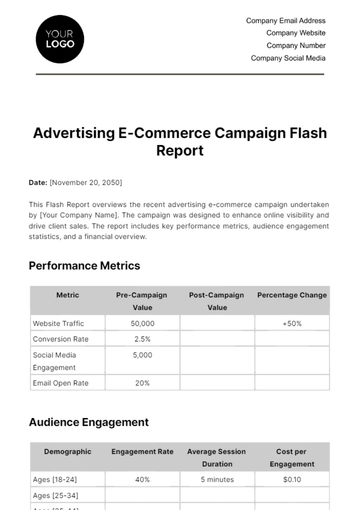
Free Multi-Country Advertising Compliance Report

I. Introduction
This report aims to provide an in-depth analysis of advertising compliance requirements across multiple countries, highlighting key regulations and best practices to ensure legal and ethical advertising. The report covers regulations in the [United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Japan, Australia, Brazil, India, and South Africa].
II. Advertising Standards and Regulations
United States:
Governed by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), focusing on truth in advertising and consumer protection.
United Kingdom:
The Advertising Standards Authority (ASA) ensures that ads are legal, decent, honest, and truthful.
Germany:
Strong regulations under the German Advertising Council, focusing on consumer protection and competitive fairness.
Japan:
Governed by the Japan Advertising Review Organization (JARO), emphasizing decency and fairness.
Australia:
The Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC) oversees advertising regulations, focusing on consumer rights.
Brazil:
The National Council for Advertising Self-Regulation (CONAR) ensures ethical advertising practices.
India:
The Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI) focuses on honest and non-offensive advertisements.
South Africa:
The Advertising Regulatory Board (ARB) oversees compliance, focusing on honesty and decency.
III. Comparative Analysis of Advertising Laws
This section offers a detailed comparative analysis of key advertising laws across different countries, highlighting their unique approaches to regulation.
Country | Comparative Advertising | Testimonials | Celebrity Endorsements |
USA | Allowed, must not mislead | FTC guidelines apply | FTC endorsement guidelines |
UK | Permitted, must be fair and not misleading | ASA guidelines for credibility | CAP code applies |
Germany | Strictly regulated, must be factual | Must be genuine and verifiable | Must be clear and truthful |
Japan | Allowed, requires fairness | Must be truthful, JARO oversight | Need clear disclosure of relationship |
Australia | Permitted, but must comply with ACCC guidelines | Testimonials must be genuine | Must not be misleading |
Brazil | Allowed, CONAR guidelines apply | Must be truthful, verifiable | Clear disclosure required |
India | Permitted, subject to ASCI guidelines | Must be genuine, ASCI oversight | Celebrity endorsements regulated by ASCI |
South Africa | Allowed, must comply with ARB standards | Must be truthful and verifiable | Must comply with ARB code |
This table illustrates the diversity in advertising laws. While comparative advertising is generally permitted, its execution varies significantly across countries, with some requiring more stringent factual backing than others. The use of testimonials and celebrity endorsements is universally regulated, with a common emphasis on truthfulness and transparency. The use of minors in advertisements is also a sensitive area, with all countries requiring some form of consent and adhering to child protection laws.
IV. Digital Advertising and Online Compliance
Digital advertising presents unique challenges due to the borderless nature of the internet and the rapid evolution of technology.
United States:
The CAN-SPAM Act regulates commercial emails, requiring opt-out mechanisms and truthful header information. Online behavioral advertising is also regulated by the FTC, emphasizing transparency and consumer choice.
European Union (including the UK and Germany):
GDPR imposes strict rules on data collection and consent, significantly impacting digital advertising strategies. The Privacy Directive, also known as the 'Cookie Law,' requires explicit consent for non-essential cookies.
Japan:
The Act on the Protection of Personal Information (APPI) governs digital advertising, focusing on personal data protection. Advertisers must obtain user consent for data collection and respect privacy rights.
Australia:
The Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) under the Privacy Act regulate the handling of personal information in digital advertising. The Spam Act [2050] governs commercial electronic messaging.
