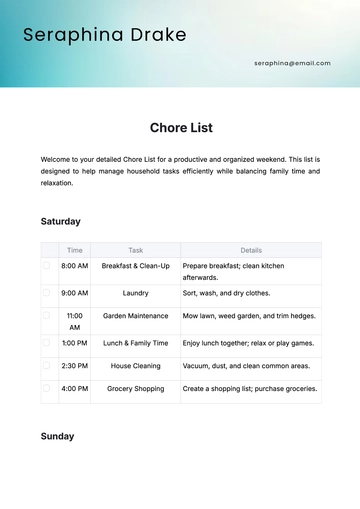
Free Email Marketing Policy & Procedure for List Management

1. Introduction
This document outlines the policy and procedures for email list management at [Your Company Name]. It sets the standard practices for acquiring, managing, segmenting, and maintaining our email lists to ensure compliance, data integrity, and effective engagement with our audience.
2. Objectives
The objectives of this Email Marketing Policy and Procedure for List Management are foundational to maintaining a best-in-class email marketing program. Each objective is designed to guide our practices, safeguard our reputation, and maximize engagement with our audience. Below is a detailed explanation for each objective.
Ensure Legal Compliance in All Jurisdictions. The first and foremost objective is to ensure that all our email marketing activities comply with the legal requirements in every jurisdiction where we operate or have subscribers. Compliance is not just a legal necessity; it also builds trust and credibility with our audience. This includes adhering to regulations like the CAN-SPAM Act in the U.S., GDPR in the European Union, and any local laws that pertain to email communication and data protection. By being compliant, we safeguard our company from potential legal penalties and protect our subscribers' rights.
Maintain High-Quality, Clean Email Lists. Maintaining a clean and high-quality email list is crucial for the effectiveness of our email campaigns. A clean list, devoid of inactive or unresponsive addresses, helps improve deliverability and engagement rates. This involves regular list hygiene practices like removing inactive subscribers, updating incorrect email addresses, and encouraging subscribers to update their own preferences. The objective is to ensure that our communications are welcome and valued by our subscribers, rather than being filtered out as spam or irrelevant content.
Enhance Customer Relationships and Trust. The quality of our email marketing efforts directly impacts our relationship with customers. By providing valuable, relevant, and timely content, we aim to enhance customer loyalty and trust. This objective aligns with the broader corporate strategy of customer relationship management, focusing on long-term engagement rather than quick wins. Personalization, useful content, and consistent communication all contribute to a trusted relationship, encouraging more interactions, purchases, and referrals over time.
Achieve Targeted and Effective Email Campaigns. Lastly, the objective of targeted and effective email campaigns means more than just hitting KPIs. It means that we're reaching the right people with the right message at the right time. Leveraging data analytics and segmentation strategies, we aim to tailor our email content so that it resonates with specific customer groups and addresses their unique needs and preferences. An effective campaign should not only meet but exceed set performance metrics, driving business results while delivering value to our subscribers.
By achieving these objectives, we aim to uphold the highest standards in email marketing, ensuring that we are both effective and respectful in our communications.
3. Definitions
Understanding the terms and jargon is crucial for everyone involved in executing our email marketing policy. This section aims to clarify the key terms that are essential for the proper implementation of our email list management practices. Each definition is accompanied by a more detailed explanation to provide context and ensure a comprehensive understanding.
Term | Definition | Additional Information |
Subscriber | An individual who has opted in to receive emails from [Your Company Name] | Subscribers are the core of any email marketing strategy and can be acquired through various channels. They have actively expressed interest in receiving email communications, either through a signup form, a purchase, or another engagement point. |
Double Opt-In | A two-step verification process for new subscribers | After a user initially signs up to become a subscriber, a follow-up email is sent to confirm their subscription. This ensures that the email address is valid and that the subscriber genuinely wants to receive communications from us. |
List Segmentation | The practice of dividing an email list into sub-groups based on criteria | Segmentation can be based on various criteria such as geographic location, purchase behavior, or engagement level. It allows for more targeted and personalized email campaigns. |
CAN-SPAM Act | A U.S. law setting standards for commercial emails | The CAN-SPAM Act outlines requirements for sending commercial emails, including the necessity for an unsubscribe link and providing a physical business address. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines. |
GDPR | The General Data Protection Regulation, applicable in the EU | GDPR is a comprehensive data protection law that requires businesses to protect the privacy and personal data of European Union citizens. It mandates explicit consent for data collection and provides guidelines for data storage and usage. |
By understanding these terms and their nuances, team members can better implement the procedures and policies outlined in this document, ensuring that our email marketing initiatives are both effective and compliant.
