Free Administration Budget Compliance Document

I. Introduction
A. Purpose of the Document
The purpose of this document is twofold:
First, it serves as a comprehensive guide to the regulatory framework, key responsibilities, and required compliance processes for the management and use of the organization’s budget. This is designed to ensure that staff members and management at all levels within the company adhere to the established procedures detailed herein.
Second, the document aims to foster transparency, accountability, and efficiency in the management of the company’s financial resources. It provides a clear roadmap for all employees to follow, ensuring consistency across all levels of the organization. The document also serves as a reference point for any queries or clarifications related to the company’s budget management.
B. Scope of the Document
Scope Coverage: The scope of this document extends to all financial operations within the company. It covers all departments and units within the company, ensuring that everyone is on the same page when it comes to budget management.
Transaction Types: The document also applies to all types of financial transactions, including but not limited to, procurement, sales, payroll, and investments. This comprehensive coverage ensures that all financial activities are conducted in accordance with the company’s budgetary guidelines.
Consequences of Non-Compliance: The document outlines the consequences of non-compliance, emphasizing the importance of adhering to the guidelines set forth in this document. This serves as a deterrent for any potential violations and underscores the company’s commitment to financial integrity.
C. Importance
The importance of this document cannot be overstated. It serves as a cornerstone for the company’s financial health, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and effectively. By providing a clear framework for budget management, the document helps to prevent financial mismanagement and promotes fiscal responsibility.
Furthermore, the document promotes a culture of accountability and transparency within the company. By clearly outlining the responsibilities of each employee in relation to budget management, it ensures that everyone is held accountable for their actions. This culture of accountability is essential for fostering trust and cooperation among employees, which in turn contributes to the overall success of the company.
II. Regulatory Framework
The company’s financial operations are governed by a set of administrative guidelines. Adherence to these guidelines is not optional; it is mandatory. Violations may lead to consequences as outlined in Section IV.
A. Adherence to the Financial Management Act (FMA)
Commitment to the FMA: The company is committed to the proper preparation and administration of its budget in accordance with the principles stipulated in the Financial Management Act (FMA). This commitment is reflected in all of the company’s financial activities, from budget planning to financial reporting.
Ethical Financial Transactions: This includes ensuring that all financial transactions are conducted in a manner that is legal, ethical, and in the best interests of the company. This commitment to ethical financial practices helps to protect the company’s financial resources and maintain its reputation for integrity.
Secure Record Keeping: The company also ensures that all financial records are maintained accurately and securely, in compliance with the FMA. This includes implementing robust data security measures to protect financial information from unauthorized access or loss.
B. Observance of Budgetary Control Measures
Budgetary Control Measures: The company has implemented stringent budgetary control measures to ensure the efficient use of its financial resources. These measures are designed to prevent overspending and ensure that financial resources are allocated in a manner that aligns with the company’s strategic objectives.
Record Keeping: These measures include the maintenance of proper records and memoranda relating to all budgetary estimates. This ensures that there is a clear record of all budgetary decisions, which can be referred to in case of any discrepancies or disputes.
Regular Audits: The company also conducts regular audits to ensure compliance with these measures. These audits provide an opportunity to identify and address any potential issues before they become significant problems.
Reporting System: In addition, the company has established a system for reporting any deviations from the budget, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly and effectively. This system encourages employees to take an active role in budget management and promotes a culture of accountability.
Training and Support: Lastly, the company provides training and support to all employees to ensure they understand and can effectively implement these control measures. This training is designed to equip employees with the knowledge and skills they need to manage their budgets effectively.
C. Compliance with Financial Reporting and Auditing Requirements
Accurate Reporting: The company is committed to ensuring accuracy, transparency, and credibility in its budgetary practices. This includes complying with all financial reporting and auditing requirements as stipulated by relevant authorities.
Timely Presentation: The company also ensures that all financial reports are prepared and presented in a timely and accurate manner. This commitment to timely reporting ensures that stakeholders have access to up-to-date financial information, enabling them to make informed decisions.
Internal Audit Function: In addition, the company has established a robust internal audit function to ensure compliance with these requirements. This function plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the company’s financial operations, identifying potential issues, and recommending corrective actions.
