Free Annual Health & Safety Legal Compliance Report

I. Executive Summary
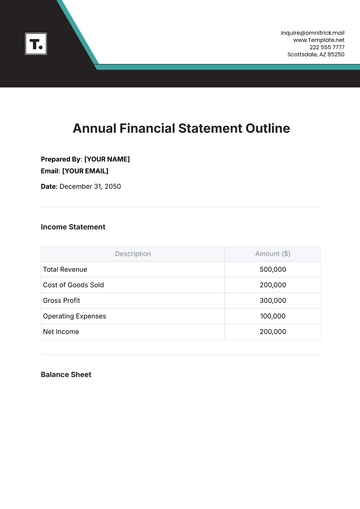
A. Introduction
Welcome to the Annual Health & Safety Legal Compliance Report for [Your Company Name]. This report provides an overview of our efforts to ensure a safe and healthy working environment for all employees and stakeholders during the reporting period.
B. Key Achievements
a. Implementation of a New Safety Training Program:
We successfully rolled out a new safety training program, reaching [95%] of employees. This initiative aimed to enhance awareness of workplace hazards and improve overall safety consciousness.
b. Reduction in Lost-Time Injuries:
We are pleased to report a [15%] reduction in lost-time injuries compared to the previous year, reflecting our commitment to continuous improvement in safety performance.
C. Challenges and Lessons Learned
a. Adapting to Remote Work Challenges:
The transition to remote work presented new challenges in ensuring home office safety. We have learned valuable lessons and are implementing guidelines for remote work safety in the coming year.
b. Addressing Near Misses:
Increased reporting of near misses highlights a proactive safety culture. We are taking steps to analyze and address these incidents to prevent potential accidents.
II. Regulatory Compliance
A. Overview of Health and Safety Laws and Regulations
[Your Company Name] operates in compliance with local, regional, and national health and safety regulations, including the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA), and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Regular updates were monitored, and necessary adjustments were made to policies and procedures to ensure continued compliance.
B. Compliance Status
Internal audits and inspections confirmed our commitment to regulatory compliance. No major instances of non-compliance were identified during the reporting period. Any minor non-conformities were promptly addressed, and corrective actions were implemented.
III. Incident Reporting and Analysis
A. Overview of Incidents
During the reporting period, a total of [25] workplace incidents were reported, including [15] minor injuries, [5] recordable injuries, and [5] near misses. This represents a slight increase from the previous year.
B. Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis was conducted for each recordable injury and near miss. Findings revealed common contributing factors, such as inadequate training and communication breakdowns. Corrective actions include targeted training programs and enhanced communication strategies.
C. Trends and Patterns
Analysis of incident data indicates a trend toward slips, trips, and falls. To address this, we will be implementing a comprehensive floor safety program and increasing awareness through targeted communication campaigns.
IV. Training and Education
A. Training Programs
a. New Employee Safety Orientation:
All new employees received a safety orientation within their first week, covering emergency procedures, hazard recognition, and reporting protocols. In response to employee feedback, an interactive online module was introduced to enhance engagement and knowledge retention.
b. Monthly Safety Toolbox Talks:
Monthly toolbox talks were conducted, addressing topics such as ergonomics, electrical safety, and mental health awareness. Attendees actively participated in discussions, and feedback sessions were introduced to gather employee insights and suggestions for future topics.
V. Emergency Preparedness
A. Emergency Response Plans
Emergency response plans were not only reviewed but also subjected to simulated scenario testing, including a tabletop exercise simulating a chemical spill response. The outcomes of these exercises were used to refine and improve our emergency response protocols, and additional training was provided to key response teams.
B. Drill and Simulation Exercises
Two fire drills and one emergency evacuation simulation were conducted successfully. Observations and feedback from these exercises were analyzed, leading to updates in evacuation routes and improvements in communication protocols. Employees actively participated in post-drill debriefing sessions to share their insights.
VI. Health and Safety Policies
A. Review of Policies
All health and safety policies were reviewed by the Safety Committee in collaboration with legal and compliance teams. The review process included input from employees through focus groups, ensuring that policies reflect the needs of the workforce. Notable changes include updates to the remote work safety policy to address the evolving work environment.
B. Communication of Policies
Acknowledgment of health and safety policies was obtained from all employees, with a [98%] completion rate. To reinforce policy awareness, a series of short, informative videos were created and shared internally. Regular quizzes were introduced to ensure ongoing understanding and compliance with policies.
