Table of Contents
- Checklist Template Bundle
- 12+ IT Audit Checklist Templates in Doc | Excel | PDF
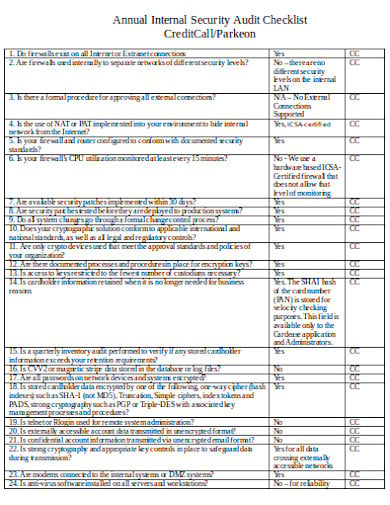
- 1. Free Annual Security IT Audit Checklist Template
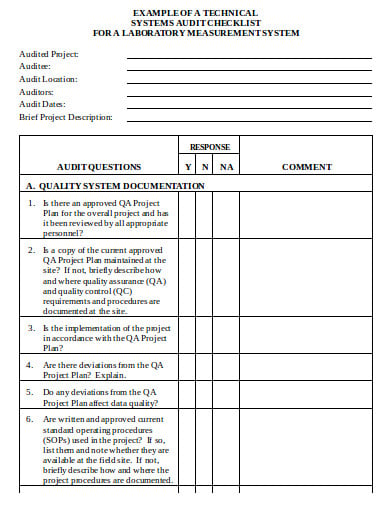
- 2. Free Technical System IT Audit Checklist Template
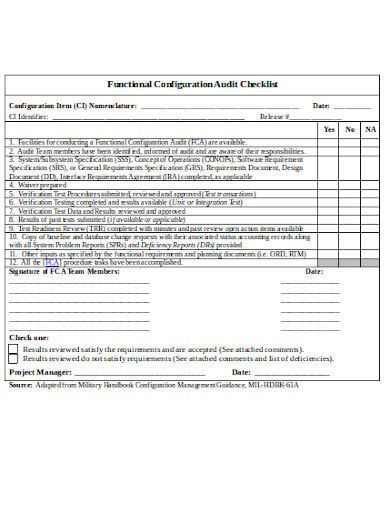
- 3. Free Functional Configuration IT Audit Checklist Template
- 4. Free Quality System IT Audit Checklist Template
- 5. Free IT Audit Checklist for Small Business
- 6. Free IT Audit Checklist Template
- 7. Free Information System IT Audit Checklist Template
- 8. Free Cloud Computing IT Audit Checklist Template
- 9. Free IT External Provider Audit Checklist Template
- 10. Free Single IT Audit Component Checklist Template
- 11. Free IT Compliance Audit Checklist Template
- 12. Free IT Blog Audit Checklist Template
- 5 Steps to Developing a Good IT Audit Program
- Types of IT Audits
12+ IT Audit Checklist Templates in Doc | Excel | PDF
An audit of information technology is also known as an audit of info systems. It refers to an examination of controls of management within an infrastructure of information and technology. In other words, it is the study and assessment of the IT infrastructure, strategies and activities of an enterprise. If you develop an IT Audit Checklist, you are creating a system for evaluating the thoroughness of the IT infrastructure in your business. You are also evaluating the IT strategies, processes and activities of the company. It is the duty of organizations to periodically inspect their activities in the area of information technology. This helps protect clients, suppliers, shareholders, and employees. You can also see more on Audit Checklist in Word.
Checklist Template Bundle

12+ IT Audit Checklist Templates in Doc | Excel | PDF
1. Free Annual Security IT Audit Checklist Template
 seattle.gov
seattle.gov2. Free Technical System IT Audit Checklist Template
 epa.gov
epa.gov3. Free Functional Configuration IT Audit Checklist Template
 dau.edu
dau.edu4. Free Quality System IT Audit Checklist Template
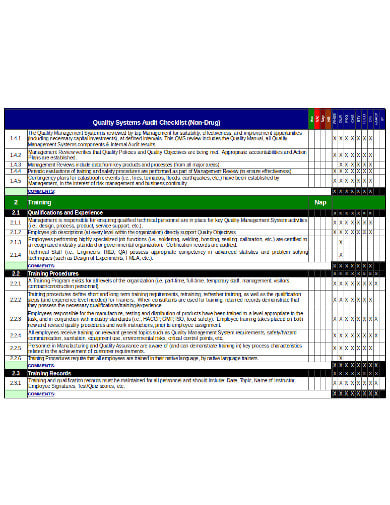 supplier.amway.com
supplier.amway.com5. Free IT Audit Checklist for Small Business
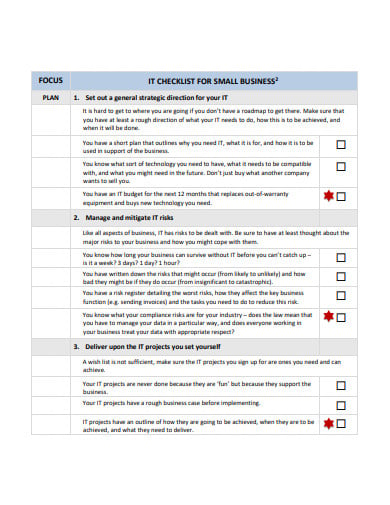 cpaaustralia.com.au
cpaaustralia.com.au6. Free IT Audit Checklist Template
 cloudfront.net
cloudfront.net7. Free Information System IT Audit Checklist Template
 underwoodandassociates.net
underwoodandassociates.net8. Free Cloud Computing IT Audit Checklist Template
 onlinelibrary.wiley.com
onlinelibrary.wiley.com9. Free IT External Provider Audit Checklist Template
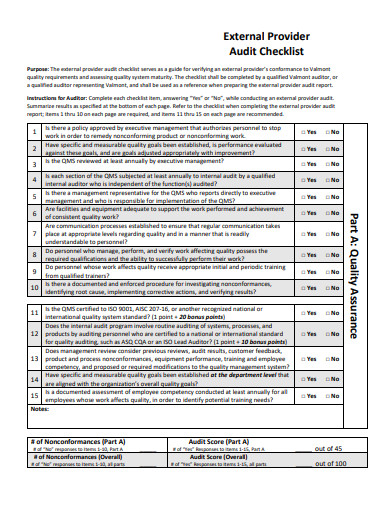 msecnd.net
msecnd.net10. Free Single IT Audit Component Checklist Template
 in.gov
in.gov11. Free IT Compliance Audit Checklist Template
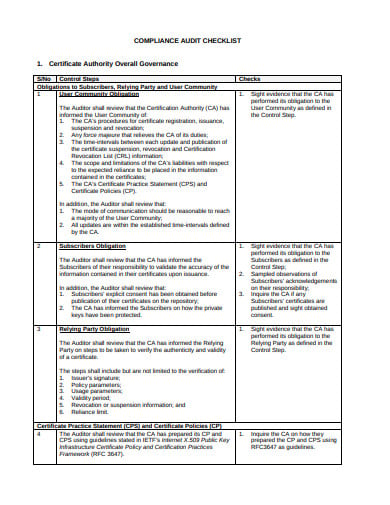 imda.gov.sg
imda.gov.sg12. Free IT Blog Audit Checklist Template
 feinternational.com
feinternational.com5 Steps to Developing a Good IT Audit Program
Step 1: Determine the Subject For Audit
The first step of making an IT audit sample program is to determine the subject for the audit. The of your audit will determine the kind of audit you would need to conduct. For example, if the audit is to be done to find out about the various systems and applications of the IT simple program, then a system and apps audit needs to be carried out.
Step 2: Determine the Object of the Audit
