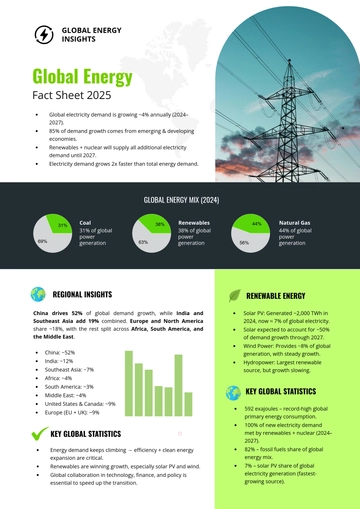
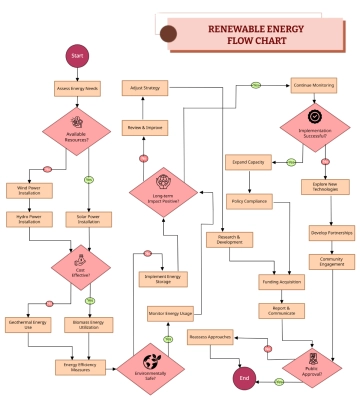
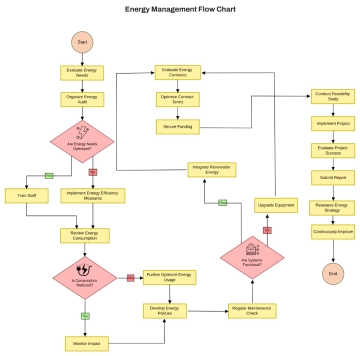
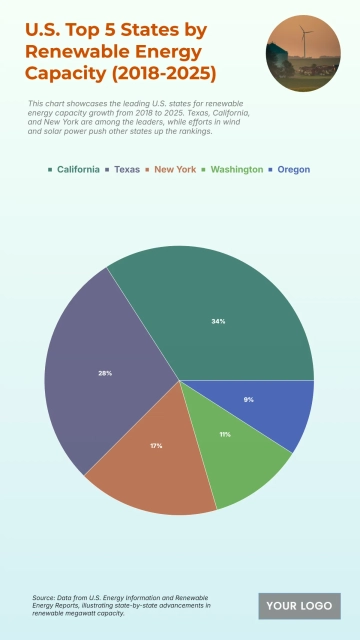
Free Solar Panel Project Specification

Prepared By: [YOUR NAME]
Date: [DATE]
I. Introduction
This Solar Panel Project Specification document outlines the technical and functional requirements for the installation of a solar panel system. Its primary objectives are to ensure optimal energy generation, adherence to safety standards, fulfillment of performance criteria, and compliance with relevant regulations. This document covers site assessment, system design, material selection, electrical specifications, installation procedures, performance criteria, quality assurance, maintenance, and compliance, aiming to promote consistency and quality throughout the project lifecycle.
II. Site Assessment
A thorough site assessment is essential for a successful solar panel installation. It involves evaluating the location and environmental conditions to identify potential challenges and opportunities.
A. Location
Geographical Coordinates: Record the exact coordinates of the installation location to guarantee precise planning and synchronization with solar tracking systems.
Altitude and Topography: Evaluate altitude and landscape; higher altitudes boost solar irradiance, while uneven terrain hinders installation and efficiency.
Accessibility: Assess site access for construction and maintenance, ensuring it is reachable by vehicles and personnel, and identify any obstacles or limitations.
Proximity to Grid Connection: Identify the closest grid connection point to minimize installation expenses and streamline integration with the local power grid.
B. Environmental Conditions
Average Solar Irradiance: Measure the site's solar radiation in kWh/m²/day to estimate solar panel energy output and efficiency.
Temperature Range: Document expected temperature extremes, as they can impact solar panel performance and system efficiency.
Wind Speed and Direction: Record average wind speed and prevailing direction. Ensure the system is designed to withstand local high wind conditions.
Snow Load: Evaluate the maximum expected snow load to ensure mounting systems and panels are designed to prevent damage and ensure safety.
Shading Analysis: Analyze and mitigate shading sources like trees or buildings to optimize solar panel efficiency.
C. Site Preparation
Clearing and Grading: Clear the site of vegetation, debris, and obstacles. Level the ground for a stable, even surface.
Foundation and Support Structures: Build sturdy foundations and supports to ensure the solar panels' stability and performance.
Drainage Systems: Implement effective drainage to manage runoff, prevent pooling, and erosion, protect the system, and ensure long-term reliability.
Security and Fencing: Implement security measures to safeguard the site and equipment, including fences or barriers, against theft, vandalism, and other threats.
