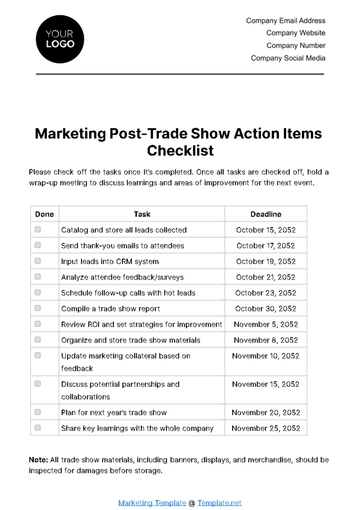
Free Basic Format Foot Assessment Checklist

Prepared By: [Your Name]
Visual Inspection
|
Palpation
|
Range of Motion
|
Sensation Testing
|
Vascular Assessment
|
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Introducing the professionally crafted Basic Foot Assessment Checklist Template, exclusively from Template.net. This versatile, editable, and fully customizable template is designed to streamline your foot assessment process. Crafted with precision, it's easily editable in our AI Editor Tool, ensuring efficiency and accuracy. Elevate your assessments with this essential tool today!
You may also like
- Cleaning Checklist
- Daily Checklist
- Travel Checklist
- Self Care Checklist
- Risk Assessment Checklist
- Onboarding Checklist
- Quality Checklist
- Compliance Checklist
- Audit Checklist
- Registry Checklist
- HR Checklist
- Restaurant Checklist
- Checklist Layout
- Creative Checklist
- Sales Checklist
- Construction Checklist
- Task Checklist
- Professional Checklist
- Hotel Checklist
- Employee Checklist
- Moving Checklist
- Marketing Checklist
- Accounting Checklist
- Camping Checklist
- Packing Checklist
- Real Estate Checklist
- Cleaning Checklist Service
- New Employee Checklist
- Food Checklist
- Home Inspection Checklist
- Advertising Checklist
- Event Checklist
- SEO Checklist
- Assessment Checklist
- Inspection Checklist
- Baby Registry Checklist
- Induction Checklist
- Employee Training Checklist
- Medical Checklist
- Safety Checklist
- Site Checklist
- Job Checklist
- Service Checklist
- Nanny Checklist
- Building Checklist
- Work Checklist
- Office Checklist
- Training Checklist
- Website Checklist
- IT and Software Checklist
- Performance Checklist
- Project Checklist
- Startup Checklist
- Education Checklist
- Home Checklist
- School Checklist
- Maintenance Checklist
- Planning Checklist
- Manager Checklist
- Wedding Checklist
- Vehicle Checklist
- Travel Agency Checklist
- Vehicle Inspection Checklist
- Interior Design Checklist
- Backpacking Checklist
- Business Checklist
- Legal Checklist
- Nursing Home Checklist
- Weekly Checklist
- Recruitment Checklist
- Salon Checklist
- Baby Checklist
- Equipment Checklist
- Trade Show Checklist
- Party Checklist
- Hospital Bag Checklist
- Evaluation Checklist
- Agency Checklist
- First Apartment Checklist
- Hiring Checklist
- Opening Checklist
- Small Business Checklist
- Rental Checklist
- College Dorm Checklist
- New Puppy Checklist
- University Checklist
- Building Maintenance Checklist
- Work From Home Checklist
- Student Checklist
- Application Checklist