Free Operations Facility Risk Management Protocol

I. Introduction
This protocol stands as a foundational framework for the identification, analysis, and mitigation of risks that may compromise the operational resilience of our production facility. Inherent in its systematic approach is a commitment to safeguarding not only the financial interests of the organization but also the well-being of our valued employees. This protocol, essential in preventing financial losses, establishes a comprehensive strategy to maintain the integrity of our operations, promoting an environment where potential risks are proactively addressed and controlled.
As a proactive tool, the protocol prioritizes a methodical examination of potential risks, emphasizing the significance of early identification and thorough analysis. By systematically evaluating and categorizing risks associated with facility operations, this protocol enables us to create tailored risk management strategies. Beyond financial considerations, its extends to ensuring the safety of our workforce, thereby fostering a workplace culture rooted in security and well-being. This protocol stands as a testament to our commitment to operational excellence, regulatory compliance, and the sustained success of our facility.
II. Objective
In pursuit of a resilient and secure operational environment, the protocol articulates the following objectives, guiding our systematic approach to risk identification, analysis, mitigation, and overall operational safety:
A. Identify potential operational risks
Systematically evaluate every facet of facility operations to pinpoint potential risks, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of vulnerabilities.
B. Implement effective risk management strategies
Develop and implement targeted strategies to mitigate identified risks, fostering a proactive and responsive approach to operational challenges.
C. Promote a proactive risk management culture
Cultivate an organizational culture that encourages proactive identification, assessment, and management of risks, involving all staff in the collective responsibility of risk prevention.
D. Maintain compliance
Uphold adherence to government regulations and industry best practices, ensuring that operational risk management practices align with established standards.
E. Continually monitor and improve processes
Establish a continuous improvement cycle, where risk management processes are subject to regular monitoring and refinement, fostering adaptability and effectiveness.
III. Scope
The scope of the protocol is expansive enveloping all facets of our manufacturing facility's operations. This encompasses the entire process chain, commencing from the receipt of raw materials and culminating in the shipment of finished products. The protocol's coverage is not confined solely to internal processes; it extends its purview to assess risks related to operational failures, safety incidents, and potential environmental impacts. This inclusive approach recognizes the dynamic nature of operational risks, acknowledging the interplay between internal processes and external factors. This integration positions the organization to not only proactively address known risks but also to establish a responsive framework for emerging threats.
IV. Definitions/Terminology
These definitions serve as a foundational guide, ensuring a common understanding across the organization:
Risk: The probability or threat of a damage, injury, liability, loss, or negative occurrence.
Risk Management: The forecasting and evaluation of risks combined with the identification of procedures to avoid or minimize their impact.
Risk Analysis: A technique used to identify and assess factors that may jeopardize the operational procedure of an organization.
Risk Assessment: The overall process of risk identification, risk analysis, and risk evaluation.
Operational Risk: The risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed procedures, systems, or policies.
Control Measure: An action or activity that can be used to prevent, eliminate, or reduce an identified risk.
Risk Register: A document that serves as a tool for identifying, assessing, and tracking risks.
Risk Owner: A person or entity with the accountability and authority to manage a risk.
Risk Mitigation: The process of selecting and implementing measures and procedures to minimize or control risks.
Compliance: The state of being in alignment with guidelines, regulations, or legislation.
V. Roles and Responsibilities
The table below outlines the roles and responsibilities for key positions within the organization, establishing a clear framework for risk governance:
Position | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
Operations Manager | Oversight of the Operational Risk management and implementation of risk mitigation strategies. |
Staff Members | Implementation of risk assessment procedures and reporting any identified risks. |
Safety Officer | Monitoring of operational safety and compliance with government and industry regulations. |
The delineation of roles and responsibilities in this protocol is instrumental in fostering a resilient and accountable organizational culture. Each role is strategically defined to contribute to the collective effort of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, thereby promoting a culture of shared responsibility and accountability. By assigning specific responsibilities to key positions, this structured framework ensures a clear and efficient distribution of tasks related to risk governance.