III. System Design
This section covers the specifications for designing the solar panel system, including the layout, mounting structures, and orientation to maximize energy output and efficiency.
A. Solar Panel Layout
Configuration: Optimize the placement of solar panels by considering site orientation, panel type, and potential shading to ensure maximum sunlight exposure.
Spacing: Ensure adequate distance between rows to prevent shading and optimize energy capture. Proper spacing allows for the effective angle of sunlight and reduces the impact of shadows on panel performance.
B. Mounting Structures
Type: Choose between fixed or tracking mounting systems. Fixed systems are cost-effective and simpler, while tracking systems adjust to follow the sun, potentially increasing energy output.
Material: Choose robust materials like aluminum, steel, or composites for mounting structures, as the selection of materials impacts the system's durability and stability.
Wind Load Capacity: Design structures to withstand local wind conditions. Ensure that mounting systems are robust enough to handle extreme weather events without compromising stability.
Slope and Orientation Adjustments: Include features that enable the mounting angle and orientation to be adjusted, as this adaptability ensures the optimal solar angle can be maintained year-round.
C. Orientation
Optimal Tilt Angle: Determine the best tilt angle for panels to maximize solar energy capture based on geographical location and seasonal variations.
Azimuth Direction: Align panels towards the true south in the Northern Hemisphere and the true north in the Southern Hemisphere for maximum sunlight.
Row Spacing: Ensure sufficient space between rows to minimize shading and maintain efficiency. Proper row spacing is crucial for preventing one row of panels from casting shadows on another.
IV. Materials and Components
Detailed list and specifications of all materials and components involved in the solar panel system, ensuring that high-quality, durable, and efficient parts are employed.
A. Solar Panels
Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, or Thin-Film |
Efficiency | >20% |
Warranty | 25 Years Performance Warranty |
B. Inverters
Specification | Details |
|---|---|
Type | String, Central, or Microinverters (depends on size/needs) |
Efficiency | Above 95% |
Warranty | 10-year warranty |
C. Batteries
Specification | Details |
|---|---|
Type | Lithium-ion (high energy density), Lead-acid, or Flow batteries |
Capacity | Sized according to system requirements for adequate energy storage |
Warranty | 10-year warranty |
D. Other Equipment
Component | Details |
|---|---|
Charge Controllers | Regulate power flow and prevent battery overcharging |
Monitoring Systems | Track system performance and provide real-time alerts |
Mounting Hardware | Use durable materials to secure panels and components |
Combiner Boxes | Connect and manage multiple circuits efficiently |
Disconnect Switches | Allow safe system isolation for maintenance and emergencies |
V. Electrical Specifications
This section details the electrical connections, wiring, grounding, and protection measures for the solar panel system to ensure safety and performance.
A. Wiring
Conductor Type and Size: Use appropriately gauged and durable conductors to handle electrical loads and environmental conditions. Opt for materials that minimize resistive losses.
Insulation Type: Employ high-quality insulation to protect against moisture, UV rays, and temperature extremes. Ensure compliance with safety standards.
Cable Management: Organize cables using ties, conduits, and trays to prevent damage and simplify maintenance. Keep cables separated from other components.
B. Connections
Connector Types: Use MC4 or equivalent connectors for secure, weather-resistant connections. Match connectors to the system’s voltage and current requirements.
Junction Boxes: Use outdoor-rated junction boxes to protect and house electrical connections, safeguarding against dust and moisture.
Splicing and Termination: Ensure reliable connections with proper splicing and termination techniques. Use suitable tools and materials for secure joints.
C. Grounding
Grounding Electrodes: Install electrodes to ensure safety and minimize electrical hazards. Proper grounding helps dissipate fault currents and reduces shock risk.
Earthing Conductors: Use correctly sized conductors to connect metal parts to grounding electrodes. Ensure secure attachment and compliance with safety standards.
Bonding Connections: Maintain effective bonding between components to ensure electrical continuity and prevent faults.
D. Electrical Protections
Surge Protection Devices: Install devices to protect against voltage spikes from lightning or disturbances. Ensure they are rated for the system’s voltage.
Overcurrent Protection: Use fuses or circuit breakers to prevent damage from excessive current. Select devices rated for the system’s load.
Isolation Devices: Include switches to safely disconnect the system for maintenance or emergencies. Ensure they are accessible and marked.
VI. Installation Procedures
Step-by-step instructions for the installation process, including safety protocols and best practices to ensure a successful and secure installation.
1. Pre-installation Planning |
|
2. Mounting Structure Installation |
|
3. Solar Panel Installation |
|
4. Electrical Installation |
|
5. Safety Protocols |
|
VII. Performance Criteria
Expected performance metrics of the solar panel installation, including energy output, efficiency, and reliability parameters.
