Free Internal Audit Accounting Software User Guide

Introduction
A. Overview
[Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software stands at the forefront of cutting-edge technology, providing a comprehensive and integrated solution for organizations seeking to optimize their internal audit processes. This software is designed to cater to the evolving needs of auditors, offering a suite of tools and features that facilitate efficient auditing, risk management, and compliance checks.
Our commitment is to empower your organization with a robust platform that goes beyond traditional audit software. From seamless data analysis to dynamic reporting, [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software ensures that your internal audit team operates at the highest level of effectiveness, enhancing overall organizational governance.
B. Purpose
The primary purpose of [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software is to transform the way internal audits are conducted. We aim to provide a centralized platform that not only streamlines audit processes but also elevates the quality of decision-making through in-depth analysis, accurate risk assessment, and adherence to regulatory standards. By utilizing this software, organizations can strengthen their financial controls, identify areas of improvement, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
C. Audience
This user guide is crafted for auditors, finance professionals, and internal audit teams across various industries. Whether you are a seasoned auditor or new to the field, [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software is designed to cater to your unique needs, providing a user-friendly interface without compromising on the depth and sophistication required for comprehensive auditing.
Getting Started
A. System Requirements
Before initiating the installation process, it's essential to ensure that your system meets the minimum requirements to run [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software smoothly.
Requirement | Minimum Specification |
|---|---|
Operating System | Windows 10 or later |
Ensuring your system aligns with these specifications guarantees optimal performance and functionality of the software.
B. Installation
The installation process of [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software is designed to be user-friendly. Follow the steps below to install the software on your system:
Download Software Package:
Visit [Your Company Website].
Locate the download section.
Click on the download link for the Internal Audit Accounting Software package.
Run the Installer:
Once the download is complete, run the installer executable.
Follow the on-screen instructions to proceed with the installation.
Ensure that you have the necessary administrative privileges.
Enter License Key:
During the installation process, you will be prompted to enter the provided license key.
Input the key accurately to activate the software.
Upon successful completion of these steps, [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software will be installed and ready for use.
C. User Authentication
To access the software, use the following credentials:
Field | Information |
|---|---|
Username | [Abernathy345] |
Password | [*****-*****] |
Dashboard
A. Overview
The Dashboard in [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software is a visual command center providing real-time insights into key audit metrics and activities. This section serves as a comprehensive overview to help auditors make informed decisions and track the progress of ongoing audits.
B. Key Metrics
The Dashboard displays critical metrics, offering a quick snapshot of the organization's audit landscape:
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Total Audits Conducted | [75] |
C. Customization
The Dashboard is customizable to meet the unique needs of each user. Users can tailor their view by selecting preferred metrics, reports, and visualizations. Customization options include:
Metric Selection:
Users can choose which key metrics to display on their Dashboard, focusing on the aspects most relevant to their current auditing priorities.
Report Widgets:
The software allows users to add or remove report widgets based on their preferences. This ensures that the Dashboard provides a personalized and actionable view of audit data.
Theme Selection:
Users can select from a range of themes to personalize the visual appearance of the Dashboard, making it both user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing.
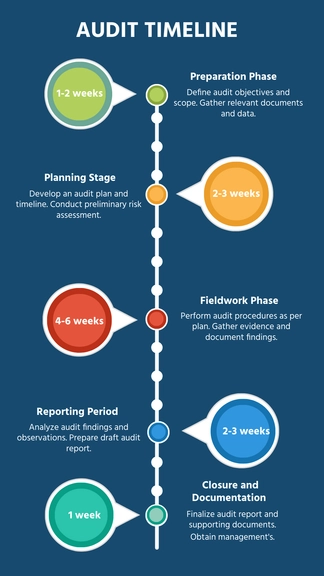
Audit Planning
A. Creating an Audit Plan
Creating a new audit plan with [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software is a straightforward process. Follow these steps:
Navigate to the Audit Planning Module:
From the main menu, select "Audit Planning."
Click on "New Audit Plan."
Define Audit Objectives:
Clearly state the objectives of the audit, outlining what you aim to achieve through the audit process.
Scope Identification:
Specify the scope of the audit, indicating the departments, processes, or areas to be included in the audit.
Risk Assessment:
Utilize the integrated risk assessment tools to identify and evaluate potential risks associated with the audit.
Team Assignment:
Assign team members to the audit plan, ensuring that roles and responsibilities are clearly defined.
Timeline and Milestones:
Set realistic timelines for different phases of the audit, establishing milestones to track progress.
B. Assigning Team Members
Allocate team members to specific audit tasks, promoting collaboration and efficiency:
Team Member | Role |
|---|---|
Mark Johnson | Compliance Specialist |
C. Timeline and Milestones
Establishing a clear timeline and milestones for the audit plan is crucial for effective planning and execution:
Phase | Start Date | End Date |
|---|---|---|
Planning | [March 20, 2050] | [April 20, 2050] |
These timelines ensure that the audit plan progresses smoothly, meeting deadlines and achieving objectives.