4. Subscriber Acquisition
Subscriber acquisition is a fundamental aspect of our email marketing strategy. A high-quality subscriber list is the backbone of effective email marketing; therefore, it's crucial to employ best practices when adding new subscribers. Below are the key areas that we focus on for subscriber acquisition.
Channels. Subscribers may be acquired through multiple touchpoints. Our website serves as a primary channel, usually through newsletter sign-up forms or during the checkout process for e-commerce. Social media platforms also offer opportunities for list growth, such as promoting a lead magnet that requires an email address to access. In-person events like trade shows or seminars can also be leveraged for list building, with attendees opting in via sign-up sheets or kiosks. It is crucial that each channel follows the standard acquisition guidelines set forth in this policy to ensure consistency and compliance.
Verification. To maintain the integrity of our list and ensure that subscribers genuinely want to receive our emails, all new subscribers must go through a double opt-in process. Upon initial sign-up, an automated email is sent to the subscriber requiring them to confirm their subscription. This not only validates the email address but also confirms the individual's interest in being on our mailing list. This practice is in line with GDPR requirements and also serves as an effective tool to keep our list clean and engagement rates high.
Record Keeping. Proper record-keeping is essential to both prove compliance with various email laws and to provide valuable data for future marketing strategies. Whenever a new subscriber opts in, the timestamp of that action and the channel through which they subscribed must be recorded. This information should be stored securely in our database. Such meticulous record-keeping aids in list segmentation, personalization strategies, and ensures that we have the necessary data on hand should any legal issues regarding consent arise.
By strictly adhering to these best practices in subscriber acquisition, we aim to build a robust and engaged email list, compliant with regulations, and primed for effective marketing campaigns.
5. Data Management
Effective data management is not just a best practice; it's a legal requirement and a critical element of ethical email marketing. This section outlines our standards and practices for the secure storage, timely update, and straightforward unsubscribe procedures for our email subscriber data.
Storage. All subscriber data must be stored securely to comply with GDPR and other relevant data protection laws. Security is a multi-faceted concern that involves both technological measures and employee training. Our database servers should be equipped with state-of-the-art encryption and firewall technology, and only authorized personnel should have access to this sensitive information. Regular audits and system checks must be conducted to ensure that data is not only secure but also up-to-date and accurate.
Updates. Providing subscribers with an option to update their profile and preferences is key for maintaining an engaged and satisfied email list. Changes in email addresses, names, or even preferences for types of content should be easily manageable by the subscribers themselves. This not only enhances the user experience but also helps us send targeted and relevant content, thereby increasing engagement rates. This feature should be easily accessible, typically via a 'Manage Preferences' link in the footer of every email sent or through the subscriber's account on our website.
Unsubscribing. A clear and simple unsubscribe option is a legal requirement and must be included in every email sent out to our subscribers. The process should be straightforward, requiring as few clicks as possible and not be obscured or made difficult in any way. A best practice is to include the unsubscribe link in both the header and footer of the email for higher visibility. Once a user opts to unsubscribe, their request should be honored promptly, and they should be removed from the mailing list to ensure compliance with regulations like the CAN-SPAM Act and GDPR.
By adhering to these data management guidelines, we aim to foster trust with our subscribers, maintain compliance with legal standards, and optimize the performance of our email marketing campaigns.
6. List Segmentation
List segmentation is the practice of dividing your email list into different categories or 'segments' to allow for more targeted and personalized email campaigns. By doing so, we can significantly improve key performance indicators like open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates. The following are the primary considerations for effective list segmentation in our email marketing initiatives.
Criteria. The criteria for segmentation can be incredibly diverse, depending on the goals of a specific campaign. Commonly used criteria include geographic location, which allows for regional targeting and time-zone optimized sending; past purchase behavior, useful for upsell or cross-sell initiatives; and engagement levels, beneficial for re-engagement campaigns or rewarding highly engaged subscribers. The choice of criteria should align with the overall objectives of the marketing campaign and be supported by data analysis to ensure efficacy.
Updates. Given that customer behavior and preferences are dynamic, it's crucial that list segments are not static. To maintain the effectiveness of our segmented campaigns, all list segments should be reviewed and updated quarterly. This review process should include an analysis of the performance of each segment to see if they are still contributing to meeting the objectives of your email campaigns. Inactive or underperforming segments may need to be adjusted or removed to keep the list optimized.
Personalization. One of the most powerful applications of list segmentation is the ability to offer highly personalized content and offers to each segment. Personalization goes beyond inserting the subscriber's first name in the email; it could mean offering products similar to what they've purchased before, sending birthday or anniversary promotions, or providing content that is relevant to their specific interests or problems. By leveraging segmentation for personalization, we aim to increase relevance for the subscriber, thereby increasing engagement and boosting ROI.