Energy Output: Estimate annual production in kWh based on system design and conditions, accounting for factors like solar irradiance and orientation.
System Efficiency: Ensure at least 85% efficiency, reflecting the ratio of converted solar energy to usable power.
Reliability: Target 99.9% uptime, indicating minimal downtime and consistent performance.
Degradation Rate: Aim for less than 0.5% annual degradation to maintain high efficiency over the system's lifespan.
VIII. Quality Assurance and Testing
Procedures and criteria for verifying the quality and performance of the solar panel installation to ensure it meets the specified standards.
A. Visual Inspections
Panel Alignment: Ensure solar panels are correctly positioned and angled for optimal exposure to sunlight. Check for any deviations that could affect energy capture.
Component Fixings: Confirm that all mounting structures, brackets, and panels are securely attached and stable. Look for signs of loose or improperly fastened parts.
Wiring and Connections: Inspect wiring for proper routing, secure connections, and effective cable management. Ensure that all connections are correctly made and protected from environmental factors.
B. Electrical Testing
Insulation Testing: Perform tests to verify the integrity of electrical insulation, ensuring it prevents leakage and protects against potential electrical hazards.
Continuity Testing: Check that all electrical pathways are intact and continuous, confirming that there are no breaks or interruptions in the circuit.
Performance Testing: Measure and evaluate the system’s output against expected performance metrics. Assess efficiency and compare actual results with design specifications to ensure the system is operating correctly.
C. Performance Monitoring
Data Logging: Continuously record performance data to track system output and identify any deviations from expected performance. This data helps in assessing long-term system health.
Remote Monitoring Systems: Utilize remote monitoring technology to keep an eye on system performance from a distance. This allows for real-time tracking and immediate response to potential issues.
Initial Operation Verification: Conduct a thorough check during the initial operation phase to ensure that all components are functioning as intended and that the system meets performance expectations.
IX. Maintenance and Operations
Guidelines and schedules for the ongoing maintenance and operational management of the solar panel system.
A. Routine Maintenance
Cleaning of Panels: Regularly clean panels to remove dirt and debris, ensuring optimal performance. Use proper methods to avoid damage.
Inspection of Mounting Structures: Check mounting structures for stability, corrosion, and wear. Ensure all components are secure.
Electrical Connection Checks: Verify connections are secure and free from corrosion. Inspect wiring and connectors for damage.
B. Performance Monitoring
Regular Data Review: Evaluate performance metrics to identify irregularities and gauge effectiveness.
Alert and Issue Resolution: Create notifications for performance problems and resolve them quickly.
System Optimization: Adjust settings and configurations based on performance data and environmental changes.
C. Repair and Replacement
Diagnosis of Faults: Employ a variety of diagnostic tools to identify potential problems and work through a systematic process to troubleshoot and resolve any issues that may arise.
Component Replacement: Swap out defective parts with suitable replacements to regain proper function.
System Upgrades: Perform a comprehensive evaluation and then apply specific improvements to boost the system's overall performance and reliability.
X. Compliance and Standards
Ensure that the solar panel installation adheres to all applicable regulations and standards for optimal performance and safety.
A. Local Regulations
Building Permits: Obtain all necessary permits before installation to ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations.
Zoning Laws: Comply with local zoning and land-use regulations to avoid legal issues and ensure that the installation is permissible at the chosen site.
Utility Interconnection Agreements: Meet the specific requirements of the local utility company for grid connection, including any necessary inspections and approvals.
B. National Standards
Electrical Codes: Adhere to national electrical codes to ensure the installation meets safety standards and regulatory requirements, minimizing risks of electrical hazards.
Renewable Energy Incentives: Follow national regulations to qualify for renewable energy incentives, rebates, and tax credits, maximizing financial benefits.
Safety Standards: Implement national safety standards to safeguard installation personnel, maintain system integrity, and reduce risks during operation and maintenance.
C. International Standards
IEC Standards: Ensure compliance with International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards for the design, performance, and safety of solar equipment.
ISO Certifications: Obtain and maintain relevant ISO certifications to verify the quality management and operational standards of the installation.
Global Best Practices: Follow international best practices for solar panel installations, including guidelines for system design, maintenance, and environmental impact, to achieve optimal performance and long-term reliability.
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Optimize your solar energy projects with Template.net's Solar Panel Project Specification Template. This editable and customizable template provides detailed guidelines for designing, installing, and maintaining solar panel systems. It's designed to ensure project success and compliance with industry standards. With our Ai Editor Tool, you can easily edit and personalize this template to meet your unique project requirements