Data Import and Export
A. Importing Financial Data
Efficiently import financial data into [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software using the following steps:
Navigate to Import Module:
Access the Import module from the main menu.
Choose the source of financial data (e.g., Excel, CSV, Database).
Select Data File:
Click on "Browse" to select the financial data file for import.
Ensure the data file follows the specified format and structure.
Mapping Fields:
Map the fields in the data file to corresponding fields in the software.
Verify the accuracy of the mapping to prevent data discrepancies.
Validation and Preview:
The software performs data validation and provides a preview of the imported data.
Review the preview to identify and resolve any issues.
Confirm Import:
Once satisfied with the preview, confirm the import process.
The software will process the data, and a confirmation message will be displayed
.
B. Exporting Audit Reports
Generate and export comprehensive audit reports effortlessly:
Access Reporting Module:
Navigate to the Reporting module from the main menu.
Select the specific audit or set of audits for which you want to generate a report.
Customize Report Parameters:
Customize report parameters such as date range, audit type, and specific metrics.
Choose the format for the exported report (e.g., PDF, Excel).
Generate Report:
Click on the "Generate Report" button to initiate the report generation process.
The software will compile the selected data into a detailed audit report.
Review and Edit:
Review the generated report and make any necessary edits or additions.
Ensure that the report aligns with the specific requirements or standards.
Export the Report:
Once satisfied with the report, export it to the desired format.
The exported report is now ready for distribution or further analysis.
Risk Assessment
A. Identifying Risks
Utilize the sophisticated tools within [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software to identify potential risks:
Risk Identification Module:
Access the Risk Identification module from the main menu.
Input relevant information about the audit, processes, or departments under assessment.
Risk Categories:
Identify risks across predefined categories (e.g., Financial, Operational, Compliance).
Specify the nature and context of each identified risk.
Risk Documentation:
Document details of each identified risk, including potential impact and likelihood.
Attach supporting documents or evidence.
B. Risk Scoring
Assign scores to identified risks based on severity, ensuring a systematic approach to risk assessment:
Risk Level | Severity Score | Likelihood Score | Risk Score |
|---|---|---|---|
High | 4 | 3 | 12 |
Medium | 3 | 2 | 6 |
Low | 1 | 1 | 1 |
C. Mitigation Strategies
Develop and implement effective mitigation strategies for high-risk areas:
Mitigation Planning:
Access the Mitigation module to plan strategies for high-risk areas.
Involve relevant stakeholders in the planning process.
Implementation Timeline:
Define a timeline for the implementation of mitigation strategies.
Allocate resources and responsibilities accordingly.
Monitoring Progress:
Regularly monitor the progress of mitigation efforts.
Adjust strategies if needed based on ongoing assessments.
These steps ensure a proactive approach to risk management, enhancing the organization's resilience to potential challenges.
Audit Execution
A. Fieldwork
Conducting on-site fieldwork is a critical phase in the audit process. Follow these steps to ensure a thorough and effective fieldwork experience:
Preparation:
Gather all necessary documentation, including the audit plan, checklist, and relevant policies.
Ensure the audit team is briefed on the scope and objectives of the fieldwork.
On-site Assessment:
Conduct on-site assessments according to the audit plan.
Interact with key personnel and departments to gather information.
Data Collection:
Collect relevant financial and operational data during on-site visits.
Utilize [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software tools for real-time data entry.
Verification and Sampling:
Verify the accuracy of financial records and transactions.
Implement sampling techniques to assess the overall integrity of data.
Issue Identification:
Identify any issues, discrepancies, or potential areas for improvement during fieldwork.
Document findings for further analysis.
B. Documentation
Maintaining accurate and organized audit documentation is crucial for transparency and accountability:
Document Management Module:
Utilize the Document Management module in [Your Company Name] software.
Upload and categorize all relevant documents, including fieldwork notes and evidence.
Version Control:
Implement version control for audit documents to track changes and updates.
Ensure that the latest version is always accessible to the audit team.
Cross-Referencing:
Cross-reference documents within the system for easy navigation.
Link documents to specific audit findings or recommendations.
C. Communication
Facilitate effective communication within the audit team to ensure a collaborative and well-coordinated audit process:
Team Meetings:
Conduct regular team meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and upcoming tasks.
Use [Your Company Name] software's integrated communication features for virtual meetings.
Stakeholder Communication:
Keep stakeholders informed about the audit progress and any significant findings.
Address any queries or concerns promptly.
Real-time Updates:
Leverage real-time updating features in the software to ensure everyone has access to the latest information.
Use chat or messaging functions for quick team communication.
Data Analysis
A. Tools and Techniques
Utilize [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software's advanced tools for in-depth data analysis:
DataAnalytics Module:
Access the Data Analytics module from the main menu.
Choose the relevant dataset for analysis.
Analytical Tools:
Utilize tools such as trend analysis, regression analysis, and anomaly detection.
