Free Sales Protocol for Ensuring Data Integrity

Introduction
The purpose of this protocol is to outline guidelines and responsibilities for the collection, entry, storage, and management of sales data. By adhering to these guidelines, we aim to ensure that our sales data remains accurate, consistent, and secure throughout its lifecycle. This protocol applies to all personnel involved in sales, data handling, and data access within [Your Company Name]. It encompasses all aspects of sales data, from its initial collection to storage, access, and eventual disposal.
Responsibilities
At [Your Company Name], we believe that clearly defined responsibilities are crucial for maintaining data integrity. Every team and individual plays a vital role in ensuring accurate and secure data management.
Data Entry
Sales Team: Sales representatives ensure accurate and timely data entry during customer interactions, order processing, and lead management. Their meticulous data entry is the foundation of our data integrity.
Sales Managers: Sales managers oversee data entry compliance within their respective teams. They provide guidance, support, and training to ensure that data is consistently and accurately recorded.
Data Verification
Data Verification Team: Our dedicated Data Verification Team is responsible for conducting periodic checks to verify the accuracy and completeness of sales data. These routine checks are essential to identify any discrepancies and inconsistencies.
Sales Managers: Sales managers collaborate closely with the Data Verification Team to address any discrepancies identified during data verification. This collaborative effort ensures that data discrepancies are promptly resolved and that necessary corrective actions are taken.
Data Storage
IT Department: The IT department maintains secure data storage systems. They implement measures to safeguard data against unauthorized access and ensure it is regularly backed up for disaster recovery.
Data Collection and Entry
Data Sources
Sales Data: Our primary source of sales data is customer interactions, order processing, and lead management. The accuracy of this data is paramount for informed decision-making and customer service.
Third-Party Data: In certain cases, we may also source data from third-party systems, if applicable. This data is subject to the same level of scrutiny and data integrity standards as our internally collected data.
Data Entry Procedures
Data Accuracy: Sales representatives are responsible for accurate and consistent data entry in CRM systems. They must meticulously record all relevant information during customer interactions, transactions, and data entry events.
Mandatory Fields: It is a requirement that all mandatory data fields are completed for every customer interaction, transaction, or data entry event. This ensures that essential information is consistently captured and recorded.
Data Validation
Regular Data Checks: The dedicated Data Verification Team conducts regular checks to ensure data accuracy and completeness. These checks serve as a safeguard against data inaccuracies or omissions.
Discrepancies Resolution: Any discrepancies found during data validation are promptly reported to the responsible sales team for correction and further action. The collaborative effort between the Data Verification Team and sales teams ensures that any data issues are addressed promptly.
By clearly defining responsibilities and implementing stringent data entry and validation procedures, we uphold the highest data integrity standards at [Your Company Name]. Our collective efforts ensure that our data remains accurate, reliable, and secure.
Data Storage and Management
Data Storage and Management form the backbone of [Your Company Name]'s data governance framework, ensuring the secure, compliant, and efficient handling of sales data. This section provides an overview of our strategic practices in data storage, encompassing secure storage locations, comprehensive backup and recovery protocols, and meticulous data retention policies.
Data Storage Locations
Secure Locations: Sales data is securely stored in cloud-based CRM systems and on company servers.
Data Protection: Data storage locations are carefully selected to ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Backup and Recovery
Regular Backups: Regular data backups are performed to prevent data loss during system failures.
Data Recovery Procedures: Procedures are in place to ensure the swift and secure recovery of information in the event of data loss incidents.
Data Retention
Data Retention Policies: Data retention policies are established to determine the period for which data is stored.
Obsolescence Management: Obsolete data is regularly identified and securely archived or deleted to maintain an efficient and accurate dataset.
Data Security
Data Security Measures: Data access is protected through encryption, secure passwords, and multi-factor authentication.
Regulatory Compliance: Sensitive customer information is handled in compliance with data protection regulations to ensure the highest level of data security.
Data Access and Permissions
This section elucidates our structured approach to controlling and auditing who can view or utilize the sales data, embodying strategies such as access control on a need-to-know basis, the institution of role-based permissions, and rigorous auditing of data access and user activities.
Access Control
Need-to-Know Basis: Access to sales data is granted on a need-to-know basis, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access specific data relevant to their roles.