VII. Audits and Inspections
A. Internal Audits
Internal audits, conducted quarterly, included a focus on cultural aspects of safety. The Safety Culture Survey was introduced to gather qualitative insights from employees about the safety climate. Results were used to tailor training programs and reinforce positive safety behaviors.
B. External Inspections
External inspections were complemented by voluntary third-party audits. Feedback from external audits led to the refinement of our safety management system. Additionally, a best practices sharing initiative was launched to foster collaboration with industry peers.
VIII. Risk Assessments
A. Identification of Risks
Regular risk assessments, conducted in collaboration with departmental teams, identified new risks associated with high-volume data processing. Cross-functional workshops were held to develop targeted risk mitigation strategies, emphasizing proactive hazard identification.
B. Mitigation Strategies
Mitigation strategies included the implementation of advanced safety controls, increased frequency of safety inspections, and the introduction of technology solutions to monitor and mitigate identified risks. Employee training programs were tailored to address the specific risks identified in each department, such as ergonomic best practices for prolonged computer use in the IT department and chemical handling safety protocols in the manufacturing unit
a. Implementation of Advanced Safety Controls for High-Volume Data Processing: This involves introducing state-of-the-art safety mechanisms tailored to the unique demands of high-volume data processing. It could include deploying more robust data encryption methods, enhancing cybersecurity protocols to protect against data breaches, and ensuring regular backups to prevent data loss.
b. Increased Frequency of Safety Inspections: Recognizing the heightened risks associated with high-volume data processing, the frequency of safety inspections is significantly increased. These inspections cover both digital infrastructure, ensuring that all data processing hardware and software are functioning optimally and securely, and physical workspace assessments to identify any potential ergonomic or occupational hazards.
c. Introduction of Technology Solutions: To effectively monitor and mitigate risks in high-volume data processing, cutting-edge technology solutions are employed. This includes real-time monitoring systems that alert to any system overloads or failures, AI-driven analytics tools for predictive risk assessment, and advanced software for efficient data management.
d. Tailored Employee Training Programs: Specialized training programs are developed focusing on the nuances of handling high-volume data. These programs educate employees on best practices in data management, cyber hygiene, and awareness of cyber threats. Additionally, training on physical health, such as proper ergonomics for computer use and stress management techniques, is provided to ensure the overall well-being of employees engaged in intensive data processing tasks.
IX. Compliance Monitoring
A. Monitoring Mechanisms
a. Refinement of Key Performance Indicators: This involves tracking metrics such as the number of near-miss incidents reported, which serve as an early warning system for potential safety risks. Additionally, measuring employee engagement in safety initiatives provides insights into the effectiveness of these programs and employee commitment to safety practices. These leading indicators offer a proactive approach to identifying and addressing safety issues before they escalate into accidents or injuries.
b. Real-Time Monitoring Through Digital Platforms: Utilizing advanced digital platforms enables [Your Company Name] to monitor safety compliance in real-time. This system allows for immediate identification of trends and potential issues as they arise. For instance, a spike in near-miss reports in a particular department can trigger an instant review and intervention. This proactive monitoring ensures that corrective actions are timely and effective, significantly enhancing the company’s ability to maintain a safe work environment.
B. Continuous Improvement
a. Employee Feedback Mechanisms: Recognizing that employees are often the first to notice potential safety issues, [Your Company Name] has implemented several channels for employee feedback. Anonymous surveys provide a safe avenue for employees to report concerns and offer suggestions without fear of reprisal. Additionally, suggestion boxes, placed in accessible areas, encourage employees to contribute ideas for safety improvements. This inclusive approach ensures that the company benefits from a wide range of perspectives and insights.
b. Safety Recognition Program: To further encourage employee engagement in safety practices, a safety recognition program was introduced. This program acknowledges and rewards employees and teams for noteworthy safety suggestions or actions. Such recognition not only boosts morale but also reinforces the company’s commitment to safety and encourages a culture where everyone feels responsible for maintaining a safe work environment.
c. Annual 'Safety Innovation Challenge': To stimulate creative thinking and innovation in safety practices, [Your Company Name] hosts an annual "Safety Innovation Challenge." This event invites employees to propose novel solutions to safety challenges, fostering a spirit of innovation and problem-solving. It serves as a platform for employees to showcase their ideas and for the company to identify and implement new, effective safety strategies. This challenge not only engages employees but also keeps the company’s safety practices dynamic and evolving.
