Free Sustainable Procurement Format
Prepared by: [Your Name]
I. Introduction
A. Purpose
Describe the objectives of integrating sustainability into procurement processes and how they align with the organization’s overall sustainability goals.
B. Key Goals
Reduce environmental impact
Promote ethical business practices
Ensure long-term economic value
C. Scope
This format applies to all procurement activities within the organization.
II. Sustainability Criteria
A. Environmental Criteria
Energy Efficiency: Preference for products/services with minimal energy consumption.
Material Sourcing: Preference for sustainable, recycled, or renewable materials.
Waste Management: Prioritize suppliers who minimize waste during production and product use.
Carbon Footprint: Suppliers with lower carbon emissions are preferred.
B. Social Criteria
Fair Labor Practices: Ensure suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices (fair wages, safe conditions, no child or forced labor).
Community Impact: Suppliers should positively contribute to local communities.
Supplier Diversity: Encourage diverse suppliers (e.g., minority-owned, women-owned businesses).
C. Economic Criteria
Cost Efficiency: Ensure goods/services provide value for money over their lifecycle.
Long-Term Viability: Select financially stable suppliers with long-term sustainability strategies.
Innovation: Support suppliers who innovate to reduce costs and environmental impact.
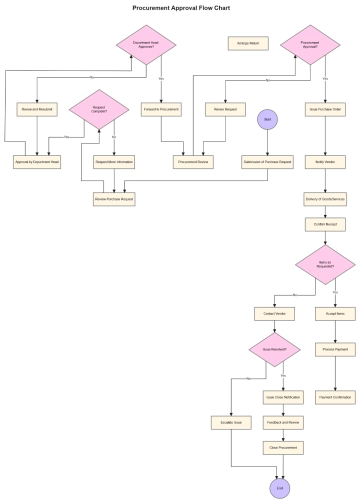
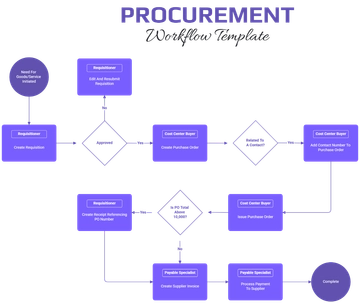
III. Procurement Process
A. Identifying Needs
Define product/service requirements with sustainability considerations (e.g., eco-friendly materials, ethical production methods).
B. Supplier Selection
Evaluate suppliers based on their sustainability performance and adherence to the sustainability criteria.
C. Tendering and Contracting
Include sustainability clauses in tenders and contracts.
Ensure performance targets related to sustainability are outlined in contracts.
IV. Supplier Evaluation
A. Sustainability Performance Metrics
Environmental Impact: Assess the supplier’s environmental management practices (e.g., waste reduction, energy use).
Social Responsibility: Evaluate labor practices, community involvement, and supplier diversity.
Compliance: Check for adherence to environmental and social regulations, and certifications (e.g., ISO 14001).
B. Continuous Improvement
Provide feedback to suppliers for improving sustainability practices.
Regular evaluations to ensure suppliers maintain sustainability standards.
V. Risk Management
A. Identifying Risks
Environmental Risks: Potential environmental hazards in the production process.
Social Risks: Risks related to unethical labor practices or human rights violations.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Risks due to natural disasters, political instability, or economic shifts.
B. Mitigating Risks
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers' sustainability practices.
Alternative Sourcing: Identify backup suppliers to reduce supply chain disruption risks.
Contractual Clauses: Include sustainability-related penalties and compliance clauses in contracts.
VI. Monitoring and Reporting
A. Tracking Performance
Regularly monitor supplier performance against sustainability criteria using audits, surveys, and assessments.
B. Reporting
Internal Reporting: Provide periodic updates to senior management on sustainability performance and challenges.
External Reporting: Share sustainability progress and achievements with customers, investors, and regulators.
Transparency: Ensure transparency in procurement decisions and supplier evaluations.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Commit to sustainability with Template.net’s Sustainable Procurement Format Template. Fully editable and customizable, this template helps you design procurement strategies that align with your environmental goals. Easily adjust it using our AI Editor Tool to ensure your sustainability criteria are met. Perfect for businesses aiming to incorporate sustainability into their procurement practices, Template.net provides the ideal format for responsible procurement.