Regular Access Reviews: Regular reviews of access permissions are conducted to ensure alignment with job roles and responsibilities.
Role-Based Permissions
Role-Based Access: Access permissions are assigned based on job roles and responsibilities, ensuring that each user has access only to the data necessary for their job functions.
Access Review Cycles: Regular review cycles are conducted to ensure that access permissions align with job roles as they evolve.
Data Auditing
Regular Audits: Regular audits of data access and user activities are performed to monitor access compliance and security.
Audit Log Review: Audit logs are reviewed for any unauthorized access or suspicious activities, with immediate action taken if anomalies are detected.
Data Validation and Quality Assurance
Ensuring data accuracy and quality is a continuous process at [Your Company Name]. Our Data Validation and Quality Assurance procedures are in place to maintain the integrity of our sales data.
Regular Audits
Conducting Regular Audits: The Data Verification Team, composed of experienced professionals, conducts regular audits of our sales data. These audits are vital for maintaining data accuracy and quality.
Findings Reporting: Findings from data audits are documented and reported to the responsible teams. This reporting includes any identified inaccuracies, inconsistencies, or data quality issues.
Corrective Actions: Upon receiving the audit findings, the responsible teams promptly initiate corrective actions to address any issues. This collaborative effort ensures that data discrepancies are quickly addressed and rectified.
Quality Checks
Regular Quality Checks: Our diligent Sales Managers conduct regular quality checks to ensure that the sales representatives consistently meet data entry standards.
Feedback and Training: Feedback on data entry and data quality is provided to sales representatives, facilitating continuous improvement. Training sessions and resources are also made available to keep sales representatives updated on the latest data entry protocols, data security measures, and regulatory requirements.
Data Cleanup
Data Cleanup Procedures: Data cleanup procedures are regularly carried out to rectify any inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and data redundancies. This proactive approach helps maintain a clean, accurate, and efficient data repository.
Obsolete Data Handling: To further enhance data accuracy, obsolete or duplicate data is systematically removed from the dataset. This practice helps to declutter the data repository and prevent any potential confusion arising from redundant or outdated information.
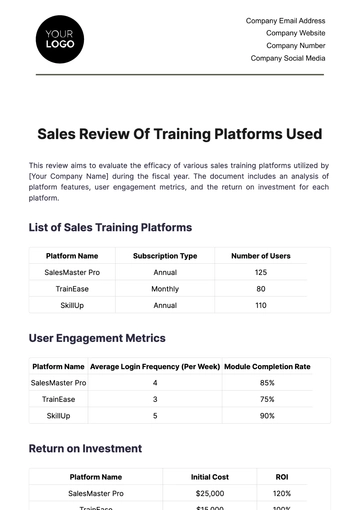
Quality Assurance Overview:
Section | Activity | Responsible Team |
|---|---|---|
Regular Audits | Conducting Regular Audits | Data Verification Team |
This table encapsulates the comprehensive measures undertaken by [Your Company Name] to ensure the highest standards of data validation and quality assurance, reflecting our commitment to maintaining the integrity and reliability of our sales data.
Training and Awareness
At [Your Company Name], we recognize that an informed and well-trained workforce is key to ensuring data integrity. Our commitment to continuous training and awareness programs is unwavering.
Employee Training
Continuous Training: Our Sales Representatives receive continuous training on data entry and data integrity best practices. This ongoing training is essential to update them with the latest industry standards, data security measures, and regulatory requirements.
Training Sessions: Regular training sessions are conducted to provide employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to maintain data accuracy and integrity. These sessions cover many topics, including best practices in data entry, data protection, and compliance with data security regulations.
Training Schedule:
Phase | Start Date | End Date |
|---|---|---|
Data Integrity Introduction | [Month Day, Year] | [Month Day, Year] |
Awareness Programs
Data Integrity Awareness: We organize awareness programs that emphasize the importance of data integrity, data security, and regulatory compliance. These programs aim to educate employees on the significance of data accuracy and integrity in our daily operations.
Reporting Culture: We encourage all employees to be proactive in reporting any data integrity concerns they may come across. A strong reporting culture is vital for promptly addressing and resolving data integrity issues. We emphasize the importance of vigilance in safeguarding data security.
