Free Account Budget Impact Study

I. Introduction
A. Background
In the dynamic landscape of financial management, a profound understanding of budget implications is vital for strategic decision-making. This study delves into the historical context of budgetary practices within the organization, tracing the evolution of financial strategies and their impacts on overall performance. By examining past budget cycles, fiscal challenges, and successes, the study aims to provide a contextual foundation for evaluating the current budget and projecting future scenarios. A retrospective analysis allows for insights into the organizational learning curve, shedding light on adaptive measures implemented in response to changing economic landscapes and industry trends.
B. Objectives of the Study
The study seeks to:
Uncover Historical Patterns
Explore historical budgeting patterns to identify recurring trends and challenges.
Evaluate Operational Efficiency
Assess the efficiency of budget allocations in supporting day-to-day operations.
Examine Investment Strategies
Investigate how budget decisions align with capital investments and strategic financial initiatives.
Quantify Revenue Dynamics
Analyze the correlation between budget adjustments and revenue generation.
Provide Cross-Departmental Insights
Offer a holistic view of budget impacts, considering interdepartmental dependencies and collaborative opportunities.
C. Scope and Applicability
The scope and applicability of the study are the following:
Budgetary Components
The study encompasses all major components of the organization's budget, including revenue sources, expenditure categories, and allocation strategies. It conducts a granular examination of budget line items to understand specific impacts at a detailed level.Timeframe
The scope includes an analysis of historical budgetary trends, allowing for insights into the organization's budgetary evolution over time. Forward-looking considerations incorporate future budget projections to anticipate potential impacts and challenges.Departmental Inclusion
The study extends its reach across various departments, considering how budgetary decisions influence the operational dynamics of each department. All functional areas, from core operations to support functions, are included to capture a holistic view of budgetary implications.Stakeholder Perspectives
The study involves perspectives from internal stakeholders, including leadership, department heads, and employees, to understand the diverse impacts on different organizational levels. Where applicable, external stakeholders such as clients, partners, and regulatory bodies are considered to gauge broader implications.Industry Benchmarking
The study compares the organization's budgetary practices against industry benchmarks, providing insights into its competitive positioning. Consideration of industry-specific factors ensures that the study accounts for unique challenges and opportunities within the sector.
II. Methodology
A. Financial Ratio Analysis
Efficiency Ratios Assessment
Examining efficiency ratios, such as asset turnover and inventory turnover, provides insights into how effectively the organization utilizes its resources to generate revenue. This quantitative analysis aids in identifying areas of operational efficiency or potential improvement.Liquidity Ratios Evaluation
The study delves into liquidity ratios, including the current ratio and quick ratio, to assess the organization's ability to meet short-term financial obligations. This quantitative approach gauges the company's liquidity position and its capacity to cover immediate liabilities.
B. Scenario Modeling and Forecasting
Scenario Sensitivity Analysis
Conducting sensitivity analyses on budgetary scenarios involves testing different variables to evaluate their impact on financial outcomes. This quantitative method aids in identifying potential risks and uncertainties that may affect the budget.Long-Term Financial Forecasting
The study employs long-term financial forecasting to project the organization's financial position over an extended period. This forward-looking quantitative analysis assists in strategic planning by anticipating future financial trends and challenges.
C. Stakeholder Interviews
Executive Leadership Perspectives
In-depth interviews with executive leaders provide qualitative insights into the overarching strategic considerations that influence budgetary decisions. Understanding the perspectives of top-level management enriches the qualitative understanding of budgetary dynamics.Departmental Insights and Challenges
Stakeholder interviews extend to departmental heads, offering qualitative data on specific departmental needs, challenges, and strategic priorities. This approach ensures that budgetary considerations align with the diverse operational requirements across the organization.
D. Comparative Analysis and Best Practices Identification
Benchmarking Against Industry Peers
The study involves a qualitative comparative analysis to benchmark the organization's budgetary practices against industry peers. Identifying areas where the organization excels or lags behind provides contextual insights into industry norms.Identification of Innovative Practices
Qualitative methods are employed to identify innovative budgetary practices within and outside the industry. This involves researching and analyzing organizations known for their forward-thinking budgetary approaches, offering qualitative benchmarks for improvement.
E. Data Collection Techniques
Trend Analysis of Historical Financial Data
The study conducts trend analysis on historical financial data to identify patterns and changes over time. This quantitative method aids in understanding the evolution of budgetary priorities and financial performance.Thematic Analysis of Budgetary Documentation
Thematic analysis of budgetary documentation involves qualitatively categorizing and interpreting key themes within budget reports. This method uncovers qualitative insights into the underlying principles and considerations shaping budgetary decisions.