Through strategic list segmentation based on well-defined criteria, regular updates, and a focus on personalization, we aim to elevate the effectiveness and efficiency of our email marketing campaigns.
7. Compliance and Regulations
Navigating the complex landscape of email marketing requires strict adherence to various laws and regulations to ensure ethical conduct and avoid legal ramifications. Failing to comply can result in not just financial penalties but also loss of reputation and customer trust. Below are key compliance measures related to GDPR, the CAN-SPAM Act, and local regulations.
A. GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a crucial framework for data protection and privacy for individuals within the European Union (EU). All data collection and storage related to email marketing must be in strict compliance with GDPR guidelines. This includes providing a clear explanation at the point of sign-up about how subscribers' data will be used and stored, and obtaining explicit consent to send them emails. Furthermore, data storage should be secure to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches, which could result in severe penalties under GDPR.
B. CAN-SPAM Act
The Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing (CAN-SPAM) Act is a U.S. law that sets the rules for commercial email. One key requirement of this act is that all emails must include a legal footer that provides an option to unsubscribe and the physical address of the sender. This ensures transparency and gives recipients a clear path to opt out of future communications. Failure to include these elements can result in hefty fines and legal consequences.
C. [Your Country's Email Laws]
In addition to global regulations like GDPR and CAN-SPAM, it's crucial to be well-versed and compliant with email marketing laws specific to the country of operation. These laws can often include specifics about the collection of data, the rights of the subscriber, and the requirements for lawful sending of commercial emails. Being unaware of or failing to adhere to these local laws can lead to legal issues and harm the brand's reputation.
By maintaining rigorous compliance with these various laws and regulations, we not only protect ourselves from legal challenges but also build a reputation as a trustworthy and ethical business entity.
8. Audits and Reviews
Regular audits and reviews are an integral part of maintaining a high-quality, compliant email list. These processes are essential for identifying areas for improvement, ensuring compliance with legal regulations, and providing actionable insights for better performance. Here are the specifics related to the frequency and responsibilities for these critical audits and reviews.
A. Frequency
Given the dynamic nature of email marketing metrics, customer behavior, and legislative updates, it is recommended that email lists be audited quarterly. This frequency allows for a timely evaluation without being too disruptive to ongoing marketing activities. A quarterly audit can include checking for inactive subscribers, analyzing engagement rates, verifying compliance with legal requirements, and assessing the overall health of the list. This practice enables us to take corrective actions before issues escalate, thus maintaining the quality of our email marketing campaigns.
B. Responsibility
The responsibility for carrying out these important audits lies with the [Marketing Team]. The team should develop a standard operating procedure for the audits to ensure consistency and thoroughness. This procedure should be documented and updated as needed to reflect any changes in regulations or business objectives. Team members should be trained in these procedures and be well-equipped with the required tools and access to carry out the audits effectively.
Through scheduled audits and assigning clear responsibilities for them, we aim to keep our email marketing program not just compliant but also optimally effective. This proactive approach can help anticipate issues before they become problems, thereby preserving the integrity and ROI of our email marketing initiatives.
9. Policy Violations
Violations of this email marketing policy are considered serious offenses, as they can lead to legal repercussions, financial penalties, and damage to the brand's reputation. Here are the consequences and processes associated with any breach of this policy.
Failure to comply with the procedures and regulations outlined in this policy document may result in disciplinary action taken against the responsible individual(s). The severity of the action is determined by the extent and impact of the violation, and it could range from a formal written warning to mandatory retraining or even financial penalties against the department responsible.
In the most severe cases, especially if the violation leads to legal consequences for the company or poses a significant risk to its reputation or customer relations, termination of employment may be considered as the final step. It is the responsibility of the [HR Department] in coordination with the [Legal Department] and [Marketing Team] to investigate any reports of violations and recommend appropriate action.
Each instance of violation will be documented, reviewed, and stored in a secure location to ensure a thorough understanding of its nature and extent, as well as to facilitate any legal procedures that may ensue. This record will also serve as a point of reference for future policy revisions and employee training.
Through strict enforcement of this policy, we aim to maintain the highest standards of ethical conduct and legal compliance in our email marketing operations.
10. Amendments and Updates
This policy is subject to updates and will be reviewed on an annual basis. Next review date is [Month Day, Year].
_____________________________________________________________________________________
By adhering to this Email Marketing Policy & Procedure for List Management, [Your Company Name] aims to execute effective and compliant email marketing strategies that serve both our organization and our subscribers.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Enhance your email marketing strategy with the Email Marketing Policy & Procedure for List Management Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable resource ensures compliance and efficiency. Tailor it effortlessly using our Ai Editor Tool, making list management a seamless part of your marketing endeavors. Elevate your campaigns with ease.