Free Health & Safety Committee Outline

Introduction
A. Purpose: To ensure a safe and healthy work environment for all employees at [Your Company Name]. This includes identifying potential hazards, implementing preventive measures, and fostering a culture of safety.
B. Scope: Covers all aspects of health and safety in the workplace, including risk management, employee training, and emergency response. The committee is responsible for staying updated on the latest industry standards and regulatory requirements.
C. Objective: To reduce workplace accidents and illnesses through proactive management and employee engagement. The committee aims to create a sustainable safety culture that is integral to [Your Company Name]'s operations.
Committee Structure
A. Chairperson: [Name], Safety Manager. The chairperson is tasked with leading the committee, setting agendas, and ensuring follow-through on action items.
B. Members: Representatives from each department. These members bring diverse perspectives and expertise to the committee, fostering comprehensive safety solutions.
C. Meetings: Held quarterly, with additional meetings scheduled as needed. Meeting minutes and action items are documented and shared with all members.
D. Contact Information: [Your Company Email], [Your Company Number]. This information provides a direct line of communication for safety concerns and suggestions.
Roles and Responsibilities
A. Chairperson
Coordinate meetings, set agendas, and monitor progress on safety initiatives. The chairperson is also responsible for liaising with senior management.
Oversee implementation of safety policies and ensure compliance with legal standards. The chairperson plays a pivotal role in policy development.
B. Members
Provide department-specific insights and feedback on proposed safety measures. They act as liaisons between their departments and the committee.
Assist in policy development and implementation, ensuring that all departmental needs and concerns are addressed.
C. Employees
Follow safety guidelines and participate in training programs. Employees are encouraged to actively engage in creating a safe workplace.
Report hazards and incidents promptly to ensure immediate action and prevent recurrence. This responsibility is crucial for maintaining a safe environment.
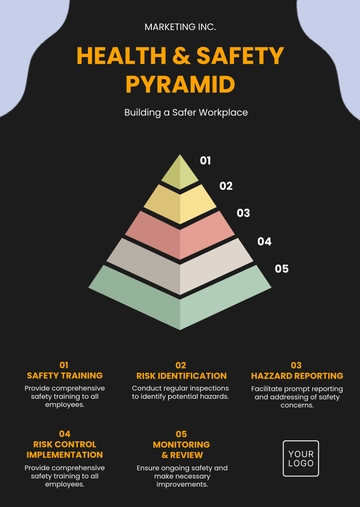
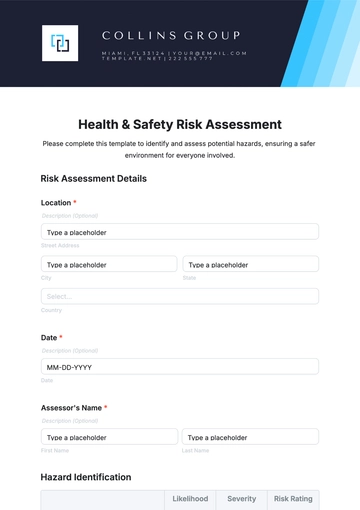
Risk Management
A. Risk Assessment
Frequency: Bi-annual, with interim reviews in case of significant changes in the workplace. These assessments are crucial for identifying new or evolving risks.
Method: Inspection and employee feedback, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of potential hazards in different areas of the workplace.
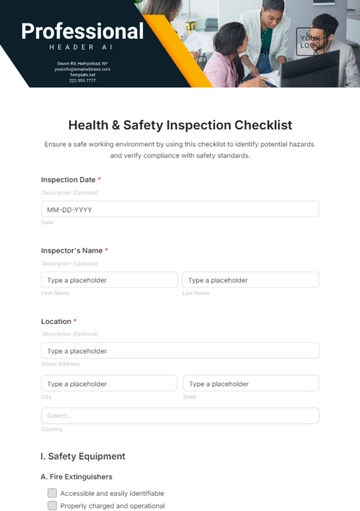
B. Hazard Identification
Process: Regular workplace inspections and accident report analysis, with a focus on continuous improvement and hazard mitigation.
Reporting: Through [Your Company Website] or [Your Company Email], enabling easy and accessible reporting for all employees.