Customize parameters to align with audit objectives.
Visualization:
Use visualization tools, including charts and graphs, to present analysis results.
Enhance data interpretation through visual representation.
B. Interpretation
Interpret the results of data analysis to derive meaningful insights for the audit:
Identify Patterns and Trends:
Analyze patterns and trends within the data.
Highlight any unusual variations or outliers.
Correlation Analysis:
Explore correlations between different variables.
Identify relationships that may impact audit conclusions.
Risk Implications:
Assess the implications of analysis results on identified risks.
Determine if risk mitigation strategies are effective.
C. Reporting
Generate comprehensive reports based on data analysis using [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software:
Report Generation Module:
Navigate to the Reporting module from the main menu.
Select the specific analysis results to be included in the report.
Customization Options:
Customize the report format, including the inclusion of charts, graphs, and textual analysis.
Add commentary and recommendations based on the analysis.
Distribution:
Export the report in the desired format (e.g., PDF, Excel).
Distribute the report to stakeholders, ensuring timely and transparent communication.
Compliance
A. Regulatory Requirements
Ensure compliance with relevant regulatory requirements by following these steps:
Regulatory Checklists:
Access the Regulatory Requirements module within [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software.
Use predefined checklists to ensure adherence to specific regulations.
Regulatory Mapping:
Map identified risks and audit findings to corresponding regulatory requirements.
Verify that audit actions address any non-compliance issues.
Documentation and Evidence:
Upload supporting documentation and evidence within the system.
Maintain a comprehensive record of compliance efforts.
Regular Audits:
Schedule regular audits specifically focused on regulatory compliance.
Use the software's audit planning tools to ensure systematic compliance checks.
B. Policy Adherence
Verify adherence to internal policies using [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software:
Policy Database:
Maintain a centralized database of internal policies within the software.
Ensure policies are regularly updated and accessible to the audit team.
Policy Gap Analysis:
Conduct a gap analysis to identify areas where current practices may deviate from established policies.
Document any policy violations or discrepancies.
Training and Communication:
Implement training programs to educate employees on internal policies.
Use communication tools within the software to disseminate policy-related information.
Audit Trail:
Utilize the audit trail feature to track changes and actions related to policy adherence.
Maintain an auditable record of policy-related activities.
Troubleshooting
A. Common Issues
Address common issues that may arise during the use of [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software:
Access and Login Issues:
Ensure users have the correct login credentials.
Verify network connectivity and system access.
Data Import Errors:
Check the data file format and structure during the import process.
Review error messages for specific details and resolution steps.
Software Performance:
Ensure that the system meets the specified requirements.
Optimize software performance by closing unnecessary background applications.
Reporting Challenges:
Verify report parameters and data selection.
Review data accuracy and completeness before generating reports.
B. FAQs
Address frequently asked questions to assist users in navigating [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software:
How to Change Password:
Navigate to the "User Settings" section.
Select the option to change the password and follow the prompts.
Trouble Accessing Documents:
Check internet connectivity.
Verify document permissions within the Document Management module.
Exporting Reports in Different Formats:
Access the Reporting module.
Choose the desired export format (e.g., PDF, Excel) during report generation.
Resetting Audit Plan Timelines:
Navigate to the Audit Planning module.
Adjust timelines and milestones as needed, considering the impact on the overall audit schedule.
Updates and Maintenance
A. Software Updates
Keep [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software up-to-date with the latest features and security enhancements:
Check for Updates:
Periodically check for updates within the software.
Access the "Updates" section in the main menu.
Update Notification Settings:
Customize notification settings to receive alerts about available updates.
Ensure that all users are informed promptly.
Update Process:
When an update is available, follow the on-screen instructions.
Allow the software to download and install the update.
Backup Data Before Updates:
Before initiating any updates, ensure that a recent backup of critical data is available.
This precautionary measure prevents data loss in case of unexpected issues during the update process.
B. Regular Maintenance
Perform regular maintenance to optimize [Your Company Name] Internal Audit Accounting Software's performance:
Database Cleanup:
Regularly clean up the database by archiving or removing outdated data.
Optimize database performance for faster query processing.
File Storage Management:
Manage file storage efficiently, especially in modules like document management.
Archive or delete files that are no longer relevant.
Performance Monitoring:
Utilize built-in performance monitoring tools to identify bottlenecks.
Address any performance issues promptly to ensure optimal user experience.
Server Health Checks:
Periodically conduct health checks on the server hosting the software.
Monitor server resources such as CPU, memory, and disk space
User Training and Support:
Provide ongoing training to users on new features or changes in the software.
Offer a responsive support system to address user queries and issues.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Navigate the world of internal audits seamlessly with our Internal Audit Accounting Software User Guide Template from Template.net. This editable and customizable guide simplifies software usage, enhancing your team's efficiency. Modify it effortlessly with our Ai Editor Tool, ensuring it aligns perfectly with your processes. Stay in control and boost productivity with this user-friendly guide tailored to your needs.