The Operations Manager, in their oversight role, contributes to strategic decision-making, aligning risk management strategies with organizational objectives. Staff members actively engage in the risk management process, bringing a collective vigilance to identify and report potential risks. The Safety Officer, with a focus on monitoring safety and compliance, plays a pivotal role in aligning operational practices with industry standards. This collaborative and strategic approach not only enhances the effectiveness of risk management efforts but also cultivates a culture where every member of the organization actively contributes to operational safety and excellence.
VI. Risk Management Procedure
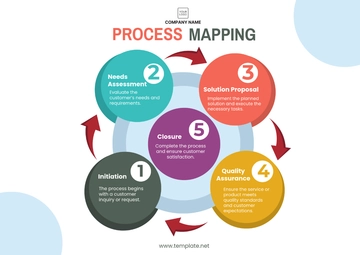
The following diagram provides a structured overview of the five steps involved in this procedure:
The streamlined procedure facilitates a comprehensive approach to risk management, encompassing identification, analysis, mitigation planning, implementation, and continuous improvement.
A. Identify potential risks
Reflecting upon the entire process allows for the recognition of areas where the probability of issues arising is significant. This step involves a thorough examination of each operational facet, encouraging stakeholders to contribute insights based on their specific roles. By fostering a collaborative environment, potential risks are identified comprehensively, ensuring a holistic understanding of vulnerabilities.
B. Analyze the identified risks
Once risks are identified, the next step involves a detailed analysis of their potential impact on operations. This includes evaluating the likelihood of occurrence, consequences if the risk materializes, and the level of controllability. Through this analysis, each risk is assigned a degree of severity, enabling prioritization for subsequent risk control measures.
C. Evaluate the risks
Risks are then systematically ranked based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This critical step aids in prioritizing risk control measures, directing resources to address the most significant threats. By categorizing risks, organizations can allocate resources efficiently, focusing on areas where intervention is most crucial.
D. Create a risk management plan
For every identified risk, a robust risk management plan is developed. This plan outlines specific measures to mitigate or control the risk, detailing the resources required and establishing a timeline for implementation. The creation of a detailed plan ensures a strategic and targeted response to each risk, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the risk management process.
E. Implement the risk management plan
With the risk management plan in place, the next step involves the implementation of control measures. These measures are applied as per the plan, and their effectiveness is regularly monitored. This proactive approach ensures that the organization is actively working to minimize or eliminate identified risks, contributing to a more secure operational environment.
F. Review and revise the plan
The risk management process is continuous, requiring regular reviews of the established risk management plan. This step involves assessing the plan's effectiveness and revising it as necessary in response to changes in operations or identified improvements. This adaptive approach ensures that the risk management process remains dynamic, aligning with evolving operational needs and industry best practices.
These five systematic steps—ranging from identifying potential risks to reviewing and revising the risk management plan—establish a comprehensive and iterative process. This approach ensures that potential risks are not only identified but also thoroughly analyzed, evaluated, and addressed through strategic plans and implementations. By fostering a continuous improvement mindset, the protocol enhances the organization's ability to adapt to dynamic operational landscapes, ultimately fortifying its capacity to navigate challenges and sustain operational excellence.
VII. Requirements and Conditions
The following list outlines the essential requirements and conditions that form the backbone of effective risk management implementation:
A. Training
Risk Identification Training
Equips staff with the skills to recognize and categorize potential risks, fostering a proactive mindset in identifying vulnerabilities within operational processes.
Risk Analysis and Evaluation Training
Provides in-depth knowledge on analyzing and evaluating risks, enabling staff to assess the potential impact, likelihood, and controllability of identified risks.
Risk Management Plan Development Training
Guides employees in creating comprehensive risk management plans, emphasizing the importance of detailing control measures, required resources, and implementation timelines.
Implementation and Monitoring Training
Instructs staff on the effective application of control measures as per the risk management plan and emphasizes the regular monitoring of their effectiveness.
Continuous Improvement Training:
Focuses on instilling a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging staff to regularly review and revise the risk management plan based on changes in operations and identified improvements.