The next step of this process is to determine the object of the audit. The object of the audit refers to the ‘why’ of the same. In other words, the object of the audit will determine why you will be conducting the audit. For instance, if you are conducting an innovative comparison audit, the aim will be to establish which innovative techniques are working better. You can also see more templates like Program Invitations.
Step 3: Determine the Scope of the Audit
Determining the audit scope is very important as the auditor will need to recognize the IT environment for the audit program and its components to determine the tools needed to conduct a thorough evaluation. A specific scope assists the auditor in assessing the test points related to the purpose of the audit. You can also see more templates like Audit Checklist in Pages.
Step 4: Do the Pre-audit Planning
Pre-audit preparation and planning involve activities such as performing a risk assessment, defining regulatory compliance criteria and determining the resources needed for the audit to be performed. This step is absolutely necessary to make sure that the actual audit process goes well smoothly without errors.
Step 5: Identify Audit Processes and Data Collection Measures
The final step of this process includes the identification of the audit processes and the measures of data collection. This identification and collection method or step includes operations such as acquiring departmental review policies, building control testing and verification methodologies, and developing test scripts plus test assessment criteria. Once the planning is complete, auditors can proceed to the phase of fieldwork, documentation and reporting. You can also see more templates like Internal Audit Templates.
Types of IT Audits
1: Technological Position Audit
This type of audit analysis the technologies currently available to the business, and that which it needs to add.
2: Information Processing Facilities
This type of audit is present to verify that the processing facility is managed under normal and potentially disruptive conditions to ensure timely, accurate and effective processing of applications. Find more audit plan Templates by visiting this link.
3: Systems Development
This type of audit is conducted to verify if the current systems being developed meet the organization’s objectives or not, and to ensure that the systems are developed according to generally accepted systems development standards. View a wider selection of audit quotation templates right here.
4: Systems and Applications
This type of audit is conducted to verify that the processes and applications are acceptable, effective, and adequately managed to ensure accurate, reliable, prompt, and safe input, processing, and output at all levels of activity within a system. You can also see more templates like HR Checklists.
5: Innovative Comparison Audit
The audit is a study of the organization being audited. This includes its technological capabilities as compared to its competitors. The process requires an evaluation of the R&D facilities of the company along with its track record in trying to produce new items. You can also see more on Price Comparisons.
6: Technological Innovation Process Audit
This type of report creates a risk profile for both new and existing projects. This audit should evaluate the size and scope of the organization’s expertise in its chosen technology, as well as its position in specific markets, the management of each project, and the structure of the business portion that deals with this project or product. You can also see more templates like Project Charts.






