Free Financial Audit Protocol

I. Introduction
This protocol aims to establish a comprehensive framework for conducting financial audits within our organization. This protocol aims to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and compliance of our financial statements with relevant accounting standards, regulations, and internal policies. As a vital tool for maintaining financial transparency and accountability, this protocol outlines the systematic approach to be followed in the examination of our financial records, internal controls, and reporting processes. This document serves as a guide for auditors involved in the assessment of our financial health, reinforcing the commitment to integrity and responsible financial management.
II. Objectives and Scope
A. Objectives
Define Protocol Standards
Establish clear and standardized guidelines for the execution of financial audits within our organization, ensuring consistency and quality in the audit process.
Enhance Compliance
Strengthen adherence to accounting standards, regulatory requirements, and internal policies to mitigate the risk of non-compliance and improve overall financial governance.
Optimize Resource Utilization
Streamline audit resources by establishing efficient protocols, maximizing productivity, and minimizing redundancies in the audit process.
Facilitate Continuous Improvement
Foster a culture of continuous improvement by integrating a protocol review process, ensuring that the financial audit framework evolves in response to changing organizational needs and external requirements.
B. Scope
The scope of this protocol encompasses the content and processes involved in conducting financial audits within the organization. It addresses the examination of financial statements, reporting processes, and internal controls directly impacting financial reporting. The protocol applies uniformly to all organizational units and subsidiaries, ensuring a standardized approach across the entire corporate structure.
III. Audit Criteria
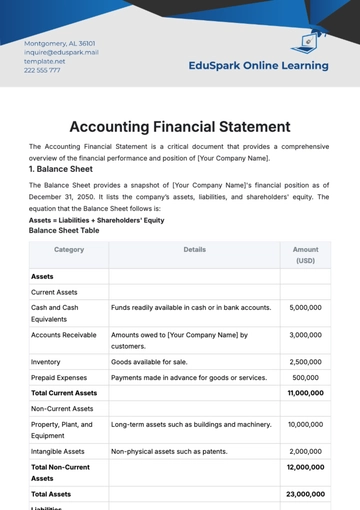
Establishing clear audit criteria is fundamental to ensure the effectiveness and consistency of the audit process. The table below outlines the key audit criteria that will guide the financial audit process:
Criteria | Description |
Financial Statement Accuracy | Evaluate the precision and reliability of financial statements, ensuring they present a true and fair view of the organization's financial position. |
The audit criteria serve as a vital tool in maintaining the credibility and reliability of financial information. By providing a standardized set of benchmarks, these criteria enable auditors to systematically evaluate the organization's financial health and integrity. These criteria collectively contribute to the robustness of the financial audit process, reinforcing the organization's commitment to sound financial management and governance.
IV. Internal Control Assessment Protocol
A. Risk Identification
Identify and assess risks that may impact the achievement of financial reporting objectives.
B. Control Design Assessment
Evaluate the design of internal controls to determine their suitability in addressing identified risks.
C. Testing and Documentation
Perform testing procedures to assess the operating effectiveness of selected internal controls, with thorough documentation of testing outcomes.
D. Control Environment Review
Review the overall control environment, including the tone set by management and the organization's commitment to ethical values.
V. Substantive Testing
A. Transaction Testing
Select and test a representative sample of transactions to ensure accuracy, completeness, and validity.
B. Account Balance Confirmation
Confirm the accuracy of account balances through detailed testing and reconciliation procedures.
C. Analytical Procedures
Perform analytical procedures to assess the reasonableness of financial information and detect any unusual trends or fluctuations.
D. Document Findings
Document the results of substantive testing, including any identified issues, exceptions, or areas requiring further investigation.
VI. Audit Evidence
A. Document Identification and Retention
Assign unique identifiers to each document to facilitate tracking and retrieval.
Retention periods must be based on regulatory requirements and internal policies.
B. External Confirmation Procedures
Develop a standardized confirmation request template.
Follow-up unresponsive external parties.
C. Technology Integration
Implement document management systems for secure storage.
Provide training on the use of technology tools for evidence gathering.
D. Cross-Referencing and Corroboration
Implement cross-referencing techniques to correlate evidence from various sources, enhancing the reliability of audit findings.
Conduct regular reviews to ensure consistency in cross-referencing practices.
E. Continuous Review and Update
Regularly review and update evidence collection procedures to align with evolving industry standards, regulatory changes, and organizational needs.
Update protocols based on lessons learned from previous audits.
VII. Sampling Techniques
A. Population Definition and Segmentation
Define the population under consideration and implement segmentation strategies to facilitate targeted sampling.
Segregate the population based on relevant criteria.
B. Random Sampling Procedures
Implement a random number generator for sample selection.
Document the methodology for ensuring randomness in sampling.
C. Sample Size Determination
Determine appropriate sample sizes based on statistical principles, considering the desired level of confidence and acceptable margin of error.
