Free Data Analysis in Academic Research

[YOUR COMPANY NAME] | [YOUR COMPANY ADDRESS]
I. Introduction
Data analysis is a crucial component of academic research, providing insights and interpretations that underpin conclusions and recommendations. As we look toward 2060 and beyond, the landscape of data analysis continues to evolve with advancements in technology, methodology, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
In this guide, we will explore the essential elements of data analysis within the context of academic research, focusing on key processes, tools, and considerations that are relevant to researchers across disciplines.
II. Research Design
Research design is the blueprint for conducting a study, outlining the methods and procedures that will be used to collect and analyze data. The choice of research design depends on the research question, objectives, and the nature of the data.
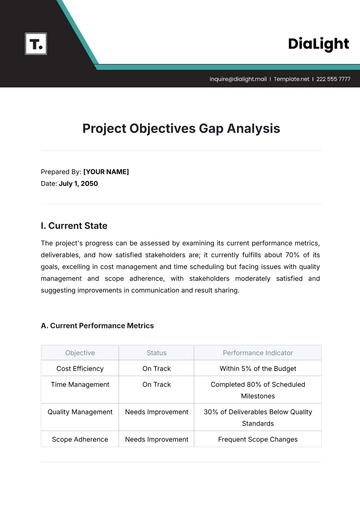
A. Types of Research Design
Quantitative Research
Employs numerical data and statistical methods to test hypotheses.
Suitable for studies requiring measurable and objective data.
Qualitative Research
Focuses on understanding phenomena through interviews, observations, and textual analysis.
Suitable for exploratory studies where context and meaning are crucial.
Mixed-Methods Research
Combines quantitative and qualitative approaches to provide a comprehensive analysis.
Suitable for studies that require both numerical insights and contextual understanding.
B. Considerations in Research Design
Validity and Reliability: Ensuring the study accurately measures what it intends to and produces consistent results.
Ethical Considerations: Protecting participant confidentiality and obtaining informed consent.
III. Data Collection
Data collection involves gathering information relevant to the research question using various methods and tools.
A. Methods of Data Collection
Surveys and Questionnaires
Effective for collecting data from large populations.
Can be administered online or offline.
Interviews and Focus Groups
Allow for in-depth exploration of participants' perspectives.
Useful for qualitative research.
Observations
Involves recording behaviors or events as they occur.
Provides real-time data.
Secondary Data Analysis
Involves analyzing existing datasets to answer new research questions.
Cost-effective and time-saving.
B. Data Collection Tools
Digital Platforms: Use of online survey tools like Qualtrics or SurveyMonkey.
Recording Devices: For interviews and focus groups, ensuring high-quality audio or video capture.
IV. Data Preparation
Before analysis, data must be prepared and organized to ensure accuracy and consistency.
A. Data Cleaning
Handling Missing Data: Deciding whether to remove, impute, or analyze missing values.
Outlier Detection: Identifying and addressing data points that deviate significantly from others.
B. Data Transformation
Normalization: Adjusting data to a common scale without distorting differences.
Categorization: Grouping data into categories for analysis.
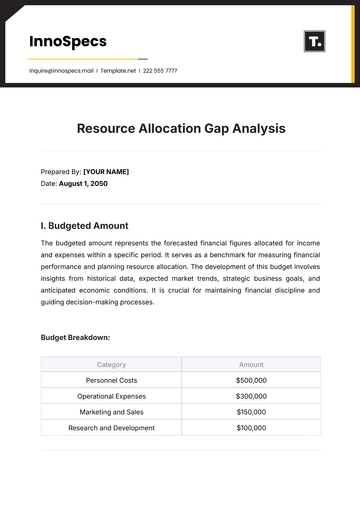
C. Data Storage
Database Management: Use of software like SQL or NoSQL for efficient data storage and retrieval.
Data Security: Ensuring data is stored securely and in compliance with relevant regulations.
V. Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis involves applying statistical and computational methods to draw insights and conclusions from data.
A. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive Statistics: Summarizing data using measures like mean, median, and mode.
Inferential Statistics: Making predictions or inferences about a population based on sample data.
B. Computational Analysis
Machine Learning: Using algorithms to identify patterns and make predictions.
Text Analysis: Analyzing textual data to extract meaningful information.
C. Data Visualization
Charts and Graphs: Using visual representations to make data more accessible and understandable.
VI. Interpretation of Results
Interpreting results involves explaining the significance of the data analysis and how it relates to the research question.
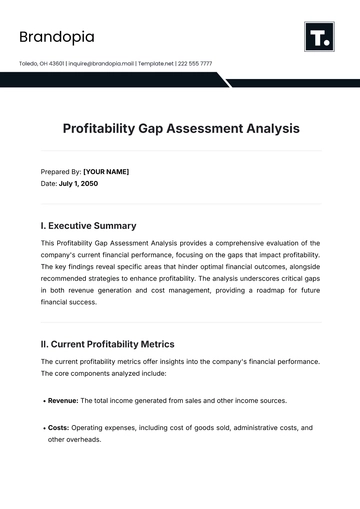
A. Drawing Conclusions
Aligning Results with Objectives: Ensuring the findings address the research question and objectives.
Considering Limitations: Acknowledging any limitations that may affect the validity of the results.
B. Implications for Future Research
Identifying Gaps: Highlighting areas where further research is needed.
Recommending Actions: Suggesting practical applications or policy changes based on findings.
VII. Reporting and Presentation
Communicating the results of a study is a critical step in the research process, requiring clear and concise reporting.
A. Writing the Research Report
Introduction: Summarizing the research question, objectives, and methodology.
Methodology: Describing the research design, data collection, and analysis techniques.
Results: Presenting the findings with supporting tables, charts, and graphs.
Discussion: Interpreting the results and discussing their implications.
Conclusion: Summarizing the key findings and recommendations.
B. Presentation of Findings
Oral Presentations: Using slides and visual aids to effectively communicate results to an audience.
Publication: Submitting the research to academic journals for peer review and dissemination.
VIII. Conclusion
Data analysis is a fundamental aspect of academic research, enabling researchers to uncover insights and contribute to the body of knowledge within their field. By following a structured approach to research design, data collection, preparation, analysis, interpretation, and reporting, researchers can produce valid, reliable, and impactful findings.
References
Smith, J. A. (2061). Advanced Data Analysis Techniques for Social Sciences. Research University Press.
Brown, R. & Lee, K. (2062). Quantitative Research Methods: A Comprehensive Guide. Academic Publishing House.
Johnson, P. (2063). Mixed-Methods Research: Bridging the Gap between Quantitative and Qualitative. Scholarly Books Ltd.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Enhance your research capabilities with Template.net’s Data Analysis in Academic Research Template. Customizable and editable in our AI Editor Tool, this template provides a framework for analyzing and interpreting data, ensuring accurate and insightful conclusions. Perfect for academics and researchers, this tool simplifies the data analysis process. Get it today!