Free Workplace Health & Safety Legal Compliance Document

I. Introduction
A. Purpose
The primary purpose of this document is to establish a comprehensive framework that ensures strict adherence to local, regional, and national laws and regulations governing health and safety within our organization. Through clear guidelines and protocols, this document aims to provide a structured approach to legal compliance, fostering a safe and secure working environment for all stakeholders.
B. Scope
Applicability to All Operations
This document applies to all departments, activities, and personnel within the organization, ensuring a consistent and unified approach to legal compliance.
Inclusive of External Partners
The scope extends to cover contractors, subcontractors, suppliers, and any external parties engaged in activities that fall within our operational domain.
Comprehensive Coverage
From daily operations to emergency response, this document encompasses the entire spectrum of workplace activities, emphasizing a holistic approach to legal compliance.
C. Objectives
Legal Clarity
To provide clarity on the specific legal requirements relevant to workplace health and safety, ensuring all stakeholders are informed and aligned with applicable laws.
Risk Mitigation
To identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with workplace activities, promoting a proactive approach to accident prevention and employee well-being.
Continuous Improvement
To establish a foundation for continuous improvement in health and safety practices, integrating feedback mechanisms and performance evaluations into our compliance initiatives.
II. Legal Framework
A. Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA)
The OSHA Act is a federal law that sets forth the basic standards for workplace safety and health. It outlines employer responsibilities, employee rights, and the enforcement authority of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
B. Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) Regulations
EHS regulations encompass a range of federal, state, and local laws addressing environmental protection, occupational health, and safety. These regulations are designed to minimize the environmental impact of business operations and safeguard the health of employees.
C. Federal Mine Safety and Health Act (MSHA)
MSHA establishes safety and health standards for workers in the mining industry. It outlines regulations related to mine inspections, accident investigations, and the implementation of safety programs to prevent injuries and illnesses.
D. Hazard Communication Standard (HazCom)
Under HazCom, employers are required to provide information to employees about the hazardous chemicals to which they are exposed. This includes ensuring proper labeling, maintaining safety data sheets, and conducting employee training programs.
E. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Codes
NFPA codes and standards address various aspects of fire safety, including the design and installation of fire protection systems, emergency response planning, and the safe handling of hazardous materials.
F. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
ADA prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities. In the context of health and safety, it requires employers to make reasonable accommodations for employees with disabilities to ensure a safe work environment.
G. State and Local Health and Safety Regulations
In addition to federal regulations, compliance with state and local health and safety regulations is imperative. These regulations may vary by location and can include specific requirements tailored to regional concerns.
III. Roles and Responsibilities
A. Health and Safety Officer
Conduct Regular Safety Inspections
Health and safety officers are tasked with conducting routine inspections to identify potential hazards and ensure adherence to safety protocols.
Coordinate and Oversee Training Programs
Responsibility for organizing and overseeing comprehensive training programs, ensuring that all employees receive proper education on safety policies and procedures.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential risks, followed by the implementation of proactive mitigation strategies.
Incident Investigation and Reporting
Leading investigations into incidents, near misses, or safety concerns and reporting findings to relevant stakeholders, guiding the implementation of corrective actions.
Maintain Safety Documentation
Meticulously documenting safety-related information, including inspections, training records, and incident reports, to ensure a comprehensive record of compliance efforts.
B. Employee Duties
Adherence to Safety Protocols
Strict adherence to prescribed safety protocols, including the proper use of personal protective equipment and compliance with established safety procedures.
Active Participation in Training Initiatives
Actively participating in scheduled training programs, including safety orientation, hazard communication, and job-specific training, to enhance knowledge and skills.
Prompt Reporting of Incidents
Promptly reporting any incidents, near misses, or unsafe conditions to designated authorities, contributing to a proactive incident reporting culture.
Utilization of Safety Equipment
Proper utilization and maintenance of safety equipment provided, ensuring that tools and gear are in good condition and used in accordance with safety guidelines.
Contribution to Safety Culture
Playing a proactive role in fostering a culture of safety within the workplace by promoting open communication and participating in safety initiatives.
C. Management Accountability
Resource Allocation for Safety Initiatives
Allocating resources, both human and financial, to support health and safety initiatives, including training, equipment procurement, and compliance efforts.
Integration of Safety Objectives into Decision-Making
Ensuring that safety objectives are integrated into organizational decision-making processes, emphasizing the importance of safety in all aspects of operations.
Recognition and Reward for Safety Practices
Acknowledging and rewarding employees for exemplary safety practices, reinforcing the value of a safety-centric workplace culture.
Communication of Safety Policies
Communicating safety policies and expectations to all levels of the organization, ensuring that every employee understands their role in maintaining a safe workplace.
Support During Regulatory Inspections
Providing support and coordination during regulatory inspections, ensuring a smooth and cooperative process that reflects the organization's commitment to compliance.
Review and Approval of Safety Procedures
Reviewing and approving safety procedures, protocols, and emergency response plans to ensure they align with regulatory standards and industry best practices.
IV. Risk Assessments and Mitigation Strategies
A. Comprehensive Risk Assessments
Thorough risk assessments are conducted regularly to identify potential hazards and assess the associated risks. These assessments form the basis for implementing targeted mitigation strategies.
B. Proactive Mitigation Strategies
Once identified, potential risks are met with proactive mitigation strategies. This involves the development and implementation of controls, employee training, and continuous monitoring to minimize the likelihood of incidents.
C. Regular Review of Risk Assessments
Risk assessments are dynamic tools. We ensure their relevance by conducting regular reviews, especially when there are changes in operations, introducing new processes, or in response to emerging safety concerns.
