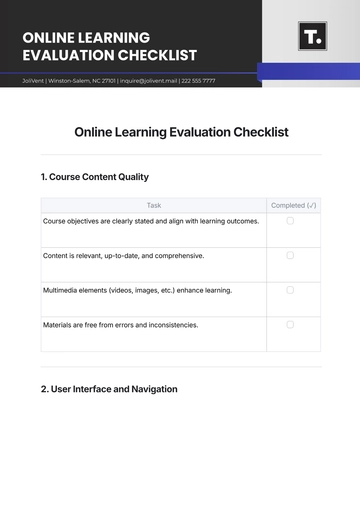
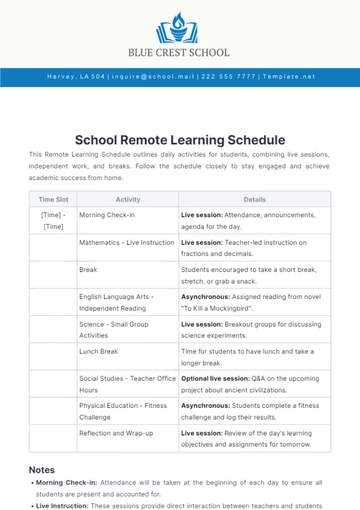
Free Experiential Learning Methodology

Prepared By: [YOUR NAME]
Date: [DATE]
I. Introduction
The Experiential Learning Methodology is designed to engage learners actively in the educational process by involving them in direct experiences and focused reflection. This methodology aims to cultivate critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and the ability to apply knowledge in real-world contexts. Through carefully structured activities and reflective practices, learners can bridge the gap between theoretical concepts and practical applications.
II. Learning Objectives
The experiential activities have been meticulously designed and developed to accomplish and fulfill a set of specific learning objectives, which are outlined as follows:
Deepen Conceptual Understanding: Facilitate a profound grasp of core concepts through interactive, hands-on experiences that bridge theory with practice.
Cultivate Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills: Engage learners in dynamic activities that challenge them to analyze complex situations, think critically, and devise innovative solutions.
Promote Self-Awareness and Personal Development: Encourage introspection and personal growth by providing opportunities for learners to reflect on their experiences and understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
Enhance Collaborative and Teamwork Abilities: Foster effective collaboration and communication skills through group activities that require coordination, negotiation, and collective problem-solving.
Apply Theoretical Knowledge Practically: Enable learners to translate theoretical insights into practical applications, reinforcing their ability to use knowledge in real-world scenarios and contexts.
III. Activity Design
A. Activity Descriptions
Each experiential activity is meticulously crafted to achieve optimal learning outcomes, incorporating real-world scenarios and hands-on tasks to deepen understanding and enhance skill development. Activities are designed to engage learners actively, stimulate critical thinking, and foster practical application of knowledge.
B. Materials Needed
Activity-Specific Tools: Relevant equipment and materials tailored to the activity's requirements (e.g., lab apparatus, art supplies).
Instructional Handouts and Guides: Comprehensive documents providing detailed instructions, guidelines, and background information for the effective execution of the activity.
Reflection Journals or Notebooks: Personal tools for learners to document their observations, insights, and reflections throughout the activity.
Audio-Visual Aids: Technology resources such as projectors, computers, and other multimedia tools to support instruction, presentation, and engagement.
C. Step-by-Step Instructions
Detailed, step-by-step instructions play a critical role in ensuring that each activity is carried out effectively and with precision.
Step | Description |
|---|---|
Preparation | Gather all necessary materials and review the activity guidelines. |
Introduction | Introduce the activity to the learners, explaining its objectives and relevance. |
Execution | Conduct the activity, ensuring active participation and engagement. |
Monitoring | Observe and facilitate the activity, offering guidance as needed. |
Completion | Conclude the activity by summarizing key points and outcomes. |
D. Expected Outcomes
By the conclusion of all the planned activities, it is expected that the learners will have achieved the following outcomes:
Achieve Comprehensive Understanding: Develop a nuanced and thorough grasp of the subject matter, integrating theoretical knowledge with practical insights.
