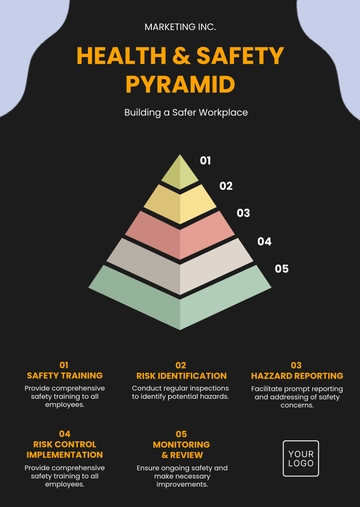
Free Health & Safety Legal Compliance Best Practices Guide

I. Introduction
A. Background
In our unwavering commitment to the health and safety of our workforce, this guide has been meticulously crafted to not only address legal requirements but to go beyond them, incorporating industry-recognized best practices. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for our company, offering practical insights and recommendations to ensure a workplace environment that prioritizes the well-being of our employees.
B. Purpose
This resource aims to provide clear and actionable guidance on legal compliance and best practices in health and safety. By articulating the purpose, we underscore our commitment to creating a workplace environment that not only meets legal standards but exceeds them through proactive and preventive measures.
C. Scope
The guide encompasses a wide range of topics, including risk assessment, training, emergency preparedness, and continuous improvement. By addressing various facets of health and safety, we ensure a holistic approach that covers all aspects of our operations.
D. Target Audience
The content is specifically designed for members of our Health and Safety Committee and individuals responsible for legal compliance within our company. This includes leaders, health and safety managers, and stakeholders directly involved in shaping and implementing health and safety policies. The guidance provided is tailored to empower these professionals in ensuring compliance with legal requirements and overseeing the overall health and safety framework within our company.
II. Regulatory Compliance and Legal Oversight
A. Overview of Health and Safety Laws
1. Key Regulations
Key health and safety regulations include OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards and OSHA regulations applicable to our industry.
2. Legal Obligations
Ensure regular safety training (such as Hazard Communication training) maintaining accurate OSHA 300 logs.
B. Regulatory Monitoring
1. Regular Compliance Checks
Conduct regular checks to ensure adherence to health and safety regulations, staying proactive in meeting legal requirements.
2. Continuous Legal Updates
Establish a system for continuous legal updates, keeping abreast of changes to regulations that may impact health and safety compliance.
C. Legal Compliance Reviews
1. Periodic Compliance Audits
Conduct periodic compliance audits to verify alignment with legal requirements and promptly address any identified gaps.
III. Risk Assessment and Prevention
A. Conducting Comprehensive Risk Assessments
1. Identify Potential Hazards
Utilize a systematic approach to identify and assess potential hazards in the workplace. Consider physical, chemical, ergonomic, and biological factors that may pose risks to employee health and safety.
2. Risk Prioritization
Prioritize identified risks based on severity and likelihood. This helps allocate resources efficiently to address the most significant threats to workplace safety.
B. Proactive Prevention Strategies
1. Implementing Engineering Controls
Integrate engineering controls to eliminate or reduce hazards at the source. This could involve modifying equipment, processes, or systems to enhance safety.
2. Administrative Controls
Develop and implement administrative controls, such as work procedures, training programs, and scheduling practices, to minimize employee exposure to hazards.
3. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Where hazards cannot be eliminated or adequately controlled by other means, provide and enforce the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) in accordance with OSHA standards.
IV. Emergency Preparedness and Response
A. Emergency Response Plans
1. Integrated Emergency Action Plan (EAP)
Develop an EAP that integrates industry best practices, encompassing various emergencies and regularly updating it to align with evolving standards.
2. Dynamic Evacuation Procedures
Enhance evacuation procedures with real-time data and communication technologies. Leverage mobile applications or automated alerts for precise and immediate evacuation instructions.