III. Compliance Duties and Responsibilities
The management of the company’s budget is a shared responsibility that involves various roles within the organization. The following table provides a detailed breakdown of these roles and their respective responsibilities:
Job Role | Duties and Responsibilities |
|---|---|
Management | Oversee the entire budgeting process, ensuring compliance with established guidelines. |
Finance Department | Establish budget protocols, prepare financial reports, and support auditing processes. |
All Employees | Adhere to the indicated budgetary rules and report any observed irregularities. |
Each role contributes to the effective management of the company’s budget, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and strategically. This collaborative approach to budget management fosters a culture of accountability and transparency, which is essential for the company’s long-term success.
The role of management is crucial in the budgeting process. They are responsible for overseeing the entire process. This involves coordinating with various departments, making strategic decisions, and ensuring that all employees understand and adhere to the budgetary rules.
The Finance department also plays a key role in establishing budget protocols, preparing financial reports, and supporting auditing processes. Their work forms the backbone of the company’s financial operations, providing the necessary data and insights for effective budget management. They also play a crucial role in ensuring transparency and accountability in the company’s financial practices.
Moreover, all employees have a part to play in adhering to the budgetary rules and reporting any observed irregularities. This collective responsibility fosters a culture of accountability and transparency, which is essential for effective budget management. It also empowers employees to take an active role in the company’s financial operations, promoting a sense of ownership and commitment.
Moreover, the importance of these roles and responsibilities extends beyond the company’s financial operations. They also contribute to the company’s reputation and credibility. By adhering to established budgetary guidelines and demonstrating transparency in its financial practices, the company enhances its standing in the eyes of stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees. This, in turn, contributes to the company’s overall success and growth. Therefore, it is crucial that each role is performed diligently and responsibly, with a clear understanding of its impact on the company’s financial health and reputation.
IV. Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with the company’s budgetary guidelines can have serious implications. It is therefore crucial for all employees to understand the potential consequences of non-compliance. The following table provides a detailed breakdown of these consequences based on the severity of the non-compliance:
Severity of Non-Compliance | Consequences |
|---|---|
Minor | May result in a formal warning and additional training. |
Moderate | May lead to a performance review and potential impact on bonus. |
Severe | Could lead to termination of employment and potential legal action. |
The consequences of non-compliance serve as a deterrent for potential violations. They underscore the seriousness with which the company views adherence to its budgetary guidelines. By clearly outlining the potential consequences of non-compliance, the company sends a clear message to all employees about the importance of adhering to these guidelines.
Minor non-compliance, may result in a formal warning and additional training. This means that if an employee fails to adhere to the company’s budgetary guidelines in a minor way, they may receive a formal warning. This is not just a slap on the wrist. It is a clear signal that the employee’s actions are not in line with the company’s expectations. In addition to the formal warning, the employee may also be required to undergo additional training. This training is designed to help the employee understand the importance of adhering to the company’s budgetary guidelines and to equip them with the knowledge and skills needed to do so.
Moderate non-compliance can lead to a performance review and potential impact on bonus. This level of non-compliance indicates a more serious deviation from the company’s budgetary guidelines. It may trigger a comprehensive review of the employee’s performance, which could potentially impact their bonus. This consequence serves as a significant deterrent, encouraging employees to adhere strictly to the company’s budgetary guidelines.
Severe non-compliance could lead to termination of employment and potential legal action. This is the most serious level of non-compliance and indicates a significant breach of the company’s budgetary guidelines. The consequences at this level are severe and could include termination of employment and potential legal action. This underscores the seriousness with which the company views adherence to its budgetary guidelines.
In a nutshell, these consequences are not just about punishment. They are also about education and improvement. By providing additional training in cases of minor non-compliance, the company demonstrates its commitment to helping its employees improve and succeed. This approach not only helps to ensure compliance with the company’s budgetary guidelines, but also contributes to the overall growth and development of its employees. Therefore, it is crucial for all employees to understand these consequences and to strive to adhere to the company’s budgetary guidelines at all times.
V. Periodic Reviews
A. Review Process
Periodic reviews are an integral part of the company’s compliance strategy. These reviews are conducted at regular intervals to ensure that the company’s budgetary practices remain in line with the latest regulatory requirements and internal policies.
