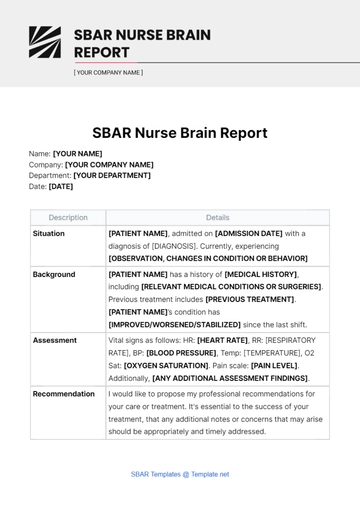
Free Nursing Report

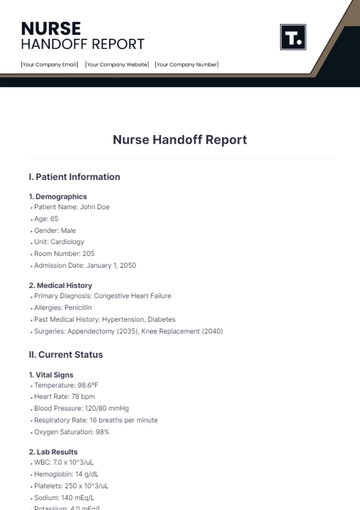
Patient Name: | Jane Martinez |
|---|---|
Patient ID: | 2050-10048 |
Date of Report | August 18, 2050 |
Report Time: | 8:00 am |
Nurse: | [YOUR NAME] |
Hospital: | [YOUR COMPANY NAME] |
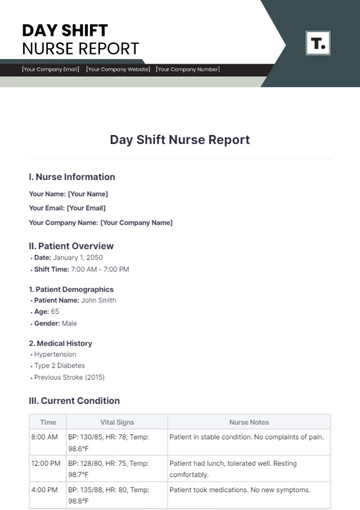
Patient Overview
Diagnosis | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension |
|---|---|
Admission Date | August 15, 2050 |
Current Room | 305B |
Primary Physician | Dr. Emily Carter |
Vital Signs
Temperature | 98.6°F |
|---|---|
Pulse | 78 bpm |
Respirations | 16 per minute |
Blood Pressure | 130/85 mmHg |
Blood Glucose Level | 142 mg/dL |
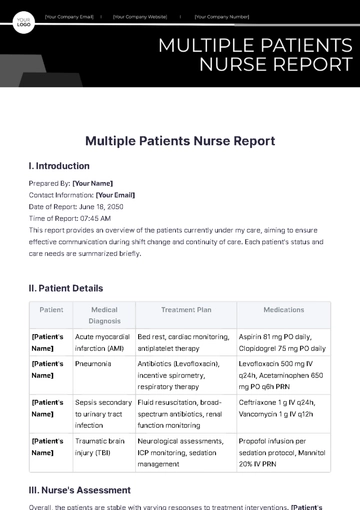
Current Medications
Metformin | 500 mg twice daily |
|---|---|
Lisinopril | 10 mg once daily |
Aspirin | 81 mg once daily |
Recent Observations
Physical Condition:
Overall Status: The patient is stable with no new complaints of pain or discomfort. The patient reports feeling generally well and denies any acute issues.
Edema: No signs of peripheral or localized edema are observed. Extremities are noted to be well-perfused with no swelling.
Distress: No signs of respiratory distress, discomfort, or unusual fatigue noted. The patient appears comfortable and alert.
Diet:
Diet Compliance: The patient is adhering to a prescribed diabetic diet plan. Meals are consumed regularly with no issues.
Appetite: Appetite is reported as good, with consistent intake of meals and snacks as recommended.
Adverse Reactions: No gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea observed. No allergic reactions or food intolerances reported.
Activity:
Mobility: The patient is able to ambulate independently without assistance. Gait is steady and unassisted.
Physical Therapy: Actively participating in scheduled physical therapy sessions. Exercises are performed as directed, and the patient is making progress as expected.
Exercise Tolerance: No signs of fatigue or shortness of breath noted during or after physical activity.
Care Plan
Short-Term Goals:
Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels will be performed to ensure they stay within the target range of 70-130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL two hours after meals. Blood glucose logs will be reviewed for any deviations.
Medication Regimen: Continuation of Metformin and Lisinopril as prescribed. Monitor for effectiveness by evaluating blood glucose trends and blood pressure readings. Assess for any adverse effects or medication interactions.
Dietary Adherence: Reinforce the diabetic diet plan with the patient. Provide assistance as needed to ensure dietary guidelines are followed. Collaborate with a dietitian if any challenges arise.
Long-Term Goals:
Blood Glucose Control: Aim to achieve and maintain optimal blood glucose control, with A1c levels ideally below 7%. This involves regular monitoring and adjustments to the care plan based on lab results.