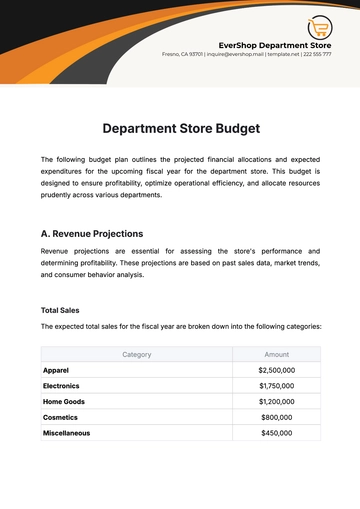
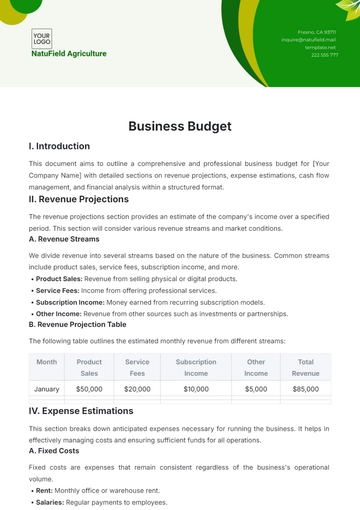
III. Budgetary Overview
A. Current Budget Allocation
The graph below illustrates the current budget allocation for key departments in the organization:
The Marketing department's budget allocation of $5,000,000, reveals a strategic emphasis on promoting the organization's products and services. This allocation suggests a commitment to market presence, brand visibility, and customer engagement. The designated budget enables targeted advertising campaigns, market research, and promotional activities. The 20.8% share of the total budget signifies the perceived importance of marketing efforts in achieving organizational objectives. Analyzing such specific allocations allows for a nuanced understanding of the financial strategy behind each department's role in the overall business strategy.
The current budget allocation acts as a financial compass guiding the organization's strategic journey. By comprehensively understanding where financial resources are directed, decision-makers can align budgetary allocations with overarching goals. This information empowers leadership to optimize resource utilization, fostering adaptability and responsiveness to dynamic market conditions. This serves as a crucial tool for organizational governance, enabling informed decision-making, resource alignment, and the pursuit of strategic excellence.
B. Historical Budget Trends
The table below outlines the historical budget trends, providing insights into the organization's financial evolution over the past five fiscal years:
Analyzing the historical budget trends, the second fiscal year (2051) witnessed a positive budget increase of $1,500,000 compared to the preceding year. This increment suggests a strategic decision to allocate additional resources, potentially driven by expansion initiatives, market opportunities, or increased operational requirements. In contrast, the third fiscal year (2052) reflects a deliberate budget reduction of $1,700,000, signaling a proactive approach to optimize costs or adapt to changing economic conditions. Understanding these trends provides context for decision-makers to identify patterns, assess the impact of strategic decisions, and forecast future budgetary requirements.
Examining historical budget trends lies in the invaluable insights gained from past financial performance. It serves as a compass for forecasting, enabling leaders to make informed decisions based on historical patterns. By understanding the factors influencing budget fluctuations, the organization can enhance financial resilience, identify areas for improvement, and align future budgets with strategic objectives. Historical budget trends provide a roadmap for navigating financial challenges and leveraging opportunities, contributing to the overall fiscal health and sustainability of the organization.
C. Factors of Influencing Budget Change
Budgetary changes within an organization are influenced by a myriad of factors, each playing a pivotal role in shaping financial allocations and priorities. The following eight factors have been identified as key influencers:
Economic Conditions
The overall economic landscape, including inflation rates and market trends, significantly impacts budgetary decisions, guiding organizations in aligning financial goals with broader economic realities.
Industry Trends
Changes in industry dynamics and emerging trends necessitate adaptive budget measures to stay competitive and responsive to evolving market demands.
Regulatory Environment
Compliance with evolving regulations demands financial adjustments, ensuring adherence to legal frameworks and minimizing potential risks.
Technological Advancements
Rapid technological changes may require investments in innovative solutions, impacting budgetary allocations for research, development, and technology adoption.
Organizational Growth
The expansion of an organization, whether through mergers, acquisitions, or organic growth, influences budgetary decisions to support increased operational demands and infrastructure requirements.
Internal Operational Efficiency
Improvements in internal processes and operational efficiency may lead to cost savings, affecting budget allocations for streamlined workflows and enhanced productivity.
Workforce Dynamics
Changes in the workforce landscape, such as hiring, training, or restructuring, directly influence budget considerations related to human resources and talent management.
Financial Performance
The organization's financial health and performance metrics play a crucial role in determining budget adjustments, ensuring sustainability and effective resource allocation.
