] | [x]% | Expansion into new markets, increased market share |
Key Insights:
Product sales are expected to remain the primary revenue driver, with a projected growth rate of [x]%.
Service revenue is forecasted to experience significant growth of [x]% due to the introduction of new services and improved customer engagement.
Other income, including investment returns and licensing fees, contributes to revenue diversification and stability.
Expense Budgeting
Expense Category | Budgeted Amount ($) | Variance from Previous Year ($) | Key Initiatives for Cost Control |
|---|---|---|---|
Salaries | $[x] | $[x] decrease | Performance-based incentives, workforce optimization |
Cash Flow Forecasting
Cash flow projections indicate sufficient liquidity to meet operational needs and investment requirements for the fiscal year [Year].
The forecast takes into account anticipated cash inflows from sales, investments, and financing activities, as well as expected cash outflows for expenses, debt repayments, and capital investments.
Contingency plans are in place to address potential cash flow challenges, such as delayed customer payments, unexpected expenditures, or fluctuations in interest rates.
A cash flow statement is prepared on a monthly basis to track actual cash movements against the forecast, allowing for timely adjustments to cash management strategies.
Working capital management techniques, such as optimizing inventory levels and negotiating favorable payment terms with suppliers, are employed to enhance cash flow efficiency and liquidity.
Surplus cash is allocated to short-term investments or retained as reserves to support future growth initiatives and mitigate liquidity risks.
Capital Expenditure Budget
The capital expenditure budget for the fiscal year [Year] includes strategic investments aimed at enhancing operational efficiency, expanding capacity, and driving long-term value creation.
Investments in technology infrastructure focus on upgrading IT systems, software platforms, and cybersecurity measures to support digital transformation initiatives and improve business agility.
Capital expenditures for production facilitiesare earmarked for equipment upgrades, facility expansion, and process optimization to meet growing demand, enhance product quality, and reduce manufacturing costs.
ROI analysis is conducted to evaluate the expected returns and payback periods of capital projects, ensuring alignment with corporate objectives and prudent allocation of resources.
Capital allocation decisions prioritize investments that offer the highest potential for revenue growth, cost savings, risk mitigation, or competitive advantage, while balancing short-term needs with long-term sustainability.
Budget Monitoring and Control
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as revenue growth, expense-to-revenue ratio, and cash flow adequacy are monitored regularly using a robust financial reporting system.
Monthly financial reviews are conducted to track actual performance against budgeted targets, identify variances, and assess the reasons behind any deviations.
Variance analysis is performed at both the aggregate and departmental levels to pinpoint areas of concern and opportunities for improvement.
Cross-functional collaboration between finance, operations, and sales teams enables timely identification and resolution of budget-related issues.
Corrective actions are taken promptly to address unfavorable variances, including revising expenditure plans, renegotiating contracts, or reallocating resources.
Budget controls are strengthened through the implementation of spending limits, approval processes, and regular audits to prevent unauthorized expenditures and ensure compliance with financial policies.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Financial risks, both internal and external, are systematically identified, assessed, and prioritized through a comprehensive risk management framework.
Internal risks, such as operational inefficiencies, resource constraints, and workforce disruptions, are mitigated through process improvements, talent development initiatives, and succession planning.
External risks, including market volatility, geopolitical uncertainty, and regulatory changes, are monitored closely using advanced analytics and scenario planning techniques.
Risk mitigation strategies are tailored to specific risk exposures, leveraging tools such as insurance, derivatives, and contractual agreements to minimize potential financial losses.
Regular stress testing and sensitivity analysis are conducted to evaluate the resilience of the budget to adverse scenarios and identify areas of vulnerability.
Contingency plans are developed to address potential risk events, outlining predefined actions and decision-making protocols to mitigate their impact on financial performance.
Budget Review and Adjustment
Quarterly budget reviews are conducted to assess performance against targets and adjust forecasts as necessary. These reviews involve a thorough examination of actual financial results compared to the budgeted figures, identifying any discrepancies or variances. Through these reviews, [Your Company Name] can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of its budgeting strategies and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
Conclusion
[Your Company Name] is well-positioned to achieve its financial goals for the fiscal year [Year] through proactive budgeting and forecasting. The comprehensive analysis and strategic planning outlined in this report provide a solid foundation for navigating uncertainties and capitalizing on growth opportunities in the market.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Introducing Template.net's Annual Account Budgeting and Forecasting Report Template! Editable and customizable, it empowers users to tailor financial analyses to their needs. Harness the power of our AI Editor Tool to seamlessly edit and adapt reports. Streamline budget planning with this comprehensive solution, optimizing financial performance effortlessly.
You may also like
- Budget Sheet
- Personal Budget
- Non Profit Budget
- Monthly Budget
- Project Budget
- HR Budget
- Company Budget
- Home Budget
- Weekly Budget
- College Budget
- Business Budget
- Construction Budget
- Small Business Budget
- Hotel Budget
- Annual Budget
- Home Renovation Budget
- Household Budget
- Student Budget
- Grocery Budget
- Marketing Budget
- Corporate Budget
- Startup Budget
- Manufacturing Budget
- Church Budget
- University Budget
- Annual Budget Plan
- Event Budget
- Operating Budget
- Travel Budget
- Food Budget
- IT and Software Budget
- School Budget
- Real Estate Budget
- Sales Budget
- Conference Budget
- Budget Finance
- Freelancer Budget
- Budget Advertising