C. Control Measures: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) distribution, regular equipment maintenance, and safety protocol updates. These measures are reviewed and updated regularly.
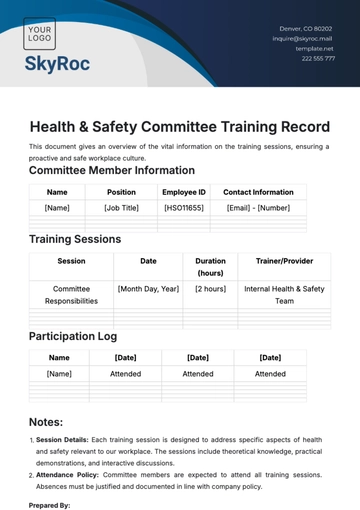
Training and Development
A. Orientation Training
For new hires, ensuring they are immediately informed about the company's safety policies and procedures.
Topics: Basic safety rules, emergency procedures, and an introduction to the company's safety culture.
B. Ongoing Training
Frequency: Annually, with additional sessions as required by changes in regulations or operations.
Topics: Advanced safety procedures, specialized equipment use, and refreshers on critical safety topics.
Emergency Procedures
A. Evacuation Plan
Assembly Points: Parking lot, cafeteria. These are designated safe areas where employees should gather in the event of an evacuation.
Role Assignments: Fire wardens, first aiders. These employees have specific responsibilities during an emergency to ensure safety and order.
B. Medical Emergency Response
In-house First Aid Team: [5 trained personnel], available to respond promptly to any medical emergencies in the workplace.
Local Hospital Contact: [Local Hospital, 555-6589-152]. A direct line of communication is established for emergencies requiring external medical assistance.
Record Keeping and Reporting
A. Accident/Incident Reports
Format: Electronic submission via [Your Company Website], making it easy for employees to report incidents promptly and accurately.
Analysis: [Quarterly] review by the committee to identify trends and areas for improvement.
B. Compliance Audits
Frequency: [Annually], to ensure ongoing compliance with health and safety regulations.
Auditor: External safety consultant, providing an unbiased evaluation of the company's safety practices.
Policy Development and Review
A. Policy Creation: Draft by committee, approval by executive team. This ensures that policies are well-rounded and effective.
B. Review and Updates
Frequency: [Biennial or as needed], to stay aligned with changing regulations and workplace environments.
Input: Employee feedback, audit findings. This input is vital for making relevant and effective policy updates.
Communication Strategy
A. Internal Communication
Tools: Email, intranet, monthly newsletters. These tools ensure consistent and effective communication of safety information to all employees.
Content: Safety updates, training schedules, and highlights of safety achievements or improvements.
B. External Communication
Stakeholders: Regulatory bodies, external partners. Communication with these stakeholders is key to maintaining transparency and compliance.
Method: [Annual] safety report via [Your Company Email], showcasing the company's commitment to health and safety.
Performance Metrics and Goals
A. Safety KPIs
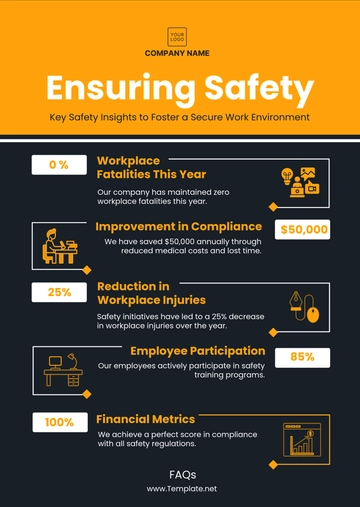
Incident Rate: Target reduction of [10% annually], reflecting the effectiveness of safety measures.
Training Completion: [100%] employee participation, ensuring that all employees are well-informed and trained.
B. Continuous Improvement: Feedback from employees, regular review of accident trends. This approach fosters a dynamic and responsive safety culture.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Structure health and safety initiatives effectively with Template.net's Health & Safety Committee Outline Template. This editable and customizable tool provides a comprehensive framework for organizing committee agendas and responsibilities. Utilize our intuitive Ai Editor Tool to tailor the outline to your organization's specific needs effortlessly, ensuring a proactive approach to workplace safety.