IV. Impact Analysis
The table below illustrates the key findings derived from a comprehensive impact analysis of the budgetary changes:
Category | Financial Impact |
|---|---|
Personnel Costs | $2,500,000 |
The substantial increase in Personnel Costs by $2,500,000 is a noteworthy revelation from the impact analysis. This surge could be attributed to various factors such as salary adjustments, hiring initiatives, or changes in employee benefits. Understanding the drivers behind this increase is crucial for management to assess the sustainability of such changes and their alignment with broader organizational goals. For instance, if the rise in Personnel Costs is linked to strategic hiring for expansion, it signals positive growth. However, if it stems from unplanned salary hikes, it necessitates a closer examination of budgetary control measures.
This serves as a crucial lens through which decision-makers can scrutinize the financial implications of budget changes. The analysis of key findings allows for a nuanced understanding of how specific budgetary allocations impact different aspects of the organization. Beyond individual line items, it aids in crafting informed strategies for resource allocation, aligning the budget with corporate objectives, and ensuring financial resilience. In essence, it is an indispensable tool for strategic financial planning and maintaining fiscal health within the organization.
V. Recommendations
A. Budget Adjustment Strategies
Dynamic Cost Allocation
Implementing dynamic cost allocation methodologies allows the organization to swiftly adapt to changing financial landscapes, ensuring optimal resource utilization. This approach enhances the agility required for prompt adjustments in response to emerging budgetary challenges.
Flexible Budget Models
Developing flexible budget models provides the organization with the ability to accommodate unforeseen changes, fostering adaptability in adjusting financial plans. This proactive approach ensures a resilient budgeting framework capable of navigating uncertainties.
Zero-Based Budgeting Approach
Adoption of a zero-based budgeting approach involves reassessing expenses from the ground up, promoting cost-effectiveness. This strategy encourages a thorough evaluation of each budget item, aligning expenditures with organizational priorities.
Scenario Analysis
Regularly conducting scenario analysis enables the organization to evaluate the impact of potential changes, facilitating proactive adjustments to the budget. This foresight-driven strategy enhances the organization's ability to navigate varying financial landscapes.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Fostering collaboration between departments ensures that budget adjustment strategies align with overall organizational objectives. This integrated approach promotes cohesive decision-making and strategic alignment across diverse functional areas.
B. Mitigation Measures
Risk Mitigation Framework
Establishing a comprehensive risk mitigation framework identifies and addresses potential risks associated with budgetary changes. This proactive approach enhances the organization's resilience by systematically addressing potential challenges.
Contingency Planning
Developing contingency plans ensures the organization's resilience in the face of unexpected financial challenges. This strategic preparedness enables swift responses to unforeseen circumstances, minimizing disruptions to budgetary stability.
Benchmarking Practices
Implementing benchmarking practices to compare budget performance against industry standards facilitates proactive adjustments. This data-driven approach ensures the organization remains competitive and adaptable within its industry.
Continuous Monitoring
Instituting continuous monitoring mechanisms promptly identifies deviations from budgetary expectations, allowing for timely corrective actions. This vigilant approach ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to changing financial dynamics.
Investment Diversification
Exploring diversification strategies in investments spreads financial risks and enhances the organization's financial stability. This strategic approach mitigates the impact of market fluctuations on overall financial health.
C. Long-Term Planning
Strategic Financial Forecasting
Engaging in strategic financial forecasting anticipates long-term financial trends, facilitating informed decision-making. This forward-looking approach empowers the organization to proactively address future financial challenges.
Investment in Technology
Allocating resources for technology investments that support long-term organizational goals enhances operational efficiency. Strategic technology investments contribute to sustained competitiveness and adaptability in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Talent Development Initiatives
Investing in talent development initiatives builds a skilled workforce capable of navigating evolving financial landscapes. This commitment to continuous learning and development ensures the organization's readiness for future challenges.
Sustainable Financial Practices
Integrating sustainable financial practices into long-term planning considers environmental and social factors impacting budgetary decisions. This holistic approach aligns the organization with broader societal goals and promotes responsible financial stewardship.
Periodic Review and Adaptation
Periodically reviewing and adapting long-term plans aligns with changing market conditions, ensuring continued relevance and effectiveness. This iterative approach allows the organization to remain agile and responsive to evolving external factors.
VI. Stakeholder Involvement
A. Identification of Key Stakeholders
Executive Leadership
Involving executive leadership ensures top-level buy-in and alignment of budgetary changes with overarching strategic objectives. Regular communication with executives provides a holistic understanding of organizational goals and financial expectations.
Department Heads and Managers
Engaging department heads and managers facilitates a detailed understanding of department-specific budgetary requirements. This collaboration ensures that budget adjustments consider the unique needs and operational nuances of different departments.
Finance and Accounting Teams
Close collaboration with finance and accounting teams ensures the technical accuracy and feasibility of proposed budget adjustments. Their expertise is crucial in translating strategic financial goals into actionable plans.
Employee Representatives
Involving employee representatives fosters transparency and addresses concerns at the grassroots level. Open communication channels with employee representatives ensure that the workforce is informed about the reasons behind budget changes and their potential impacts.