Calculate sample sizes using statistical formulas.
Document the rationale for chosen sample sizes.
D. Documentation of Sampling Plan
Document the sampling plan, including the rationale for sample selection, methods employed, and any adjustments made during the audit process.
Include a review and approval process for the sampling plan.
E. Quality Assurance Checks
Integrate quality assurance checks to validate the reliability of the sampling process and ensure adherence to established protocols.
Implement a peer-review process for sampling methodologies.
VIII. Financial Statement Reporting Protocol
A. Internal Reporting Controls
Implement robust internal controls over the financial reporting process to minimize the risk of errors and misstatements.
Remediate control deficiencies promptly and document corrective actions.
B. External Audit Coordination
Facilitate seamless coordination with external auditors, providing them with the necessary information and documentation to perform an effective audit.
Establish a designated contact person for external audit inquiries.
Provide auditors with timely access to relevant financial information.
C. Board and Stakeholder Communication
Establish clear communication channels with the board of directors and stakeholders, providing them with insights into financial performance and significant accounting matters.
Schedule regular financial reporting sessions with the board.
IX. Audit Protocol Validation
A. Pre-Audit Validation
Verify the completeness and accuracy of the audit protocol before initiating fieldwork.
Confirm that the audit protocol aligns with the established audit objectives and scope.
B. Testing of Audit Procedures
Execute a sample of audit procedures outlined in the protocol to ensure practicality and effectiveness.
Evaluate the clarity and specificity of each procedure for consistent interpretation by the audit team.
C. Feedback Collection
Solicit feedback from audit team members regarding the clarity and feasibility of the audit procedures.
Encourage open communication to identify potential challenges or improvements.
D. Documentation Review
Review the documentation associated with each audit procedure to confirm alignment with audit objectives.
Check for consistency in terminology and clarity in documenting evidence.
E. Revision and Approval Process
Ensure a systematic process for revising the audit protocol based on feedback and findings.
Obtain formal approval from relevant stakeholders, including senior management and the audit committee.
F. Communication of Validated Protocol
Communicate the validated audit protocol to the entire audit team.
Provide clear instructions on the use of the protocol during fieldwork.
X. Communication with Management and Governance Protocol
A. Preliminary Meetings
Initiate discussions with senior management and board representatives to discuss the audit objectives, scope, and anticipated timelines.
Emphasize the importance of cooperation and transparency during the audit process.
B. Progress Updates
Provide regular updates on completed audit procedures, significant findings, and any emerging issues.
Schedule interim meetings with management to discuss preliminary observations and address concerns promptly.
C. Identified Issues and Remediation Plans
Communicate control deficiencies, material misstatements, or other audit issues promptly.
Collaborate with management to establish corrective action plans and timelines for addressing identified issues.
D. Request for Additional Information
Issue formal requests for specific information or documentation necessary to complete audit procedures.
Clearly outline the purpose and urgency of the requested materials.
E. Final Presentation of Findings and Audit Opinion
Schedule a concluding meeting to present the audit report, including key findings, audit opinion, and any recommendations.
Allow for a question-and-answer session to address inquiries from management or governance representatives.
F. Post-Audit Follow-Up
Ensure post-audit communication to address any lingering questions or additional information needs.
Provide contact information for the audit team members who can assist with any follow-up discussions.
XI. Continuous Improvement and Protocol Review
A. Post-Audit Debriefing
Conduct a post-audit debriefing session to gather feedback from audit teams, identifying successes and areas for improvement.
Facilitate open discussions on challenges encountered during the audit.
Document lessons learned and best practices.
B. Stakeholder Feedback Mechanism
Solicit feedback from key stakeholders, including management, governance entities, and external auditors.
Develop a structured feedback survey for stakeholders.
C. Analyze feedback to identify patterns and trends.
Benchmarking and Best Practices Integration
Regularly benchmark the audit protocol against industry best practices and integrate relevant improvements.
Conduct periodic benchmarking assessments.
Prioritize the adoption of best practices aligned with organizational goals.
D. Protocol Review Committee
Form a dedicated protocol review committee comprising cross-functional representatives to oversee the continuous improvement process.
Schedule regular meetings to review and discuss potential protocol enhancements.
E. Documentation of Revisions
Document all revisions made to the audit protocol, providing a clear record of changes for reference and future audits.
Maintain a version control system for the audit protocol.
Clearly document the rationale behind each revision.
F. Training and Communication
Ensure that all relevant stakeholders are informed and trained on updated protocols to facilitate consistent implementation.
Develop training materials for new protocol elements.
Conduct training sessions for audit teams and other stakeholders.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Enhance financial accountability with Template.net's Financial Audit Protocol Template. This editable and customizable resource, empowered by our Ai Editor Tool, streamlines audit procedures. Tailor protocols to your organization's needs, ensuring thorough examination of financial records and compliance with regulatory standards. Elevate financial transparency and integrity with this comprehensive template.