Free Annual Budget Project Specification

1. Overview
This document outlines the financial plan for the fiscal year at [Your Company Name], detailing how resources will be allocated and managed to ensure alignment with organizational goals and effective utilization of funds. It serves as a comprehensive guide for budgeting activities, financial management, and performance monitoring.
2. Executive Summary
Purpose: Provide a high-level overview of the budget’s objectives and key financial strategies.
Scope: Outline the areas covered by the budget, including revenue, expenses, and capital investments.
Financial Highlights: Summarize key figures such as total revenue, total expenses, and projected net income.
3. Revenue Forecast
3.1 Sources of Revenue
The following table presents a detailed breakdown of projected revenue from various sources for the fiscal year, illustrating how each revenue stream contributes to the overall financial plan:
Revenue Source | Projected Amount | Description |
|---|---|---|
Sales Revenue | $5,000,000 | Income from product sales and services. |
Grants and Donations | $1,200,000 | Funding was received from grants and charitable donations. |
Investment Income | $300,000 | Earnings from investments and financial instruments. |
Other Income | $150,000 | Miscellaneous sources of revenue. |
3.2 Revenue Projections
The following table outlines the projected revenue for each quarter of the fiscal year, detailing expected income across the four quarters:
Quarter | Projected Revenue |
|---|---|
Q1 | $1,200,000 |
Q2 | $1,300,000 |
Q3 | $1,400,000 |
Q4 | $1,800,000 |
4. Expense Breakdown
4.1 Operating Expenses
The following table details the projected operating expenses for the fiscal year, outlining the allocation of funds across various expense categories:
Expense Category | Projected Amount | Description |
|---|---|---|
Salaries and Wages | $2,000,000 | Compensation for employees. |
Rent and Utilities | $600,000 | Costs for office space and utility services. |
Supplies and Materials | $400,000 | Expenditures for office supplies and raw materials. |
Marketing and Advertising | $500,000 | Budget for marketing campaigns and promotional activities. |
Insurance | $200,000 | Coverage for business-related risks. |
4.2 Capital Expenditures
The following table outlines the projected capital expenditures for the fiscal year, detailing the planned investments in long-term assets and improvements:
Capital Expense | Projected Amount | Description |
|---|---|---|
Equipment Purchase | $750,000 | Investment in new machinery and technology. |
Facility Upgrades | $300,000 | Renovations and improvements to physical premises. |
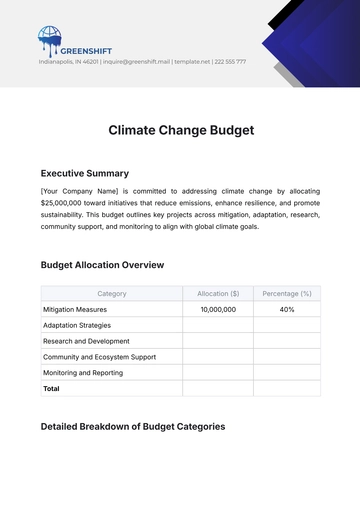
5. Budget Allocation
The budget is allocated across different departments to support various organizational functions. The table below illustrates the distribution of funds for each department:
Department | Allocated Budget | Percentage of Total Budget |
|---|---|---|
Research & Development | $1,000,000 | 20% |
Sales and Marketing | $900,000 | 18% |
Operations | $1,200,000 | 24% |
Administration | $800,000 | 16% |
Human Resources | $500,000 | 10% |
IT and Systems | $600,000 | 12% |
6. Risk Assessment
6. 1 Economic Risks
Market Fluctuations: Potential impact on sales revenue due to economic downturns or market volatility.
Inflation: Rising costs of goods and services affecting budgeted expenses.
6.2 Operational Risks
Supply Chain Disruptions: Potential delays or shortages in materials affecting production schedules.
Project Execution: Risks associated with project delays or cost overruns.
6.3 Financial Risks
Investment Performance: Variability in returns on investments impacting overall income.
Liquidity: Ensuring sufficient cash flow to meet operational and financial obligations.
7. Funding Sources
Internal Funds: Utilizes existing reserves and operational savings for expenses and investments. Efficient reserve management is crucial.
External Funding: Includes loans, grants, and investments. Loans require repayment, grants do not, and investments provide capital in exchange for equity or other terms. Securing external funds involves careful planning.
8. Variance Analysis
Budget vs. Actual: Compares actual performance to budgeted figures to identify and address deviations. Regular reviews ensure financial alignment.
Adjustments: Involves revising the budget based on performance and unexpected changes. This may include reallocating funds and updating projections.
9. Approval and Signatures
Reviewed By:

[Reviewer's Name], [Position]
Approved by:

[Approver's Name], [Position]
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Plan your financial year efficiently with the Annual Budget Project Specification Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable template helps you outline and manage your budgetary needs with precision. Tailor each section to fit your organization's specific requirements, ensuring comprehensive financial planning. Streamline your budget creation process and achieve your financial goals with this practical, user-friendly tool designed for effective annual budgeting.
You may also like
- Budget Sheet
- Personal Budget
- Non Profit Budget
- Monthly Budget
- Project Budget
- HR Budget
- Company Budget
- Home Budget
- Weekly Budget
- College Budget
- Business Budget
- Construction Budget
- Small Business Budget
- Hotel Budget
- Annual Budget
- Home Renovation Budget
- Household Budget
- Student Budget
- Grocery Budget
- Marketing Budget
- Corporate Budget
- Startup Budget
- Manufacturing Budget
- Church Budget
- University Budget
- Annual Budget Plan
- Event Budget
- Operating Budget
- Travel Budget
- Food Budget
- IT and Software Budget
- School Budget
- Real Estate Budget
- Sales Budget
- Conference Budget
- Budget Finance
- Freelancer Budget
- Budget Advertising