B. Compliance
Mandatory Adherence to Regulations
Emphasizes the mandatory nature of adhering to government and industry operational safety regulations. Compliance with these regulations is critical to mitigating risks and maintaining a secure working environment.
Alignment with Legal Standards
Stresses the importance of aligning risk management practices with established guidelines to ensure legal compliance. This alignment is integral to sustaining operational integrity and minimizing legal liabilities.
Regular Regulatory Updates
Encourages regular updates on government and industry regulations to ensure that risk management practices stay current and aligned with evolving standards.
Internal Audits for Compliance
Internal audits needs to be regularly conducted to assess and ensure ongoing compliance with operational safety regulations. This proactive approach helps identify and address any potential compliance gaps.
C. Documentation
Comprehensive Risk Management Plan
Requires meticulous documentation of the risk management plan, serving as a tangible reference for all staff members. This documentation includes identified risks, corresponding mitigation plans, and implementation timelines.
Accessibility and Transparency:
Emphasizes the importance of making the risk management documentation easily accessible to all staff members. This transparency ensures clear communication and understanding of risk management processes throughout the organization.
D. Reporting
Prompt Reporting Mechanism
Establishes a prompt reporting mechanism for any identified risks through designated channels. Timely reporting facilitates swift response and intervention, preventing potential issues from escalating.
Anonymous Reporting Option
Introduces an anonymous reporting option to encourage staff to report identified risks without fear of retribution. This additional measure aims to create an environment where individuals feel comfortable reporting concerns for the overall safety and well-being of the organization.
E. Evaluation
Regular Evaluation of Control Measures
Mandates the regular evaluation of control measures implemented in response to identified risks. This ongoing assessment ensures that the risk management plan remains dynamic and adaptive to evolving operational conditions.
Culture of Continuous Improvement
Promotes a culture of continuous improvement through regular evaluations, contributing to the overall efficacy of risk management strategies. Encourages staff to actively participate in refining and enhancing the risk management processes based on experience and emerging best practices.
VIII. Enforcement and Consequences
A structured approach is established for both enforcement and consequences, ensuring the effective implementation of risk management procedures:
A. Enforcement
Mandatory Adherence
The protocol unequivocally mandates the adherence of all staff members, emphasizing that compliance is not optional but mandatory. This provision establishes a foundational expectation for every individual to actively participate in and abide by the risk management procedures.
Regular Monitoring
To reinforce the importance of adherence, the protocol incorporates a system of regular monitoring. This ensures that the implementation of risk management procedures is consistently reviewed, enabling the identification of any deviations or lapses in compliance.
Swift Addressing of Non-Compliance
The enforcement mechanism is designed to be prompt and responsive. Instances of non-compliance are swiftly addressed to rectify deviations from the established risk management procedures. This proactive approach aims to maintain the integrity and effectiveness of the risk management framework.
B. Consequences
Progressive Penalties
The consequences for non-compliance are outlined in a progressive manner. The protocol introduces a system of penalties that escalate in severity based on the nature and gravity of the infringement. This ranges from initial warnings and retraining to more severe measures like suspension or termination.
Fair and Proportional Actions
The consequences are designed to be fair and proportional to the level of non-compliance. This approach ensures that individuals face appropriate repercussions for their actions, fostering a sense of accountability within the organization.
Ignorance Not Accepted
The protocol explicitly communicates that ignorance of the risk management procedures will not be accepted as a valid excuse for non-compliance. This provision reinforces the importance of ongoing awareness and understanding, making it clear that all staff members are expected to be familiar with and adhere to the established risk management protocols.
Repeat Violations
The protocol acknowledges that repeat violations will result in progressively more severe consequences. This provision underscores the importance of learning from past instances of non-compliance and emphasizes the organization's commitment to maintaining a culture of responsibility and adherence to risk management standards.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Ensure the safety and resilience of your facilities with the Operations Facility Risk Management Protocol Template on Template.net! This editable protocol offers a customizable approach to managing and mitigating risks in your facilities. Establish a secure and compliant facility environment confidently with this template empowered by our AI Editor Tool!