Acquire Practical Skills: Gain hands-on experience and technical abilities relevant to the specific activity, enhancing their competence in real-world applications.
Strengthen Collaborative Abilities: Improve teamwork and communication skills through active participation in group-based tasks, fostering effective collaboration and mutual support.
Apply Knowledge Effectively: Demonstrate the capability to translate theoretical concepts into practical solutions, showcasing their ability to apply learned knowledge in diverse scenarios.
IV. Reflection
Post-activity reflection is a critical component of the experiential learning process. Encourage learners to think critically about their experiences through the following guidelines:
A. Reflection Questions
Key Insights: What were the most significant insights or lessons learned from the activity?
Connection to Theory: How did the experience link to the theoretical concepts and principles discussed in class?
Challenges and Solutions: What obstacles did you face during the activity, and what strategies did you employ to overcome them?
Self-Discovery: What personal insights did you gain about your strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences?
Future Application: In what ways can you apply the knowledge and skills acquired from this activity to future academic, personal, or professional situations?
B. Reflection Methods
Journaling: Encourage learners to capture their reflections, thoughts, and insights in a structured journal, allowing for ongoing personal analysis and growth.
Group Discussion: Facilitate a collaborative debriefing session where learners can openly share their experiences, exchange feedback, and gain diverse perspectives from peers.
Personal Essays: Assign reflective essays that challenge learners to integrate and synthesize their experiences, critically evaluate their learning, and articulate how these experiences influence their understanding and future actions.
V. Application
To ensure that the knowledge and skills gained from learning are successfully applied in real-life situations, it is recommended to suggest the following application strategies:
Role-Playing: Create and manage realistic scenarios for learners to practice new skills and knowledge. These controlled settings let them simulate real-world situations, make decisions, and solve problems safely.
Projects: Assign projects that apply theory to practice, requiring creative problem-solving, critical thinking, and multiple skills, showcasing learners' understanding.
Case Studies: Use detailed case studies to demonstrate and analyze the practical application of theoretical concepts in professional settings, evaluate outcomes, and extract applicable lessons.
Internships/Fieldwork: Encourage internships or fieldwork to help learners apply knowledge, gain skills, and make industry connections.
VI. Assessment
Evaluating the success and impact of the hands-on learning experience, as well as gauging the results and achievements of participants, can be accomplished by utilizing a variety of methods as outlined below:
A. Formative Assessment
Observations: Continuously monitor and assess learner engagement, participation, and interaction during activities to gauge their involvement and understanding.
Feedback: Offer prompt and helpful feedback throughout and following activities to assist learners in honing their skills, overcoming obstacles, and improving their learning experience.
Self-Assessment and Peer-Assessment: Utilize self-assessment and peer-assessment worksheets to encourage learners to evaluate their own and others' performance, fostering self-awareness and collaborative improvement.
B. Summative Assessment
Reflective Journals or Portfolios: Evaluate learners’ reflective journals or portfolios, which capture their learning experiences, insights, and growth over time, offering a comprehensive view of their progress.
Project and Presentation Performance: Assess learners' performance on projects and presentations, focusing on their ability to apply knowledge, demonstrate skills, and convey their understanding effectively.
Written Exams or Quizzes: Conduct written exams or quizzes that test learners' ability to apply theoretical concepts to practical scenarios, ensuring a thorough understanding of the material.
C. Feedback Mechanisms
Learner Feedback: Collect detailed feedback from learners through surveys, interviews, or feedback forms to gather insights on their experiences, challenges, and suggestions for improvement.
Collaborative Review: Engage in collaborative meetings to review and discuss feedback, sharing insights and perspectives to identify areas for enhancement.
Activity Adjustments: Utilize the feedback to refine and tailor activities and methodologies, ensuring their effectiveness, relevance, and alignment with the learners' needs and objectives.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Empower hands-on education with the Experiential Learning Methodology Template from Template.net. This fully editable and customizable template is designed to help educators and trainers structure immersive, experience-based learning activities. Editable in our Ai Editor Tool, it allows for easy adaptation to specific teaching goals, ensuring that learners gain practical knowledge through active engagement.