X. Employee Involvement
A. Safety Committees
a. Mentorship Program: Safety committees at [Your Company Name] have pioneered a mentorship program, which is a cornerstone of our safety culture. This initiative pairs seasoned employees with new hires, ensuring a transfer of critical safety knowledge and best practices. It allows experienced workers to impart wisdom and safety insights, fostering a nurturing environment where newcomers can learn and adapt quickly.
b. Committee-Led Safety Workshops and Forums: The safety committees actively organize workshops and open forums. These platforms serve as collaborative spaces where employees from various departments come together to discuss, brainstorm, and exchange ideas on safety-related topics. By conducting these workshops and forums, the committees ensure that safety is not just a top-down directive but a collective responsibility.
B. Employee Feedback
a. Town Hall Meetings and Anonymous Surveys: To foster an open and transparent safety culture, [Your Company Name] utilizes various channels for employee feedback, including town hall meetings and anonymous surveys. Town hall meetings provide a platform for employees to voice their concerns and suggestions directly to management in a structured yet open setting. Anonymous surveys, on the other hand, offer a confidential way for employees to share feedback, especially on sensitive issues.
b. Safety Innovation Recognition Program: In recognizing the vital role employees play in enhancing workplace safety, [Your Company Name] has introduced the Safety Innovation Recognition program. This program celebrates and rewards employees who demonstrate exceptional initiative in identifying and mitigating safety risks. It’s a way of acknowledging their proactive efforts and encouraging others to follow suit. Recognizing these contributions not only boosts morale but also reinforces the company’s commitment to a safety culture driven by employee involvement and innovation.
IX. Conclusion
The reporting period underscored our unwavering commitment to safety excellence. The collaborative efforts of our teams resulted in concrete achievements, from reduced incidents to innovative safety solutions. Through transparent reporting, we aim to inspire confidence in our stakeholders while continually learning from challenges. [Your Company Name] remains dedicated to continuous improvement, utilizing lessons learned to further refine our safety programs. We will amplify employee engagement, leverage technology for real-time monitoring, and explore emerging best practices. Together, we shape a safer future, where every team member actively contributes to and benefits from our collective commitment to a secure and healthy workplace.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Discover Template.net's Annual Health & Safety Legal Compliance Report Template, an essential resource for ensuring regulatory adherence. Effortlessly customize and edit reports with our AI Editor Tool to meet legal requirements. Enhance compliance and reporting accuracy with this editable and customizable solution, streamlining your annual health and safety assessments.
You may also like
- Sales Report
- Daily Report
- Project Report
- Business Report
- Weekly Report
- Incident Report
- Annual Report
- Report Layout
- Report Design
- Progress Report
- Marketing Report
- Company Report
- Monthly Report
- Audit Report
- Status Report
- School Report
- Reports Hr
- Management Report
- Project Status Report
- Handover Report
- Health And Safety Report
- Restaurant Report
- Construction Report
- Research Report
- Evaluation Report
- Investigation Report
- Employee Report
- Advertising Report
- Weekly Status Report
- Project Management Report
- Finance Report
- Service Report
- Technical Report
- Meeting Report
- Quarterly Report
- Inspection Report
- Medical Report
- Test Report
- Summary Report
- Inventory Report
- Valuation Report
- Operations Report
- Payroll Report
- Training Report
- Job Report
- Case Report
- Performance Report
- Board Report
- Internal Audit Report
- Student Report
- Monthly Management Report
- Small Business Report
- Accident Report
- Call Center Report
- Activity Report
- IT and Software Report
- Internship Report
- Visit Report
- Product Report
- Book Report
- Property Report
- Recruitment Report
- University Report
- Event Report
- SEO Report
- Conference Report
- Narrative Report
- Nursing Home Report
- Preschool Report
- Call Report
- Customer Report
- Employee Incident Report
- Accomplishment Report
- Social Media Report
- Work From Home Report
- Security Report
- Damage Report
- Quality Report
- Internal Report
- Nurse Report
- Real Estate Report
- Hotel Report
- Equipment Report
- Credit Report
- Field Report
- Non Profit Report
- Maintenance Report
- News Report
- Survey Report
- Executive Report
- Law Firm Report
- Advertising Agency Report
- Interior Design Report
- Travel Agency Report
- Stock Report
- Salon Report
- Bug Report
- Workplace Report
- Action Report
- Investor Report
- Cleaning Services Report
- Consulting Report
- Freelancer Report
- Site Visit Report
- Trip Report
- Classroom Observation Report
- Vehicle Report
- Final Report
- Software Report