Incident Response
At [Your Company Name], we understand that despite our best efforts to maintain data integrity, incidents can occur. The incident response procedures outlined in this section are crucial for promptly addressing and resolving data integrity concerns.
Open Reporting
We foster a culture of open reporting where all employees, regardless of their role, are encouraged to promptly report any data integrity concerns they may encounter. Whether it's a suspicion of data inaccuracy, a potential breach, or any anomaly that could jeopardize data integrity, your vigilance is essential. We provide an easy and confidential reporting system to facilitate this process.
Incident Documentation
Upon receiving reports of data integrity concerns, our incident response team immediately initiates the documentation process. Thorough and accurate documentation is vital for several reasons:
Thorough Investigation: Comprehensive documentation provides a foundation for a thorough investigation. Every detail, no matter how small, can be essential in determining the root causes and the responsible parties.
Resolution and Accountability: Documentation ensures that every incident is appropriately addressed and resolved. It also helps establish accountability, allowing us to identify patterns or recurring issues.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: In certain situations, such as data breach incidents, having a well-documented incident report is essential for legal and regulatory compliance.
Incident Resolution
Upon receipt of a data integrity incident report, our incident response team launches a comprehensive investigation. The primary objectives of this investigation include:
Determining Root Causes: Identifying the root causes of the incident is paramount. This involves a detailed analysis of the incident's history, triggers, and contributing factors.
Responsible Parties: Establishing who or what is responsible for the incident is crucial. This may involve tracing the incident back to an employee, a system failure, external factors, or a combination thereof.
Impact Assessment: Assessing the impact of the incident, including potential data integrity compromise, legal implications, and consequences for stakeholders.
Corrective Measures
Once the incident investigation is complete, we implement corrective measures to address the root causes and prevent the recurrence of data integrity issues. These measures may include:
Procedural Changes: If the incident reveals flaws in our data entry, storage, or access procedures, necessary revisions are made to address these weaknesses.
Security Enhancements: In the case of data breaches or unauthorized access, security enhancements may include updated access controls, strengthened encryption, and additional authentication measures.
Employee Training: If the incident is linked to human error or lack of awareness, targeted employee training programs are developed and executed.
System Improvements: If the incident is tied to system failures or vulnerabilities, improvements to our IT infrastructure are implemented.
Further Actions: In certain cases, further actions may be necessary. This could involve legal actions against external parties responsible for security breaches or additional monitoring and auditing to ensure compliance with data integrity standards.
[Your Company Name] is committed to maintaining the highest data integrity standards, and our incident response procedures are designed to swiftly and effectively address any challenges that may arise. The confidentiality of incident reporters is upheld, and we encourage all employees to be proactive in reporting data integrity concerns. Your diligence and collaboration are crucial in safeguarding our data and ensuring our continued success.
Documentation and Reporting
Record-keeping
Document Storage: All data and documents related to data integrity protocols are securely stored and organized for future reference.
Record Maintenance: Records of data audits, access control, incident reports, and corrective actions taken are maintained for documentation and auditing purposes.
Reporting Requirements
Regular Reporting: Regular reports are generated to monitor data integrity compliance and identify any deviations from the established standards.
Findings Documentation: Reports include findings from data audits, access reviews, and incident investigations, along with actions taken to address data integrity issues.
Data Security
Data Security Measures: Data security measures include encryption, secure password management, and multi-factor authentication to protect data from unauthorized access.
Employee Education: Employees are educated about data security best practices to ensure they understand their role in maintaining data security.
Conclusion
The [Your Company Name] Sales Protocol for Ensuring Data Integrity is a comprehensive framework designed to safeguard the accuracy, reliability, and security of sales data. By adhering to these guidelines and fulfilling their respective responsibilities, all employees and stakeholders contribute to maintaining the highest data integrity standards. This, in turn, supports informed decision-making, enhances customer experiences, and ensures a competitive edge in the market.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Ensure the highest standard of data quality with Template.net's Sales Protocol for Ensuring Data Integrity Template. Designed for customization and easy editing, this template provides a robust framework for safeguarding data integrity within your sales processes. Utilize our Ai Editor Tool for precise adaptations, establishing a trustworthy foundation for decision-making.