Brazil:
The General Data Protection Law (LGPD) closely mirrors GDPR, impacting digital advertising practices, particularly in data collection and user consent.
India:
The Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures and Sensitive Personal Data or Information) Rules regulate digital advertising, focusing on consent and data protection.
South Africa:
The Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA) governs digital advertising, with a focus on consumer privacy and the lawful processing of personal information.
This global patchwork of laws requires advertisers to be vigilant and adaptive, especially in the realms of data protection, consent management, and privacy rights.
V. Special Regulations for Specific Product Categories
This section delves into the unique advertising regulations for specific product categories that are subject to heightened scrutiny due to their nature and impact on consumers.
Pharmaceuticals:
USA: Governed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), pharmaceutical ads must include information about side effects and effectiveness.
UK: The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) regulates advertising, emphasizing accurate information and no misleading claims.
Germany: Strict regulations by the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM), including mandatory scientific evidence.
India: The Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act prohibits advertisements of certain drugs for specific diseases and conditions.
Alcohol:
Australia: Alcohol advertisements must not encourage excessive drinking or associate alcohol with personal success, as per the Alcohol Beverages Advertising Code (ABAC).
Brazil: Alcohol ads are not allowed to target minors or associate alcohol consumption with athletic performance, according to CONAR guidelines.
South Africa: The ARB enforces that alcohol ads must not glamorize alcohol or suggest that it contributes to social or sexual success.
Tobacco:
Japan: Tobacco advertising is regulated by the Health Promotion Act, which imposes restrictions on advertising, especially near schools.
UK and Germany: Strict bans on public tobacco advertising, including sponsorships and promotions.
Financial Services:
USA: The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees advertising of financial services, focusing on truthful and non-misleading information.
India: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) imposes guidelines to ensure financial ads are fair, transparent, and not misleading.
VI. Case Studies of Regulatory Breaches and Consequences
This section presents real-world scenarios where companies faced legal and reputational consequences due to non-compliance with advertising regulations.
Case Study 1 (USA): A leading beverage company faced a multi-million dollar fine for misleading health claims in their advertising. The campaign suggested unverified health benefits, leading to consumer deception and a significant FTC fine.
Case Study 2 (Germany): A well-known car manufacturer was penalized for using unsubstantiated environmental claims in their ads. The German Advertising Council deemed the ads misleading, resulting in fines and a mandate to modify the advertising campaign.
Case Study 3 (India): A cosmetics company encountered legal issues due to ads that were deemed offensive and discriminatory by the ASCI. The ads perpetuated stereotypes and did not adhere to the guidelines of responsible advertising, leading to a ban on the campaign and negative public backlash.
Case Study 4 (Brazil): An international tech company faced sanctions from CONAR for false advertising, where their product's capabilities were exaggerated. The company had to revise their marketing strategy and issue public clarifications.
Case Study 5 (UK): A financial services company was reprimanded by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) for misleading ads about investment returns. The company was required to compensate affected customers and revise their advertising policies.
These case studies demonstrate the importance of adhering to advertising regulations and the potential financial and reputational damages that can arise from non-compliance.
VII. Best Practices for Multi-Country Compliance
Adhering to multi-country compliance in advertising requires a strategic and informed approach:
Regular Legal Updates: Stay abreast of changes in advertising laws and regulations in all operative countries. Consider subscribing to legal update services or partnering with local law firms.
Training and Awareness: Conduct regular training sessions for the marketing team, focusing on international advertising laws and cultural sensitivities. This can include workshops, webinars, and online courses.
Compliance Auditing: Implement a regular auditing process to review current campaigns for compliance. Use internal or external auditors to ensure objectivity and thoroughness.
Localized Compliance Teams: Establish compliance teams in each country or region, responsible for ensuring that advertising campaigns adhere to local laws and cultural norms.
Checklist Development: Develop detailed checklists for each country's advertising regulations. These checklists should be easy to understand and accessible to all team members involved in campaign creation and execution.
Consultation with Legal Experts: Regular consultation with legal experts in each country can provide valuable insights and help mitigate risks.
Crisis Management Plan: Have a plan in place to address potential legal issues or public backlash from non-compliant advertising, including steps for immediate response and long-term strategy adjustments.