Frequency of Reviews: The frequency of these reviews is determined by the complexity and volatility of the company’s financial operations. However, as a general rule, these reviews are conducted at least once a year.
Scope of Reviews: The scope of these reviews includes all aspects of the company’s budgetary practices, from the preparation and administration of the budget to the adherence to budgetary control measures and financial reporting requirements.
Review Team: The reviews are conducted by a team of internal auditors, finance professionals, and management representatives. This team is responsible for assessing the effectiveness of the company’s budgetary practices and identifying areas for improvement.
B. Communication of Changes
Any changes resulting from these reviews are communicated promptly to all relevant parties.
Communication Channels: The company uses various communication channels to disseminate these changes, including email notifications, company meetings, and updates to the company’s internal portal.
Responsibility for Communication: The responsibility for communicating these changes lies with the management team, who ensure that all employees are aware of the changes and understand their implications.
Training on Changes: In addition to communicating these changes, the company also provides training to help employees understand and implement the changes effectively.
C. Continuous Improvement
The process of periodic review is not just about compliance; it’s also about continuous improvement.
Learning from Reviews: The company uses the insights gained from these reviews to improve its budgetary practices and enhance its financial performance.
Innovation and Adaptation: The company is committed to innovation and adaptation, continually seeking ways to improve its budgetary practices and adapt to changing regulatory requirements and business conditions.
Commitment to Excellence: Through this process of continuous improvement, the company demonstrates its commitment to excellence in financial management, striving to achieve the highest standards of accuracy, transparency, and accountability in its budgetary practices.
By conducting periodic reviews and communicating changes effectively, the company ensures that it stays compliant with any changes in relevant legislation, as well as internal changes within the organization. This process of periodic review and communication ensures that the company’s financial operations remain transparent, accountable, and efficient.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
This Administration Budget Compliance Document Template is a comprehensive solution from Template.net! It is easily editable with our AI Editor Tool, providing an efficient way to manage budget compliance. This resource is fully customizable, ensuring fair and efficient use of available resources. Grab your copy right now to get started!
You may also like
- Budget Sheet
- Personal Budget
- Non Profit Budget
- Monthly Budget
- Project Budget
- HR Budget
- Company Budget
- Home Budget
- Weekly Budget
- College Budget
- Business Budget
- Construction Budget
- Small Business Budget
- Hotel Budget
- Annual Budget
- Home Renovation Budget
- Household Budget
- Student Budget
- Grocery Budget
- Marketing Budget
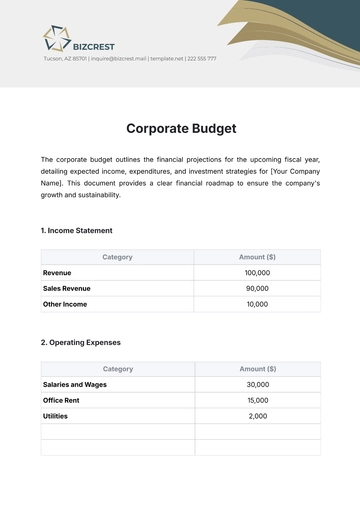
- Corporate Budget
- Startup Budget
- Manufacturing Budget
- Church Budget
- University Budget
- Annual Budget Plan
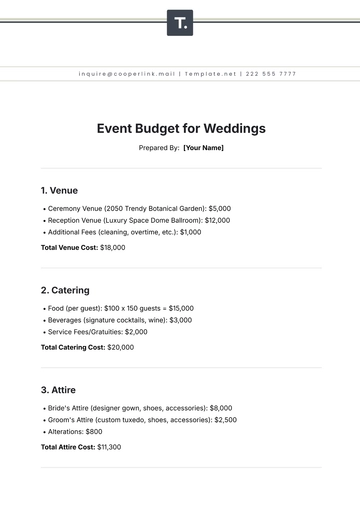
- Event Budget
- Operating Budget
- Travel Budget
- Food Budget
- IT and Software Budget
- School Budget
- Real Estate Budget
- Sales Budget
- Conference Budget
- Budget Finance
- Freelancer Budget
- Budget Advertising