B. First Aid and Medical Response
1. Advanced First Aid Training
Provide advanced first aid training that goes beyond basic requirements. Include comprehensive skills, trauma response, and specialized medical scenarios for personnel empowerment.
2. Collaborative EMS Coordination
Establish collaborative relationships with local EMS providers. Actively participate in joint training exercises to ensure seamless integration between in-house emergency response teams and external medical services.
C. Communication and Reporting
1. Cutting-edge Emergency Communication Systems
Implement state-of-the-art emergency communication systems, incorporating multi-modal alerting, real-time location tracking, and two-way communication channels using emerging technologies.
2. Incident Reporting and Analysis Framework
Develop a robust incident reporting framework with data analytics and trend analysis for proactive risk identification. Foster a culture of continuous improvement that goes beyond legal mandates.
D. Psychological Support Programs
1. Critical Incident Stress Management (CISM)
CISM is a set of crisis intervention techniques designed to help individuals and groups cope with the emotional and psychological impact of critical incidents or traumatic events. Introduce this for psychological support after traumatic incidents, demonstrating a commitment to mental health and well-being beyond basic legal requirements.
V. Employee Assistance Program (EAP)
Set the industry standard by establishing EAPs offering counseling and mental health resources. Promote awareness and encourage utilization as part of a holistic approach to employee well-being.
Employee Well-being Initiatives
A. Mental Health and Wellness Programs
1. Comprehensive Mental Health Support
Extend our commitment to employee well-being by offering comprehensive mental health support programs. These initiatives go beyond legal obligations, fostering a work environment that prioritizes mental health.
2. Wellness Workshops and Resources
Provide wellness workshops and resources that promote a healthy work-life balance. These practices contribute to the overall well-being of our employees and create a supportive workplace culture.
B. Work-Life Integration
1. Flexible Work Arrangements
Introduce flexible work arrangements that consider the diverse needs of our workforce. This best practice recognizes the importance of balancing work responsibilities with personal well-being.
2. Promotion of Work-Life Balance
Actively promote and encourage a healthy work-life balance. This includes setting realistic expectations and providing resources that support employees in managing their professional and personal commitments.
C. Occupational Health and Wellness
1. Holistic Wellness Programs
Expand wellness programs to encompass holistic health, addressing physical, mental, and social well-being. This not only aligns with legal requirements but also reflects a commitment to fostering a healthy and thriving workforce.
2. Ergonomics and Workplace Design
Prioritize ergonomic workplace design to enhance employee well-being and prevent occupational injuries. This includes providing ergonomic furniture, promoting proper workstation setups, and conducting regular assessments to optimize ergonomic conditions.
VI. Technology Integration
A. Advanced Safety Technologies
1. Digital Incident Reporting Systems
Integrate digital incident reporting systems that allow for real-time reporting and analysis. This not only ensures compliance but also enhances incident response efficiency and provides valuable data for proactive risk mitigation.
2. IoT-enabled Safety Monitoring
Leverage Internet of Things (IoT) technology for safety monitoring. Implement sensors and wearables to track environmental conditions and employee well-being, contributing to a proactive approach in identifying and addressing potential hazards.
B. Data Analytics for Predictive Safety
1. Predictive Analytics Tools
Adopt predictive analytics tools to analyze historical data and predict potential safety risks. This forward-looking approach allows for preventive measures, reducing the likelihood of incidents and enhancing overall safety performance.
2. Continuous Improvement
Utilize data-driven insights for continuous improvement. Regularly analyze safety data to identify trends, assess the effectiveness of implemented measures, and refine strategies for optimal health and safety performance.
VII. Sustainability and Environmental Health
A. Eco-Friendly Practices
Integrate green building standards to promote environmental sustainability. This includes adopting energy-efficient technologies and practices that align with environmentally friendly construction and maintenance principles.