Complication Prevention: Implement strategies to prevent complications related to diabetes, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy. Manage hypertension to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Health Promotion: Encourage lifestyle modifications including regular physical activity, smoking cessation, and stress management to enhance overall well-being and support diabetes management.
Medication Administration:
Metformin and Lisinopril: Administer medications as per the prescribed schedule. Monitor for side effects such as gastrointestinal issues from Metformin or dizziness from Lisinopril.
Documentation: Record administration times, doses, and any reactions observed. Report any issues to the oncoming shift.
Vital Signs Monitoring:
Frequency: Vital signs should be checked every 4 hours. This includes monitoring temperature, pulse, respiration rate, and blood pressure.
Assessment: Evaluate trends in vital signs to detect any changes that might require medical attention. Notify the physician if any abnormal values are noted.
Patient Education:
Diet and Medication Adherence: Educate the patient on the importance of sticking to the prescribed diet and medication regimen. Discuss strategies to manage blood glucose levels effectively.
Diabetes Management: Provide written and verbal instructions on managing diabetes at home, including signs of hypo- and hyperglycemia, and when to seek medical help.
Documentation:
Changes: Document any changes in the patient’s condition, such as new symptoms or changes in vital signs. Update the care plan and communicate these changes during handover to ensure continuity of care.
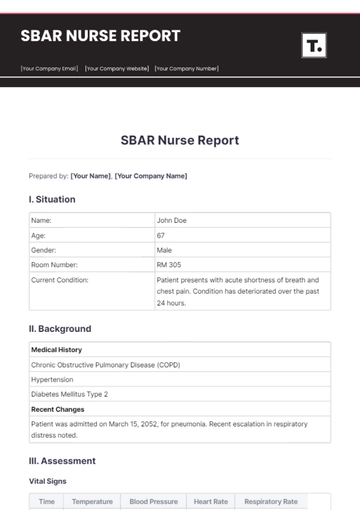
Notes and Recommendations
Follow-Up:
Blood Glucose Levels: Review blood glucose levels at the end of the shift and adjust medications if necessary based on trends and physician recommendations.
Dietitian Consultation: Schedule a follow-up with the dietitian to address any dietary concerns or adjustments required. Ensure that dietary plans are reviewed and updated as needed.
Special Instructions:
Monitoring: Watch for signs of hypotension (e.g., dizziness, lightheadedness) and hypoglycemia (e.g., sweating, tremors). Implement measures to manage these conditions if they occur.
Physician Notification: Notify the physician immediately if there are significant changes in the patient’s condition, such as uncontrolled blood glucose levels, persistent high blood pressure, or any new symptoms.
Signature:

[Your Name]
RN
Date: August 28, 2054
- 100% Customizable, free editor
- Access 1 Million+ Templates, photo’s & graphics
- Download or share as a template
- Click and replace photos, graphics, text, backgrounds
- Resize, crop, AI write & more
- Access advanced editor
Elevate your nursing documentation with Template.net's Nursing Report Template. This fully editable and customizable template simplifies report creation, ensuring precision and efficiency. Enhanced by an AI Editable Tool, it adapts seamlessly to your needs, streamlining your workflow. Perfect for healthcare professionals seeking a versatile, user-friendly solution to manage and record patient information effortlessly.
You may also like
- Sales Report
- Daily Report
- Project Report
- Business Report
- Weekly Report
- Incident Report
- Annual Report
- Report Layout
- Report Design
- Progress Report
- Marketing Report
- Company Report
- Monthly Report
- Audit Report
- Status Report
- School Report
- Reports Hr
- Management Report
- Project Status Report
- Handover Report
- Health And Safety Report
- Restaurant Report
- Construction Report
- Research Report
- Evaluation Report
- Investigation Report
- Employee Report
- Advertising Report
- Weekly Status Report
- Project Management Report
- Finance Report
- Service Report
- Technical Report
- Meeting Report
- Quarterly Report
- Inspection Report
- Medical Report
- Test Report
- Summary Report
- Inventory Report
- Valuation Report
- Operations Report
- Payroll Report
- Training Report
- Job Report
- Case Report
- Performance Report
- Board Report
- Internal Audit Report
- Student Report
- Monthly Management Report
- Small Business Report
- Accident Report
- Call Center Report
- Activity Report
- IT and Software Report
- Internship Report
- Visit Report
- Product Report
- Book Report
- Property Report
- Recruitment Report
- University Report
- Event Report
- SEO Report
- Conference Report
- Narrative Report
- Nursing Home Report
- Preschool Report
- Call Report
- Customer Report
- Employee Incident Report
- Accomplishment Report
- Social Media Report
- Work From Home Report
- Security Report
- Damage Report
- Quality Report
- Internal Report
- Nurse Report
- Real Estate Report
- Hotel Report
- Equipment Report
- Credit Report
- Field Report
- Non Profit Report
- Maintenance Report
- News Report
- Survey Report
- Executive Report
- Law Firm Report
- Advertising Agency Report
- Interior Design Report
- Travel Agency Report
- Stock Report
- Salon Report
- Bug Report
- Workplace Report
- Action Report
- Investor Report
- Cleaning Services Report
- Consulting Report
- Freelancer Report
- Site Visit Report
- Trip Report
- Classroom Observation Report
- Vehicle Report
- Final Report
- Software Report