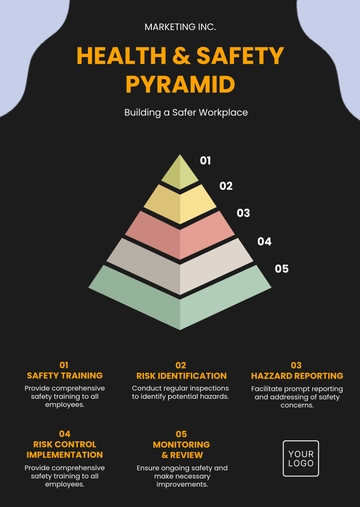
V. Training Programs
Ensuring a comprehensive approach to employee education, our training programs are designed to instill a culture of safety and legal compliance. The table below outlines key aspects of our training program:
Training Type | Frequency | Target Audience | Training Content |
Safety Orientation | Bi-annually | All Employees | Introduction to company safety policies and procedures |
Comprehensive training is essential to maintaining a secure and legally compliant workplace. The systematic approach outlined in our training program addresses various aspects, including foundational safety policies, responsible handling of materials, swift emergency response, and role-specific expertise. This approach aims to reduce incidents, cultivate a safety-centric culture, and ensure adherence to legal standards throughout our operations.
VI. Monitoring Protocols
A. Regular Workplace Inspections
Scheduled and unscheduled workplace inspections are conducted to assess the ongoing adherence to legal requirements. These inspections encompass physical conditions, equipment safety, and employee practices to identify potential non-compliance issues.
B. Incident Reporting and Investigation
A robust incident reporting system is in place, encouraging employees to report any accidents, near misses, or unsafe conditions promptly. Each reported incident undergoes a thorough investigation to identify root causes, implement corrective actions, and prevent future occurrences.
C. Audits by External Experts
Periodic audits conducted by external health and safety experts provide an impartial evaluation of our compliance status. These audits offer valuable insights, ensuring an objective assessment and alignment with industry best practices.
VII. Reporting Procedures
A. Incident Reporting Protocol
A clear and accessible incident reporting protocol is established. Employees are informed of the procedures for reporting incidents, near misses, or any unsafe conditions promptly. This ensures timely response and intervention.
B. Anonymous Reporting Mechanism
To encourage open reporting, an anonymous reporting mechanism is in place for sensitive matters. This ensures that employees feel comfortable reporting without fear of reprisal, facilitating a culture of transparency.
C. Regular Reporting to Regulatory Authorities
Adherence to legal obligations includes regular reporting to regulatory authorities as mandated. Timely and accurate reporting ensures compliance with legal requirements and maintains positive relationships with regulatory bodies.
VIII. Recordkeeping
A. Documented Compliance Records
All aspects of legal compliance, including training records, risk assessments, inspection reports, and incident investigations, are meticulously documented. This documentation serves as a comprehensive record of our commitment to meeting legal standards.
B. Secure Record Storage
Records are securely stored to ensure their integrity and accessibility. This includes electronic and physical storage solutions with controlled access, safeguarding the confidentiality and accuracy of our compliance records.
C. Regular Record Audits
Regular audits of compliance records are conducted to verify their completeness and accuracy. This proactive measure ensures that our records align with legal requirements and provides a foundation for continuous improvement.
IX. Audits and Inspections
A. Internal Compliance Audits
Internal compliance audits are conducted at regular intervals to assess our adherence to legal requirements. These audits, often performed by qualified internal auditors, provide insights into potential areas for improvement.
B. External Regulatory Inspections
We welcome external regulatory inspections as an opportunity to showcase our commitment to compliance. Cooperation with regulatory bodies during inspections reinforces our dedication to transparency and alignment with legal standards.
C. Continuous Improvement Plans
Findings from audits and inspections are used to develop continuous improvement plans. These plans outline specific actions to address identified weaknesses, enhance compliance measures, and prevent reoccurrence of non-compliance issues.
X. Communication Plan
A. Regular Health and Safety Updates
Scheduled communications disseminate regular health and safety updates to all stakeholders. These updates include relevant legal changes, reminders of safety protocols, and insights into organizational health and safety initiatives.
B. Emergency Communication Protocols
Clear protocols are established for communicating during emergencies. This includes effective channels for disseminating urgent information, evacuation procedures, and ensuring all employees are well-informed and prepared.
C. Two-Way Communication Channels
Two-way communication channels are encouraged to facilitate feedback from employees. This ensures that concerns, suggestions, and observations related to health and safety are actively considered, fostering a culture of collaboration.
XI. Continuous Improvement Initiatives
A. Root Cause Analysis and Corrective Action
Systematic root cause analyses are conducted following incidents or non-compliance findings. The insights gained inform targeted corrective actions, addressing underlying issues and preventing recurrence.
B. Employee Feedback Integration
Actively seeking and integrating employee feedback into our improvement initiatives ensures that frontline perspectives contribute to the evolution of our health and safety measures.
C. Benchmarking Against Industry Best Practices
Regular benchmarking against industry best practices allows us to identify emerging trends and adopt innovative approaches to health and safety, ensuring our practices remain at the forefront of industry standards.
XII. Conclusion
In summary, our document underscores our firm dedication to legal adherence and prioritizing the safety of our workforce. Through the implementation of robust monitoring protocols, transparent communication strategies, and a commitment to continuous improvement, we not only meet legal requirements but strive for excellence in safety practices. This document serves as a living guide, subject to regular review and enhancement, ensuring our organization remains at the forefront of legal compliance, fostering a workplace environment where the health and safety of all stakeholders are of utmost importance.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Ensure workplace safety and legal compliance effortlessly with Template.net's Workplace Health & Safety Legal Compliance Document Template. This editable and customizable template, powered by our AI Editor Tool, simplifies the process of drafting precise and comprehensive legal documents. Safeguard your business and employees with Template.net's innovative solutions.