VIII. Conclusion and Recommendations
The report highlights the diversity and complexity of advertising regulations across various countries. Key findings include the stringent regulation of specific product categories, the varying approaches to digital advertising compliance, and the critical importance of understanding local advertising laws to prevent legal and reputational risks. Below are actionable strategies for ensuring multi-country compliance in advertising.
Establish a Global Compliance Framework: Create a policy that incorporates the highest standards from all covered countries, ensuring baseline compliance. Tailor this policy to meet the specific needs of each country, overseen by local compliance teams.
Enhance Training and Education: Implement ongoing training for marketing and compliance teams, focusing on the latest legal developments and cultural sensitivities in advertising. Use intranet portals or internal communication tools to share updates, case studies, and compliance tips.
Implement Robust Monitoring and Auditing Systems: Conduct internal and external audits of advertising campaigns to ensure adherence to local and global standards. Utilize software solutions for real-time monitoring of advertising campaigns, flagging potential compliance issues.
Cultivate Strong Relationships with Regulatory Bodies: Foster open communication channels with advertising regulatory authorities in each country. Actively participate in advertising industry forums and regulatory discussions to stay abreast of evolving standards and practices.
Build a Resilient Crisis Management Plan: Prepare a comprehensive plan to address potential compliance breaches, including immediate corrective actions and long-term preventative measures. Assemble a dedicated team responsible for managing communications and public relations in the event of an advertising compliance issue.
Navigating multi-country advertising compliance is an ongoing, dynamic process that requires commitment, resources, and a strategic approach. By implementing these recommendations, companies can not only minimize legal risks but also build a reputation for ethical and responsible advertising.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Enhance global advertising compliance with Template.net's Multi-Country Advertising Compliance Report Template. This editable and customizable tool, featuring our Ai Editor Tool, simplifies the process of monitoring and ensuring adherence to advertising regulations across multiple countries. Streamline reporting and mitigate risks with this comprehensive template from Template.net.
You may also like
- Sales Report
- Daily Report
- Project Report
- Business Report
- Weekly Report
- Incident Report
- Annual Report
- Report Layout
- Report Design
- Progress Report
- Marketing Report
- Company Report
- Monthly Report
- Audit Report
- Status Report
- School Report
- Reports Hr
- Management Report
- Project Status Report
- Handover Report
- Health And Safety Report
- Restaurant Report
- Construction Report
- Research Report
- Evaluation Report
- Investigation Report
- Employee Report
- Advertising Report
- Weekly Status Report
- Project Management Report
- Finance Report
- Service Report
- Technical Report
- Meeting Report
- Quarterly Report
- Inspection Report
- Medical Report
- Test Report
- Summary Report
- Inventory Report
- Valuation Report
- Operations Report
- Payroll Report
- Training Report
- Job Report
- Case Report
- Performance Report
- Board Report
- Internal Audit Report
- Student Report
- Monthly Management Report
- Small Business Report
- Accident Report
- Call Center Report
- Activity Report
- IT and Software Report
- Internship Report
- Visit Report
- Product Report
- Book Report
- Property Report
- Recruitment Report
- University Report
- Event Report
- SEO Report
- Conference Report
- Narrative Report
- Nursing Home Report
- Preschool Report
- Call Report
- Customer Report
- Employee Incident Report
- Accomplishment Report
- Social Media Report
- Work From Home Report
- Security Report
- Damage Report
- Quality Report
- Internal Report
- Nurse Report
- Real Estate Report
- Hotel Report
- Equipment Report
- Credit Report
- Field Report
- Non Profit Report
- Maintenance Report
- News Report
- Survey Report
- Executive Report
- Law Firm Report
- Advertising Agency Report
- Interior Design Report
- Travel Agency Report
- Stock Report
- Salon Report
- Bug Report
- Workplace Report
- Action Report
- Investor Report
- Cleaning Services Report
- Consulting Report
- Freelancer Report
- Site Visit Report
- Trip Report
- Classroom Observation Report
- Vehicle Report
- Final Report
- Software Report