B. Pollution Prevention and Control
1. Efficient Waste Management
Implement efficient waste management systems, including recycling programs and responsible disposal practices, to minimize environmental impact.
2. Emission Reduction Initiatives
Invest in technologies and practices that reduce emissions and pollutants, aligning with sustainability goals and regulatory emission standards.
C. Hazardous Materials Handling
1. Safe Storage and Handling Protocols
Develop and enforce safe storage and handling protocols for hazardous materials to prevent spills, leaks, and other incidents that could harm both employees and the environment.
2. Chemical Inventory Management
Maintain a comprehensive inventory of chemicals, ensuring accurate tracking, documentation, and adherence to regulatory requirements for reporting and safety data sheets.
VIII. Training and Education
A. Regular Training Programs
1. Ongoing Training Initiatives
Implement continuous training programs to keep employees informed about evolving health and safety practices, ensuring they stay up-to-date with industry standards.
2. Specialized Training Modules
Introduce specialized training modules addressing specific safety concerns within our industry, fostering expertise among our workforces.
3. Employee Involvement and Feedback
Encourage active employee involvement in health and safety initiatives, establishing channels for suggestions and feedback to create a culture of shared responsibility.
Implement mechanisms for employees to contribute improvement suggestions regularly, promoting a dynamic and responsive safety framework.
IX. Continuous Improvement
A. Periodic Health and Safety Audits
1. Regular Audits
Conduct regular health and safety audits to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
2. Third-party Audits
Consider engaging third-party auditors periodically for an unbiased assessment of health and safety practices.
B. Employee Training and Engagement
1. Ongoing Training Programs
Provide continuous training programs to keep employees informed about evolving health and safety practices.
2. Employee Feedback Mechanism
Always improve systems for employees to provide feedback on health and safety practices, encouraging their active involvement.
C. Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
1. Stay Informed
Stay abreast of changes in health and safety regulations to ensure continuous compliance.
2. Legal Compliance Reviews
Conduct regular reviews to confirm adherence to current legal requirements and promptly address any gaps.
X. Data Security and Confidentiality
A. Secure Information Handling
1. Advanced Data Encryption Protocols
Implement state-of-the-art data encryption protocols to ensure the highest level of security for sensitive health and safety information. Regularly update encryption measures to align with industry standards and evolving cybersecurity threats.
2. Granular Access Control Measures
Establish granular access control measures, employing role-based access protocols to restrict the retrieval and dissemination of confidential health and safety data. Periodically review and update access permissions to align with personnel changes and evolving compliance needs.
3. Robust Data Storage and Retention Policies
Develop and enforce a comprehensive data retention framework to ensure the timely disposal of obsolete health and safety information while adhering to legal requirements. Implement automated systems for efficient data lifecycle management.
B. Employee Training on Data Security
1. Mandatory Data Security Training
Institute mandatory training programs for all personnel to educate them on data security best practices, emphasizing their role in maintaining the confidentiality of health and safety information.
2. Regular Phishing Awareness Programs
Conduct regular phishing awareness programs to empower employees to recognize and mitigate potential cyber threats, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.
3. Key Contacts and Support Services
The table below provides an overview of key contacts and support services essential for maintaining a robust health and safety compliance framework within our company:
Resource Type | Details | Contact Information |
Emergency Services | Local Fire Department, Police, and Medical Services | Emergency Number: 911 |
Access to reliable resources and contact information is paramount. The information presented serves as a quick reference guide, offering contact details to ensure a robust health and safety compliance framework. Familiarizing ourselves with these key contacts ensures efficient communication and a prompt response to both routine and emergency situations, reinforcing our commitment to a safe and secure workplace.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Rise above standards with a proactive approach to compliance using the Health & Safety Legal Compliance Best Practices Guide Template from Template.net. More than just editable, it's your ultimate compliance companion. Versatile and customizable, effortlessly navigate regulations, ensuring seamless alignment of policies. Stay ahead in compliance – get your copy now!