B. Communication Strategies
Regular Briefings and Updates
Providing regular briefings and updates to stakeholders ensures transparency in the budget impact study. Clear communication about the progress, key findings, and potential adjustments builds trust and maintains stakeholder confidence.
Interactive Workshops and Forums
Conducting interactive workshops and forums allows stakeholders to actively participate in discussions about budgetary changes. This participatory approach fosters a sense of ownership and collective responsibility for the financial well-being of the organization.
Feedback Mechanisms
Establishing feedback mechanisms invites stakeholders to share their insights, concerns, and suggestions. This two-way communication ensures that the budget impact study benefits from diverse perspectives and addresses potential challenges proactively.
Tailored Communication for Different Stakeholder Groups
Recognizing the diverse needs and interests of different stakeholder groups, communication strategies should be tailored accordingly. This approach ensures that each group receives information in a manner that is relevant and meaningful to their roles and responsibilities.
C. Integration of Stakeholder Input
Incorporation of Feedback into Decision-Making
Actively incorporating stakeholder feedback into the decision-making process demonstrates a commitment to inclusive governance. This collaborative approach leads to well-informed and widely accepted budgetary decisions.
Alignment of Budget Adjustments with Stakeholder Expectations
Ensuring that budget adjustments align with stakeholder expectations enhances the likelihood of successful implementation. When stakeholders see their input reflected in the final decisions, it fosters a sense of shared responsibility and commitment.
Conflict Resolution Mechanisms
Establishing effective conflict resolution mechanisms anticipates and addresses disagreements constructively. Proactive conflict resolution ensures that potential roadblocks are navigated smoothly, maintaining the momentum of the budget impact study.
Celebrating Successes and Acknowledging Challenges
Recognizing and celebrating successes, as well as acknowledging challenges, reinforces a culture of transparency and accountability. Stakeholders appreciate being kept informed about the positive outcomes achieved and the lessons learned from challenges encountered.
VII. Implementation Plan
A well-structured implementation plan is essential for the successful execution of budgetary changes. The table below outlines key components of the implementation plan, providing a roadmap for integrating the recommended adjustments into the organization's financial framework:
Task | Responsible Party | Timeline | Resources Required | Progress Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Conduct Training Programs | Human Resources | Q3 2055 | Training materials, trainers | In Progress |
The initiation of training programs led by the Human Resources department in Q3 2055 signifies a proactive approach to managing the forthcoming budgetary changes. By equipping employees with the necessary skills and knowledge during this phase, the organization is not only investing in its workforce but also fostering a culture of adaptability. The targeted training aims to address potential challenges head-on, ensuring that employees understand the intricacies of the revised financial procedures. It positions the workforce to confidently navigate the evolving financial landscape, fostering a sense of ownership and competence.
The emphasis on conducting training programs underscores the recognition that successful budget implementation goes beyond procedural adjustments. This comprehensive approach sets the stage for a smoother transition, reducing resistance, and enhancing the likelihood of successful implementation. Moreover, it promotes a positive organizational culture where employees feel supported and confident in adapting to new financial norms.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the study serves as a critical compass for [Your Company Name], guiding its financial trajectory through the ever-evolving landscape. The comprehensive analysis, spanning budgetary allocations, historical trends, and operational considerations, has illuminated key insights for strategic decision-making. By delving into the financial nuances and intricacies, this study provides a roadmap that aligns the organization's budget with its operational imperatives.
This study underscores the dynamic nature of financial management and the need for continuous adaptation. The recommendations will pave the way for a resilient financial future, balancing fiscal responsibility with operational efficiency. In the face of changing economic landscapes and industry demands, the company stands poised to navigate the upcoming fiscal year with strategic prowess, underpinned by the insights gleaned from this impactful study.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Assess the impact of your budget with our Account Budget Impact Study Template on Template.net! This editable template empowers you with insights and best practices. Customize effortlessly with the AI Editor Tool, ensuring a study that aligns with your organizational budgeting goals. Get the benefits of this customizable template now!
You may also like
- Budget Sheet
- Personal Budget
- Non Profit Budget
- Monthly Budget
- Project Budget
- HR Budget
- Company Budget
- Home Budget
- Weekly Budget
- College Budget
- Business Budget
- Construction Budget
- Small Business Budget
- Hotel Budget
- Annual Budget
- Home Renovation Budget
- Household Budget
- Student Budget
- Grocery Budget
- Marketing Budget
- Corporate Budget
- Startup Budget
- Manufacturing Budget
- Church Budget
- University Budget
- Annual Budget Plan
- Event Budget
- Operating Budget
- Travel Budget
- Food Budget
- IT and Software Budget
- School Budget
- Real Estate Budget
- Sales Budget
- Conference Budget
- Budget Finance
- Freelancer Budget
- Budget Advertising